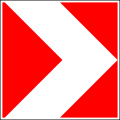
5.1 Motorway
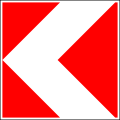
5.2 End of the motorway
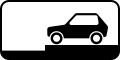
5.3 Road for cars
5.4 End of the road for cars
5.5 One-way road
5.6 End of one-way road
5.7.1 Exit to a one-way road
5.7.2 Exit to a one-way road
5.8.1 Lane directions
5.8.2 Lane directions
5.8.2 Lane directions
5.8.2 Lane directions
5.8.2 Lane directions
5.8.2 Lane directions
5.8.2 Lane directions
5.8.2 Lane directions
5.8.3 The beginning of the lane
5.8.3 The beginning of the lane
5.8.4 The beginning of the lane
5.8.5 End of the lane
5.8.6 End of the lane
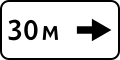
5.8.7 Lane direction
5.8.8 Lane direction
5.8.8 Lane direction
5.9.1 Bus lane
5.9.2 End of bus lane
5.10.1 A road with a line for fixed-route vehicles
5.10.2 End of the road with a lane for fixed-route vehicles
5.10.3 Exit to the road with a lane for fixed-route vehicles
5.10.4 Exit to the road with a lane for fixed-route vehicles
5.11.1 U-turn
5.11.2 U-turn
5.12.1 Bus and/or trolleybus stop location
5.12.2 Bus and (or) trolley bus stop
5.13 Tram stop location
5.14.1 Express route stop
5.14.2 Parking place for passenger taxis
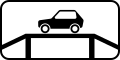
5.15 Parking
5.16.1 Pedestrian crossing (also uses

)
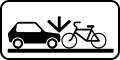
5.16.2 Pedestrian and
cyclists crossing 5.16.3 Pedestrian crossing (also uses

)
5.16.4 Pedestrian and cyclists crossing
5.17.1
Subway (underpass) (also uses

)
5.17.2 Subway (underpass) (also uses

)
5.17.3
Footbridge (also uses

)
5.17.4 Footbridge (also uses

)
5.18.1 Recommended speed
5.18.2 End of recommended speed zone
5.19.2 Dead end
5.19.3 Dead end
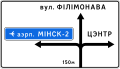
5.20.1 A preliminary sign of directions
5.20.1 A preliminary sign of directions
5.20.1 A preliminary sign of directions
5.20.1 A preliminary sign of directions
5.20.2 A preliminary sign of direction
5.20.2 A preliminary sign of direction
5.20.3 Traffic scheme
5.21.1 Pointing direction
5.21.1 Pointing direction
5.21.1 Pointing direction
5.21.2 Pointing directions
5.22.1 Entrance to built-up area
5.22.2 Entrance to built-up area
5.23.1 End of built-up area
5.23.2 End of built-up area
5.24 Entrance to locality
5.25 End of locality
5.26.1 Object name (river name)
5.26.2 Object name (street name)
5.27.1 Distance indicator
5.27.2 Distance indicator
5.28 Kilometer sign
5.28 Kilometer sign
5.29.1 Route number (
European route number)
5.29.1 Route number (Highway or state roads)
5.29.1 Route number (Regional roads)
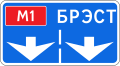
5.30.1 Direction of movement for trucks
5.30.2 Direction of movement for trucks
5.30.3 Direction of movement for trucks
5.31 Detour scheme
5.32.1 Detour direction
5.32.2 Detour direction
5.32.3 Detour direction
5.34.1 Preliminary index of the lane change to another carriageway
5.34.2 Preliminary index of the lane change to another carriageway
5.35 Reversible lane
5.36 End of reversible lane
5.37 Entrance to a road with reversible lane
5.38 Residential area (also uses

)
5.39 End of residential area (also uses

)
5.40 Pedestrian zone (also uses

)
5.41 End of pedestrian zone (also uses

)
5.42 Toll road
5.43 End of toll road
5.4.4 Directions to the toll collection