The Victoria Bridge is a heritage-listed timber trestle truss road bridge across the Stonequarry Creek, located at Prince Street in the south-western Sydney town of Picton in the Wollondilly Shire local government area of New South Wales, Australia. The bridge is owned by Transport for NSW, an agency of the Government of New South Wales. The bridge is also known as the Victoria Bridge over Stonequarry Creek. It was added to the New South Wales State Heritage Register on 20 June 2000. Designed by Percy Allan and opened on 7 October 1897, Victoria Bridge employs Allan trusses and was built by C. J. Ford of Sydney.

The Goodradigbee River Bridge is a heritage-listed road bridge that carries Main Road across the Goodradigbee River in Wee Jasper, New South Wales, Australia. It was designed by Percy Allan and built in 1896 by W. J. Lansdown. The bridge is also known as the Wee Jasper Bridge over Goodradigbee River. The bridge is owned by Transport for NSW. It was added to the New South Wales State Heritage Register on 20 June 2000.

The Wallaby Rocks Bridge is a heritage-listed road bridge that carries Hill End Road across the Turon River, at Wallaby Rocks near Sofala, New South Wales, Australia. It was designed by Percy Allan and built in 1897 by E. Taylor of Balmain. The bridge is owned by Transport for NSW. It was added to the New South Wales State Heritage Register on 20 June 2000.

The Murray River bridge is a heritage-listed road bridge that carries Main Road across the Murray River located at Barham in the Murray River Council local government area of New South Wales, Australia. It was designed by Department of Public Works and built in 1904 by John Monash. The bridge is also known as the Barham Bridge over Murray River and the Barham bridge. The bridge is owned by the Murray River Council and was added to the New South Wales State Heritage Register on 20 June 2000.

The Murrumbidgee River bridge, Carrathool is a heritage-listed road bridge that, until its closure in 2019, carried Carrathool Road across the Murrumbidgee River in Carrathool, New South Wales, Australia. The bridge is owned by Transport for NSW. The bridge is also called the Carrathool Bridge over Murrumbidgee River and provides a key connection between the Sturt Highway and the Murrumbidgee Road. It was added to the New South Wales State Heritage Register on 20 June 2000.

The Coonamit Bridge is a heritage-listed road bridge that carries Swan Hill Road across the Wakool River, connecting Mallan and Dilpurra in the Riverina region of New South Wales, Australia. The bridge was designed by Harvey Dare and built in 1929. The bridge is owned by Transport for NSW and was added to the New South Wales State Heritage Register on 20 June 2000.

The Murray River road bridge is a heritage-listed road bridge that carries Swan Hill Road across the Murray River, on the border between New South Wales and Victoria, Australia. The bridge connects Murray Downs in New South Wales with McCallum Street in Swan Hill, Victoria. The bridge was built in 1896 and is owned by Transport for NSW. The bridge is also called the Swan Hill Bridge and the Swan Hill-Murray River Road Bridge. It was added to the New South Wales State Heritage Register on 20 June 2000.

The Tooleybuc Bridge is a dual heritage-listed road bridge that carries Tooleybuc Road across the Murray River, located in Tooleybuc, New South Wales, Australia. It was built in 1925. The bridge is owned by the Transport for NSW, and is also called the Tooleybuc Bridge over Murray River. The bridge was added to the New South Wales State Heritage Register on 20 June 2000 and the Victorian Heritage Register on 10 July 2008.
The Junction Bridge is a heritage-listed road bridge that carries the Tumut Plains Road across the Tumut River, from Tumut to Tumut Plains in New South Wales, Australia. The bridge is owned by Transport for NSW. It was added to the New South Wales State Heritage Register on 20 June 2000.
The Paterson River bridge, Vacy is a heritage-listed road bridge that carries Gresford Road across the Paterson River located in Vacy, New South Wales, Australia. The bridge was designed by Percy Allan and built in 1888 by Taylor and Littleproud. The bridge is also known as the Vacy Bridge over Paterson River. The bridge is owned by Transport for NSW. It was added to the New South Wales State Heritage Register on 20 June 2000.

The Williams River bridge, Clarence Town is a heritage-listed road bridge that carries Limeburners Creek Road across the Williams River located in Clarence Town, New South Wales, Australia. It was designed by the New South Wales Public Works Department and built by J. K. McKenzie. The property is owned by Transport for NSW. It was added to the New South Wales State Heritage Register on 20 June 2000.

The Karuah River bridge is a heritage-listed road bridge that carries the Weismantels-Dingadee Road across the Karuah River, located at Monkerai, New South Wales, Australia. The bridge is also known as the Monkerai Bridge over Karuah River. The bridge is owned by Transport for NSW. It was added to the New South Wales State Heritage Register on 20 June 2000.
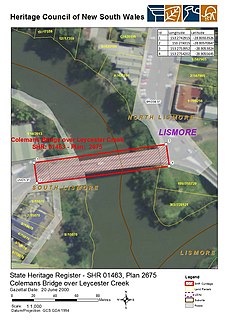
The Colemans Bridge is a heritage-listed road bridge that carries Union Street across the Leycester Creek in Lismore, New South Wales, Australia. It was designed by Harvey Dare and built in 1907 by W. F. Oakes. The bridge is owned by Transport for NSW. It was added to the New South Wales State Heritage Register on 20 June 2000.
The Dunmore Bridge is a heritage-listed road bridge that carries Clarence Town Road across the Paterson River in Woodville, New South Wales, Australia. It was designed by Percy Allan and built in 1899 by Morpeth contractor, S. McGill. The property is owned by Transport for NSW. It was added to the New South Wales State Heritage Register on 20 June 2000.

The Hinton Bridge over Paterson River is a heritage-listed road bridge that carrier the Hinton-Morpeth Road across the Paterson River at Hinton, New South Wales, Australia. The bridge was designed by Ernest de Burgh and built in 1901. The bridge is owned by Transport for NSW. The bridge was added to the New South Wales State Heritage Register on 20 June 2000.

The McKanes Falls Bridge is a heritage-listed road bridge at McKanes Falls Road, South Bowenfels, New South Wales, Australia. It was designed by John McDonald and NSW Engineer for Bridges and built from 1892 to 1893 by NSW Public Works. It is also known as McKanes Bridge. The property is owned by Transport for NSW. It was added to the New South Wales State Heritage Register on 20 June 2000.

The MacDonald River bridge is a heritage-listed road bridge that carries St Albans Road across the MacDonald River at St Albans, New South Wales, Australia. It was designed by Ernest de Burgh and built by John Ahearn and Son. It is also known as Norton Bridge. The property is owned by Transport for NSW. It was added to the New South Wales State Heritage Register on 20 June 2000.
Beckers Bridge is a heritage-listed timber truss road bridge that carries Main Road across Webbers Creek, located in Glendon Brook, New South Wales, Australia. It was designed by Ernest de Burgh. The Bridge is owned by Transport for NSW. It was added to the New South Wales State Heritage Register on 20 June 2000.
The Glennies Creek Bridge is a heritage-listed road bridge that carries the Rixs Creek-Falbrook Road across the Glennies Creek, located at Middle Falbrook, New South Wales, Australia. The bridge was designed by Ernest de Burgh and built in 1902-03 by William Murphy and James Taylor. The property is owned by Transport for NSW. The bridge was added to the New South Wales State Heritage Register on 20 June 2000.
The Wollombi Brook bridge is a heritage-listed road bridge that carries Putty Road across the Wollombi Brook at Bulga, New South Wales, Australia. The bridge was designed by Harvey Dare and built in 1912. The bridge is owned by Transport for NSW. The bridge was added to the New South Wales State Heritage Register on 20 June 2000.














