
Pears are fruits produced and consumed around the world, growing on a tree and harvested in the Northern Hemisphere in late summer into October. The pear tree and shrub are a species of genus Pyrus, in the family Rosaceae, bearing the pomaceous fruit of the same name. Several species of pears are valued for their edible fruit and juices, while others are cultivated as trees.

A plum is a fruit of some species in Prunus subg. Prunus. Dried plums are called prunes.

Fruit tree propagation is usually carried out vegetatively (non-sexually) by grafting or budding a desired variety onto a suitable rootstock.

Carambola, also known as star fruit, is the fruit of Averrhoa carambola, a species of tree native to tropical Southeast Asia. The mildly poisonous fruit is commonly consumed in parts of Brazil, Southeast Asia, South Asia, the South Pacific, Micronesia, parts of East Asia, the United States, and the Caribbean and contains the neurotoxin caramboxin. The tree is cultivated throughout tropical areas of the world.

Guava is a common tropical fruit cultivated in many tropical and subtropical regions. The common guava Psidium guajava is a small tree in the myrtle family (Myrtaceae), native to Mexico, Central America, the Caribbean and northern South America. The name guava is also given to some other species in the genus Psidium such as strawberry guava and to the pineapple guava, Feijoa sellowiana. In 2019, 55 million tonnes of guavas were produced worldwide, led by India with 45% of the total. Botanically, guavas are berries.

The quince is the sole member of the genus Cydonia in the Malinae subtribe of the Rosaceae family. It is a deciduous tree that bears hard, aromatic bright golden-yellow pome fruit, similar in appearance to a pear. Ripe quince fruits are hard, tart, and astringent. They are seldom eaten raw, but are processed into marmalade, jam, paste or alcoholic beverages.

The Granny Smith, also known as a green apple or sour apple, is an apple cultivar which originated in Australia in 1868. It is named after Maria Ann Smith, who propagated the cultivar from a chance seedling. The tree is thought to be a hybrid of Malus sylvestris, the European wild apple, with the domesticated apple Malus domestica as the polleniser.

Cider apples are a group of apple cultivars grown for their use in the production of cider. Cider apples are distinguished from "cookers" and "eaters", or dessert apples, by their bitterness or dryness of flavour, qualities which make the fruit unpalatable but can be useful in cidermaking. Some apples are considered to occupy more than one category.

A cooking apple or culinary apple is an apple that is used primarily for cooking, as opposed to a dessert apple, which is eaten raw. Cooking apples are generally larger, and can be tarter than dessert varieties. Some varieties have a firm flesh that does not break down much when cooked. Culinary varieties with a high acid content produce froth when cooked, which is desirable for some recipes. Britain grows a large range of apples specifically for cooking. Worldwide, dual-purpose varieties are more widely grown.

Gravenstein is a triploid apple cultivar that originated in the 17th century or earlier. The fruit has a tart flavor, and it is heavily used as a cooking apple, especially for apple sauce and apple cider. It does not keep well, and it is available only in season. This is in part because neither cold storage, nor regular controlled atmosphere keeps the apples distinctive aroma, but nsapples.com states that "recently however, low oxygen CA storage has shown promise in retaining this harvest-time quality".

Cripps Pink is a cultivar of apple. It is one of several cultivars sold under the trade mark name Pink Lady. It was originally bred by John Cripps at the Western Australia Department of Agriculture, by crossing the Australian apple Lady Williams with a Golden Delicious; the result is a combination of the firm, long-storing property of Lady Williams with the sweetness and lack of storage scald of Golden Delicious.

The Kingston Black, also known as Black Taunton, is a cultivar of apple originating from the United Kingdom and used in making cider. The name of the cultivar comes from the apples' dark red or purplish skin, though despite the name, the fruit does not have a black hue.

The Norfolk Biffin, also spelt Norfolk Beefing, is a local apple cultivar originating from the English county of Norfolk, also known by several other names including Reeds Baker, Tallesin, and Winter Coleman.

An apple is an edible fruit produced by an apple tree. Apple trees are cultivated worldwide and are the most widely grown species in the genus Malus. The tree originated in Central Asia, where its wild ancestor, Malus sieversii, is still found today. Apples have been grown for thousands of years in Asia and Europe and were brought to North America by European colonists. Apples have religious and mythological significance in many cultures, including Norse, Greek, and European Christian tradition.
'Brown Snout' is a 19th-century cultivar of cider apple originating in Herefordshire in the United Kingdom, though now grown in other counties and parts of the world.
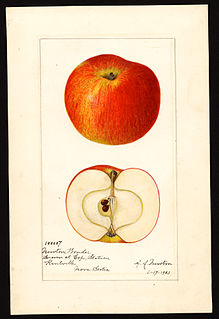
Malus domestica Newton Wonder is a cultivar of apple which is usually eaten cooked due to its sourness. The variety has a similar but slightly sweeter taste than the Bramley apple and is usually used in pies or as a preserve.

White Transparent is an early-season cultivar of apple which is usually used for cooking due to its sharp taste. It is sometimes said to be the same as 'Yellow Transparent', but 'Yellow Transparent' is sometimes described differently, with fine rather than coarse flesh, and a sub-acid rather than acid flavour. Weight 75 g, density 0.75 g/cc, sugar 10.5%, acid 11 g/litre, vitamin C 15 mg/100g.

The Leccino olive is one of the primary olive cultivars used in the production of Italian olive oil. Across Italy, it is one of the primary olive cultivars found in olive groves. It is believed to have originated in Tuscany, and it is now grown all over the world. Due to its delicate flavor, the olive oil it produces is commonly blended with Frantoio, Coratina, Moraiolo and Pendolino in order to create more flavor.

Anna apple is a dual purpose cultivar of domesticated apple that is very early ripening and does well in warm climates.

'Duchess of Oldenburg' is an old Russian cultivar of cultivated apple which has attractive streaks of yellow and red. It was commonly but not universally known in America simply as 'Oldenburg' after the American Pomological Society listed that as the official name, a name also used for the 'Geheimrat Dr. Oldenburg' cultivar. The skin of the apple is more prominently striped than that of 'Geheimrat Dr. Oldenburg'.




















