This article may need to be rewritten to comply with Wikipedia's quality standards.(April 2022) |







Road signs in India are governed by the Indian Roads Congress. For the most part, they tend to follow European practices closely, usually identical to United Kingdom or the Vienna Convention on Road Signs and Signals. However yellow rectangular signs that do carry such messages like "Be gentle on my curves" and "Danger creeps when safety sleeps" are present nationwide. [1]
Contents
- History
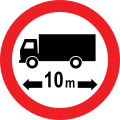
- Mandatory/Regulatory signs
- Compulsory signs
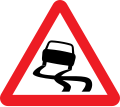
- Cautionary/Warning signs
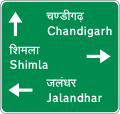
- Informatory signs
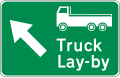
- Facility informatory signs
- Parking signs
- Route Marker signs
- Retired signs
- 1937 to 1950 road signs
- References
The official typeface for road signs in India is Transport and Arial. [2] The Official typeface for Highway shields is Highway Gothic. [2] Though sometimes, road signs may use hand-painted fonts. [3] [4] Most urban roads and state highways have signs in the state language and English. National highways have signs in the state language, Hindi and English.