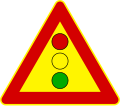
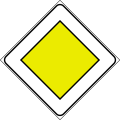
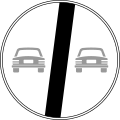
Albania is a signatory to the Vienna Convention on Road Signs and Signals. Therefore, road signs do not differ much from the rest of Europe, such as Italy, San Marino, Montenegro and Kosovo. The Ministry of Infrastructure and Energy regulates them. Albania drives on the right as with the rest of Europe, except for Cyprus, Ireland, Malta and the United Kingdom. Although Albania is not a member of the European Union, the road signs largely follow the general European conventions concerning the use of shape and colour to indicate their function. [1] [2]