
Cox's Orange Pippin, in Britain often referred to simply as Cox, is an apple cultivar first grown in 1825, at Colnbrook in Buckinghamshire, England, by the retired brewer and horticulturist Richard Cox. Though the parentage of the cultivar is unknown, Ribston Pippin seems a likely candidate. DNA analysis of major apple pedigrees has suggested Margil as the parent of Cox, with Ribston Pippin being another Margil seedling. The variety was introduced for sale by the 1850s by Charles Turner, and grown commercially from the 1860s, particularly in the Vale of Evesham in Worcestershire, and later in Kent. A paper by Howard et al seems to suggest that the Cox Orange Pippin is a hybrid between the Cultivars: Rosemary Russet and Margil based on the SNP data 7

James Grieve is an old variety of apple. It gets its name from its breeder, James Grieve, who raised the apple from pollination of a Pott's Seedling or a Cox's Orange Pippin apple in Edinburgh, Scotland some time before 1893.

A cooking apple or culinary apple is an apple that is used primarily for cooking, as opposed to a dessert apple, which is eaten raw. Cooking apples are generally larger, and can be tarter than dessert varieties. Some varieties have a firm flesh that does not break down much when cooked. Culinary varieties with a high acid content produce froth when cooked, which is desirable for some recipes. Britain grows a large range of apples specifically for cooking. Worldwide, dual-purpose varieties are more widely grown.

The Braeburn is a cultivar of apple that is firm to the touch with a red/orange vertical streaky appearance on a yellow/green background. Its color intensity varies with different growing conditions.

Gala is an apple cultivar with a sweet, mild flavour, a crisp but not hard texture, and a striped or mottled orange or reddish appearance. Originating from New Zealand in the 1930s, similar to most named apples, it is clonally propagated. In 2018, it surpassed Red Delicious as the apple cultivar with the highest production in the United States, according to the US Apple Association. It was the first time in over 50 years that any cultivar was produced more than Red Delicious.

Honeycrisp is an apple cultivar developed at the Minnesota Agricultural Experiment Station's Horticultural Research Center at the University of Minnesota, Twin Cities. Designated in 1974 with the MN 1711 test designation, patented in 1988, and released in 1991, the Honeycrisp, once slated to be discarded, has rapidly become a prized commercial commodity, as its sweetness, firmness, and tartness make it an ideal apple for eating raw. "...The apple wasn't bred to grow, store or ship well. It was bred for taste: crisp, with balanced sweetness and acidity." It has larger cells than most apple cultivars, a trait which is correlated with juiciness, as theoretically a higher number of cells rupture when bitten, releasing more juice in the mouth. The Honeycrisp also retains its pigment well and has a relatively long shelf life when stored in cool, dry conditions. Pepin Heights Orchards delivered the first Honeycrisp apples to grocery stores in 1997. The name Honeycrisp was trademarked by the University of Minnesota, but university officials were unsure of its protection status in 2007. It is now the official state fruit of Minnesota. A large-sized honeycrisp will contain about 113 calories.

Jazz is a trademarked brand of the Scifresh cultivar of domesticated apple. Scifresh is a cross between Royal Gala and Braeburn. It was developed in New Zealand as part of a collaboration between apple marketer ENZA, orchardists, and the Plant & Food Research institute. The original cross was made in 1985 on trees at Goddard Lane, Havelock North, Hawkes Bay, New Zealand. It launched commercially in April 2004. It is hard and crisp but juicy. The colour is flushes of red and maroon over shades of green, yellow and orange. Jazz is a close relative of the Kanzi apple, which is easier to bite and has a more delicate sweet-tart taste.

Blenheim Orange (Kempster's Pippin) is a cultivar of apple. It was found at Woodstock, Oxfordshire near Blenheim in England in about 1740. It has been described as a cooking apple.

'Ambrosia' is a cultivar of apple originating in British Columbia, Canada in the early 1990s. The original tree was first cultivated by the Mennell family of Similkameen Valley, British Columbia, who discovered it growing in their orchard.

The 'Rhode Island Greening' is an American apple variety and the official fruit of the state of Rhode Island.

The Newtown Pippin, also known as Albemarle Pippin, is an American apple that originated in the late 17th or early 18th century and is still cultivated on a small scale. At one time, there were two very similar apple cultivars known as the 'Yellow Newtown' and 'Green Newtown', one of which perhaps originated as a sport of the other.
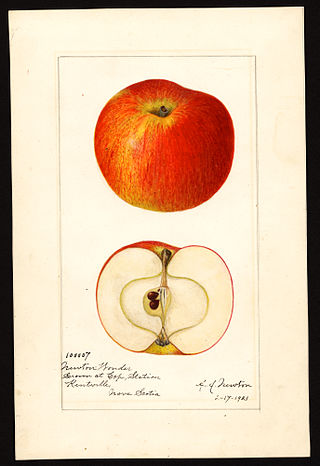
Malus domestica Newton Wonder is a cultivar of apple which is usually eaten cooked due to its sourness. The variety has a similar but slightly sweeter taste than the Bramley apple and is usually used in pies or as a preserve.

Bismarck is an apple cultivar. The fruit from the tree is used for cooking due to its sharp flavour and is most commonly pureed when cooking.

The Golden Spire apple was first discovered in Lancashire, England in about 1850. It was later grown in Gloucestershire where it was known as Tom Matthews and grown for cider production, although it had previously been used for both cider and eating. It can also be used for juicing and cooking.

The 'Sunset' is an apple cultivar derived from the Cox's Orange Pippin cultivar. Both are found in Great Britain. The fruit has red stripes and an orange flush over a gold background. Usually, part of the apple is red while part of it is yellow. It is similar to 'Cox's Orange Pippin' in that it displays some russetting. The 'Pixie' apple is a distant descendant.

Anna apple is a dual purpose cultivar of domesticated apple that is very early ripening and does well in warm climates.

Fiesta is a modern cultivar of domesticated apple which is often marketed as Red Pippin. It was developed in the United Kingdom by breeders at the East Malling Research Station, combining the Cox's Orange Pippin with the Idared apple. According to the Orange Pippin website, it is one of the best Cox's style apples, but much easier to grow having good disease resistance.

Ellison's Orange is an English cultivar of domesticated apple, it is a cross between the famous Cox's Orange Pippin and Cellini, which it resembles at most in looks and taste, but can develop a distinct aniseed flavor in storage. The variety is much more disease resistant than Cox's and therefore easier to cultivate.

Golden Russet is an old American cultivar of domesticated apple which is excellent for fresh eating as well as for apple cider production. It is a russet apple and is therefore especially used as a cider apple. It is sometimes known as 'English Golden Russet', and has frequently been confused with 'English Russet'.

Winston is an English cultivar of domesticated apple which was first named Winter King because of its availability in the winter, but was renamed as Winston in 1944 or in 1945, after Winston Churchill.




















