
Tharwa Bridge is a four span Allan truss bridge that provides a high-level crossing point across the Murrumbidgee River, allowing traffic between Canberra and Tharwa village. It is the oldest surviving bridge in the Australian Capital Territory.
The Victoria Bridge is a heritage-listed timber trestle truss road bridge across the Stonequarry Creek, located at Prince Street in the south-western Sydney town of Picton in the Wollondilly Shire local government area of New South Wales, Australia. The bridge is owned by Transport for NSW, an agency of the Government of New South Wales. The bridge is also known as the Victoria Bridge over Stonequarry Creek. It was added to the New South Wales State Heritage Register on 20 June 2000. Designed by Percy Allan and opened on 7 October 1897, Victoria Bridge employs Allan trusses and was built by C. J. Ford of Sydney.

The Crookwell railway line is a disused branch railway line in the south of New South Wales, Australia. Although it has never officially been closed, the line has not seen services since the late 1980s. It branched from the Main South line at North Goulburn and passed north through the localities of Kenmore and Roslyn to the town of Crookwell. As of 2020, there were proposals to convert the line into a rail trail.

The Peats Ferry Bridge is a steel truss bridge that carries the Pacific Highway (B83) across the Hawkesbury River, between Kangaroo Point and Mooney Mooney Point, located 40 kilometres (25 mi) north of Sydney in New South Wales, Australia. The bridge carries the Hornsby to Kariong section of highway, while the adjacent Brooklyn Bridge carries the Pacific Motorway (M1).

The Prince Alfred Bridge is a wrought iron truss and timber beam partially-disused road bridge over the Murrumbidgee River and its floodplain at Middleton Drive, Gundagai, Cootamundra-Gundagai Regional Council, New South Wales, Australia. The heritage-listed road bridge was designed by William Christopher Bennett and built from 1864 to 1867 by Francis Bell. It is also known as Prince Alfred Bridge – Iron Road Bridge and Iron Bridge over Murrumbidgee River at Gundagai. The iron bridge is owned by Transport for NSW and the timber viaduct is owned by Crown Lands. The bridge was added to the New South Wales State Heritage Register on 5 July 2019 and on the Register of the National Estate on 21 March 1978.

Sadliers Crossing Railway Bridge is a heritage-listed railway bridge at over Bremer River between Tallon Street, Sadliers Crossing and Dixon Street, Wulkuraka, Queensland, Australia on the Main Line (this section is now the Ipswich and Rosewood railway line. It was added to the Queensland Heritage Register on 13 November 2008.

Morpeth Bridge is a heritage-listed road bridge over the Hunter River at Morpeth, New South Wales, Australia. It was designed by Percy Allan and built from 1896 to 1898 by Samuel McGill. It is also known as Morpeth Bridge over the Hunter River. The property is owned by Transport for NSW.

The Wallaby Rocks Bridge is a heritage-listed road bridge that carries Hill End Road across the Turon River, at Wallaby Rocks near Sofala, New South Wales, Australia. It was designed by Percy Allan and built in 1897 by E. Taylor of Balmain. The bridge is owned by Transport for NSW. It was added to the New South Wales State Heritage Register on 20 June 2000.

The Lachlan River railway bridge is a heritage-listed former railway bridge which carried the Blayney–Demondrille railway line over the Lachlan River at Cowra, Cowra Shire, New South Wales, Australia. It was designed by John Whitton in his capacity as Engineer-in-Chief for Railways. The bridge was built from 1886 to 1887 by contractors Fishburn & Co. It is also known as the Cowra Rail Bridge over Lachlan River and the Cowra Lattice Railway Bridge. The property is owned by Transport Asset Holding Entity, an agency of the Government of New South Wales. It was added to the New South Wales State Heritage Register on 2 April 1999.

The Paterson River bridge, Vacy is a heritage-listed road bridge that carries Gresford Road across the Paterson River located in Vacy, New South Wales, Australia. It is situated about 300 metres south of the junction of Gresford Road and Summer Hill Road. The bridge was designed by Percy Allan and built in 1888 by Taylor and Littleproud. The bridge is also known as the Vacy Bridge over Paterson River. The bridge is owned by Transport for NSW. It was added to the New South Wales State Heritage Register on 20 June 2000.

The Williams River bridge, Clarence Town is a heritage-listed road bridge that carries Limeburners Creek Road across the Williams River located in Clarence Town, New South Wales, Australia. It was designed by the New South Wales Public Works Department and built by J. K. McKenzie. The property is owned by Transport for NSW. It was added to the New South Wales State Heritage Register on 20 June 2000.
The Goulburn Viaduct is a heritage-listed railway bridge that carries the Main Southern railway line across the Mulwaree River at Goulburn, in the Goulburn Mulwaree Council local government area of New South Wales, Australia. It was built in 1915. It is also known as Mulwaree River Railway Viaduct. The property is owned by Transport Asset Holding Entity, an agency of the Government of New South Wales. It was added to the New South Wales State Heritage Register on 2 April 1999.

Colemans Bridge is a heritage-listed road bridge that carries Union Street across the Leycester Creek in Lismore, New South Wales, Australia. It was designed by Harvey Dare and built in 1907 by W. F. Oakes. The bridge is owned by Transport for NSW. It was added to the New South Wales State Heritage Register on 20 June 2000.

Murrumbidgee River railway bridge is a heritage-listed disused railway bridge on the Tocumwal railway line crossing from Narrandera to Gillenbah, both in Narrandera Shire, New South Wales, Australia. It was designed by John Whitton in his capacity as Engineer-in-Chief for Railways, and built in 1884–85 by Halliday & Owen with ironwork supplied by English firm Westwood, Baillie. It is also known as Narrandera Lattice Railway Bridge. The property was added to the New South Wales State Heritage Register on 2 April 1999 and was added to the Register of the National Estate on 15 May 1990.

The Queanbeyan railway bridges over Queanbeyan and Molonglo Rivers are two heritage-listed railway bridges that carry the Bombala railway line in the Queanbeyan-Palerang Region local government area of New South Wales, Australia. Both bridges were built between 1926 and 1927. The westernmost bridge crosses the Queanbeyan River from Queanbeyan to Queanbeyan East at 35.3424°S 149.2317°E, while the easternmost bridge crosses the Molonglo River at Burbong at 35.3371°S 149.3191°E. The two railway bridges are owned by Transport Asset Holding Entity, an agency of the Government of New South Wales. Together, the two bridges were added to the New South Wales State Heritage Register on 2 April 1999.

The Hinton Bridge over Paterson River is a heritage-listed road bridge that carrier the Hinton-Morpeth Road across the Paterson River at Hinton, New South Wales, Australia. The bridge was designed by Ernest de Burgh and built in 1901. The bridge is owned by Transport for NSW. The bridge was added to the New South Wales State Heritage Register on 20 June 2000.
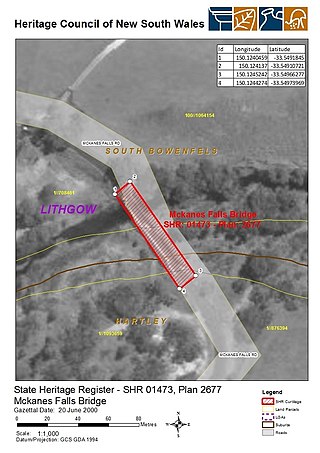
The McKanes Falls Bridge is a heritage-listed road bridge at McKanes Falls Road, South Bowenfels, New South Wales, Australia. It was designed by John McDonald and NSW Engineer for Bridges and built from 1892 to 1893 by NSW Public Works. It is also known as McKanes Bridge. The property is owned by Transport for NSW. It was added to the New South Wales State Heritage Register on 20 June 2000.

The MacDonald River bridge is a heritage-listed road bridge that carries St Albans Road across the MacDonald River at St Albans, New South Wales, Australia. It was designed by Ernest de Burgh and built by John Ahearn and Son. It is also known as Norton Bridge. The property is owned by Transport for NSW. It was added to the New South Wales State Heritage Register on 20 June 2000.
Beckers Bridge is a heritage-listed timber truss road bridge that carries Main Road across Webbers Creek, located in Glendon Brook, New South Wales, Australia. It was designed by Ernest de Burgh. The bridge is owned by Transport for NSW.
The Glennies Creek Bridge is a heritage-listed road bridge that carries the Rixs Creek-Falbrook Road across the Glennies Creek, located at Middle Falbrook, New South Wales, Australia. The bridge was designed by Ernest de Burgh and built in 1902-03 by William Murphy and James Taylor. The property is owned by Transport for NSW. The bridge was added to the New South Wales State Heritage Register on 20 June 2000.

















