5.1. Motorway
5.2. End of motorway
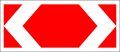
5.3. Controlled access road
5.4. End of controlled access road
5.5. One-way street
5.6. End of one-way street
5.7.1. One-way street
5.7.2. One-way street
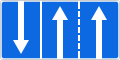
5.8.1. Lane directions
5.8.2. Directions of movement along the lane
5.8.2. Directions of movement along the lane
5.8.2. Directions of movement along the lane
5.8.2. Directions of movement along the lane
5.8.2. Directions of movement along the lane
5.8.3. Added lane
5.8.3. Added lane
5.8.4. Added lane
5.8.5. End of the lane
5.8.6. End of the lane
5.8.7. Lane direction
5.8.7. Lane direction
5.8.8. Lane direction
5.9. Bus lane
5.10.1. Road with a contraflow bus lane
5.10.2. Exit to road with a contraflow bus lane
5.10.3. Exit to road with a contraflow bus lane
5.10.4. End of road with a contraflow bus lane
5.11.1. U-turn
5.11.2. U-turn area
5.12. Bus stop
5.13. Tram stop
5.14. Parking place for passenger taxis
5.15. Parking
5.16.1. Pedestrian crossing
5.16.2. Pedestrian crossing
5.17.1. Underground pedestrian crossing
5.17.2. Underground pedestrian crossing
5.17.3. Aboveground pedestrian crossing
5.17.4. Aboveground pedestrian crossing
5.18. Advisory speed
5.19.1. No through road
5.19.2. No through road on right
5.19.3. No through road on left
5.20.1. Preliminary direction indicator
5.20.1. Preliminary direction indicator
5.20.2. Preliminary direction indicator
5.20.3. Traffic scheme
5.21.1. Direction indicator
5.21.1. Direction indicator
5.21.1. Direction indicator
5.21.2. Direction indicator
5.21.2. Direction indicator
5.22. Start of city limit
5.23. End of city limit
5.24. Start of city limit
5.25. End of city limit
5.26. Name of the object
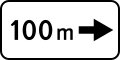
5.27. Distance indicator
5.28. Kilometer sign
5.29.1. Route number
5.29.2. Route number
5.29.2. Route number
5.29.2. Route number
5.30.1. Direction of movement for trucks
5.30.2. Direction of movement for trucks
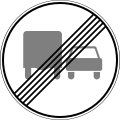
5.30.3. Direction of movement for trucks
5.31. Detour scheme
5.32.1. Detour direction
5.32.2. Detour direction
5.32.3. Detour direction
5.33. Stop line
5.34.1. Preliminary index of the lane change to another carriageway
5.34.2. Preliminary index of the lane change to another carriageway
5.35. Reversible lane
5.36. End of reversible lane
5.37. Exit to road with reversible lane
5.38. Street direction
5.39. Warning or prohibitory signs at intersections
5.40. No parking zone
5.41. End of no parking zone
5.42. No parking zone at certain time period
5.43. End of no parking zone at certain time period
5.44. Parking zone
5.45. End of parking zone
5.46. Speed limit zone
5.47. End of speed limit zone
5.48.1. Emergency stopping lane
5.48.2. Emergency stopping lane
5.50.1. Motorway exit countdown
5.50.2. Motorway exit countdown
5.50.3. Motorway exit countdown
5.51. Living zone
5.52. End of living zone
5.53. Permanent right turn