This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page . (Learn how and when to remove these messages)
|

Road signs in Iceland are visual communication devices placed along roads and highways throughout the country to provide information, warnings, and guidance to motorists and pedestrians. Iceland never ratified the Vienna Convention on Road Signs and Signals, but road signs in Iceland conform to the general pattern of those used in most other European countries, with certain design elements borrowed from Danish and Swedish practice. Signs tend to be more sparsely employed than in other European countries, especially in rural areas.
Contents
- Design
- Colours and shapes
- Typeface
- Gallery
- Warning signs
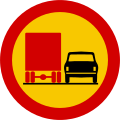
- Prohibitory signs
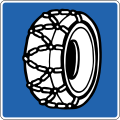
- Mandatory signs
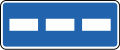
- Information signs
- Service signs
- Route and direction signs
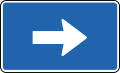
- Direction signs
- Temporary signs
- Additional signs
- Old signs
- Traffic lights
- References
- External links
Most road signs in Iceland are not retroreflective, making them harder to see at night.