| 6.01 Security strip (white, solid) | Designates centre of carriageway or border of lanes. Crossing, traversing, or passing over it by vehicles is not permitted. |
 | 6.02 Double security strip (white, solid) | Separates driving directions on roads with 3 or more lanes (or expressways). Crossing, traversing, or passing over it by vehicles is not permitted. |
| 6.03 Directing strip (white, broken) | Designates either centre of carriageway on two-lane roads, or separates lanes. Crossing, traversing, passing over for overtaking is allowed. |
 | 6.04 Double strip (combination of a security strip and a directing strip on either side of the security strip) | Crossing, passing, or traversing, or starting an overtaking manoeuvre, is allowed only from the side with the broken directing strip. |
 | 6.05 Advance warning strip (white, closely broken) | Announces either security or double strips. Any overtaking manoeuvres must be completed. |
 | 6.06 Pre-selecting arrows (white) | Indicates permitted manoeuvres from each lane for a junction; the chosen direction is compulsory (corresponds to 2.31–2.36, see also 4.43). Yellow arrows indicate directions for public transport only and their permitted manoeuvres can differ. |
 | 6.07 Pull arrows (white, arranged obliquely) | Orders to leave the lane in the indicated direction. |
 | 6.08 Bus lane (yellow, solid or broken strips; BUS text in yellow) | Indicates lanes exclusive to public transport. Any exceptions to this may be indicated with the use of supplementary panels under sign 2.64. It is permitted to cross the line if the yellow strip is broken. |
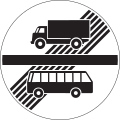
 | 6.10 Stop line (white, wide, solid) | Traffic must stop at this line. Always accompanied by a stop sign. It may also be used at traffic lights (though traffic need not stop when the light is green), level crossings and on lanes for turn off traffic. Stop lines are yellow if exclusively addressed to bicycles and mopeds (e.g. on bicycle paths and lanes; see also 6.26) |
| 6.11 Stop text (white) | May appear alongside a stop line |
| 6.12 Longitudinal strip (white, solid) | May appear alongside a stop line |
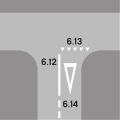 |
| 6.13 Give way line (white, small triangles in a row) | Traffic must give way at this line. Always accompanied by a give way sign. Can be combined with traffic lights (though traffic need not stop while traffic lights are working. Give way lines are yellow if exclusively addressed to bicycles and mopeds (e.g. on bicycle paths and lanes) |
| 6.14 Announcement of give way line (white, large triangle) | May announce the give way line on main roads and important minor roads |
 | 6.15 Border strip (white, solid) | Designates the edge of a carriageway |
| 6.16 Guidestrip (white, broken) | Visually guides traffic through a junction. They may continue stop or waiting lines, separating the side road from the main road (see example 1), or indicate the course of the principal road in cases of a turn in the principal road at a crossing (see example 2). Guidestrips do not appear on side roads with valid priority to the right rule. |
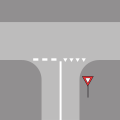 | Example 1 |
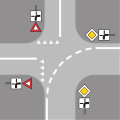 | Example 2 |
 | 6.17 Pedestrian crossing (longitudinal, wide, yellow; on cobble stones if need be white) |
| 6.18 Prohibition of stopping strip | Stopping voluntarily is prohibited. |
 | 6.19 Pedestrian area (yellow, two longitudinal strips on each side connected by bias bindings) | Area marked on roads for use by pedestrians only |
 | 6.20 Restricted area (white, shaded and framed) | Visually guides traffic; crossing, traversing, or passing is strictly prohibited. |
 | 6.21 Zigzag lines (yellow) | Designate public bus stop area. Parking is prohibited. It can be used to pick up or drop off passengers, but only if public traffic is in no way obstructed. |
 | 6.22 Prohibition of parking strip (yellow, longitudinal strip broken with diagonal crosses) |
 | 6.23 Prohibition of parking area (yellow, framed, diagonally crossed) | Exclusive parking for designated traffic users, indicated by the word TAXI or a license plate number. If labelled, it can be used to pick up or drop off passengers, but only if valid traffic user is in no way obstructed. |
 | Parking (usually marked by white, blue, red, or yellow solid strips) | Parking spaces can be signposted (see 4.17–4.21) and/or marked by white (parking free, unless signposted with 4.20; or 4.18), blue, or red solid strips (sometimes only indicated by partial markings); blue markings indicate Blue Zone parking spaces with mandatory use of parking disc/card; red markings indicate Red Zone parking spaces (exist only in a few cantons); yellow parking spaces are reserved for private or special purposes (prohibited to the general public). In areas with parking markings, it is prohibited to park anywhere else; only parking spaces of appropriate size for the relevant vehicle type, whether bicycle/moped, motorbike, car, bus (indicated by word CAR) or lorries should be used. Blue Zones can be indicated by a thick white-blue crossline at the start and a thick blue-white crossline at the end of the zone. |
 | 6.25 Prohibition of stopping strip (yellow, longitudinal solid strip with endings) | Voluntarily stopping is prohibited |
 | 6.26 Extended bicycle lane (waiting area placed in front of stop line with an additional yellow stop line and a bicycle icon in front of the white stop line) | During red traffic light bicycles and mopeds are allowed to wait in front of first motor vehicle and next to each other, motor vehicles must stop in front of the white stop line; when traffic light becomes green, motor vehicles must show patience and give way to bicycles and mopeds in front of them in order to let them clear the crossing first. |
 | 6.30 Guide post, right | Placed on the right-hand side of the carriageway, facing the driver on the right. It can also appear on the left-hand side of the carriageway on roads with either separated directions or without oncoming traffic. |
 | 6.31 Guide post, left | Placed on the left-hand side of the carriageway, facing the driver on the right. |