
Cox's Orange Pippin, in Britain often referred to simply as Cox, is an apple cultivar first grown in 1825, at Colnbrook in Buckinghamshire, England, by the retired brewer and horticulturist Richard Cox. Though the parentage of the cultivar is unknown, Ribston Pippin seems a likely candidate. DNA analysis of major apple pedigrees has suggested Margil as the parent of Cox, with Ribston Pippin being another Margil seedling. The variety was introduced for sale by the 1850s by Charles Turner, and grown commercially from the 1860s, particularly in the Vale of Evesham in Worcestershire, and later in Kent. A paper by Howard et al seems to suggest that the Cox Orange Pippin is a hybrid between the Cultivars: Rosemary Russet and Margil based on the SNP data 7

Sturmer is a village in the county of Essex, England, 2 miles (3 km) SE of Haverhill and close to the county border with Suffolk. Its name was originally "Stour Mere", from the River Stour and is explicitly mentioned in the Domesday Book of 1086. A Tudor illustration of the mere from the summer of 1571 exists in the National Archives. The mere still exists today to the east of the village. The village also gives its name to the Sturmer Pippin apple which was raised by Ezekiel Dillistone from 1831, and grown in the orchards of the village.

'Ribston Pippin' is a triploid cultivar of apples, also known by other names including 'Essex Pippin', 'Beautiful Pippin', 'Formosa', 'Glory of York', 'Ribstone', 'Rockhill's Russet', 'Travers', and 'Travers's Reinette'.

Claygate Pearmain is an apple cultivar. It was found at Claygate, Surrey in England and brought to the attention of the Royal Horticultural Society by John Braddick in 1821. The apple was a popular eating apple in Victorian times and spread through England and to America.
Table apples are a group of apple cultivars grown for eating raw as opposed to cooking or cidermaking. Table apples are usually sweet and the most prized exhibit particular aroma variations that differentiate them from other apples. D = Dual purpose

Golden Noble is an old English cultivar of domesticated apple, which is especially used as a cooking apple, since it is resulting in a sweetish puree when cooked and is a good choice for apple sauce.

The 'Laxton's Superb' is an apple cultivar that was developed in England in 1897. It is a cross breed between Cellini and 'Cox's Orange Pippin' and is not a cross between Wyken Pippin and Cox Orange Pippin. It is a British apple with a green color and a dull red flush. It is a firm-textured dessert apple. The fruit is well known for its sweet and aromatic taste which is likened to the parent species it is derived from, the 'Cox's Orange Pippin'.
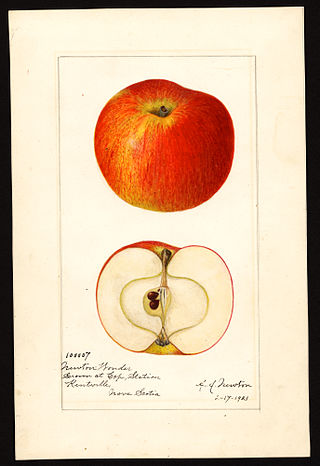
Malus domestica Newton Wonder is a cultivar of apple which is usually eaten cooked due to its sourness. The variety has a similar but slightly sweeter taste than the Bramley apple and is usually used in pies or as a preserve.
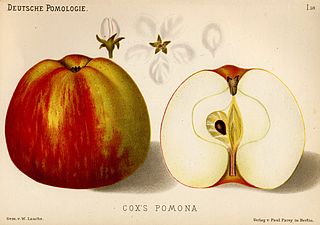
Richard Cox was an English brewer and horticulturist who bred the apple varieties Cox's Orange Pippin and Cox's Pomona.

Lord Lambourne is an apple cultivar with a sweet sharp flavor. It was raised by Laxtons Brothers Ltd in 1907 in Bedford, England. Received a Royal Horticultural Society Award of Merit in 1923.

The 'Sunset' is an apple cultivar derived from the Cox's Orange Pippin cultivar. Both are found in Great Britain. The fruit has red stripes and an orange flush over a gold background. Usually, part of the apple is red while part of it is yellow. It is similar to 'Cox's Orange Pippin' in that it displays some russetting. The 'Pixie' apple is a distant descendant.

'Worcester Pearmain' is an early season English cultivar of domesticated apple, that was developed in Worcester, England, by a Mr. Hale of Swanpool in 1874. It was once the most popular cultivar in England for early autumn harvest and is still popular to keep in the garden. It has been extensively used in apple breeding.

King of the Pippins or Reine des Reinettes (French), Goldparmäne, Wintergoldparmäne german is an old cultivar of domesticated apple originating from France, and is still used in its original form as well as in many derivative cultivars that have been bred from it. It was also formerly known as Golden Winter Pearmain, because of its ripening period at late fall.

'Alkmene' is a German cultivar of domesticated apple, also called 'Early Windsor'.

'Delbarestivale', also called 'Delcorf', is a cultivar of domesticated apple, which was developed by the Delbard nursery in France. It is a very sweet apple. 'Delcorf' is a parent of the 'Zari' apple and the 'Nicogreen' apple.

Ellison's Orange is an English cultivar of domesticated apple, it is a cross between the famous Cox's Orange Pippin and Cellini, which it resembles at most in looks and taste, but can develop a distinct aniseed flavor in storage. The variety is much more disease resistant than Cox's and therefore easier to cultivate.

Winston is an English cultivar of domesticated apple which was first named Winter King because of its availability in the winter, but was renamed as Winston in 1944 or in 1945, after Winston Churchill.

Jupiter is a modern cultivar of domesticated apple which was developed in England, by crossing a Cox's Orange Pippin with a Starking Delicious apple. According to the Orange Pippin website, it is one of the best Cox-style apples, with somewhat a more robust flavor, but more importantly, much more disease resistant. It is a heavy cropper and has a tendency to biennial bearing if not thinned. It is also frost resistant, and earned the Award of Garden Merit by the Royal Horticultural Society in 1993.

Grenadier is an English cultivar of domesticated apple mainly used for cooking. It originated in the mid-19th century in Buckinghamshire. It was first recorded in 1862 in Maidstone, Kent, exhibited by Charles Turner of Slough, Berkshire, and then commercially introduced by Bunyard Nursery.


















