
Salvia rosmarinus, commonly known as rosemary, is a shrub with fragrant, evergreen, needle-like leaves and white, pink, purple, or blue flowers. It is native to the Mediterranean region, as well as Portugal and Spain. Until 2017, it was known by the scientific name Rosmarinus officinalis, now a synonym.

Salix alba, the white willow, is a species of willow native to Europe and western and central Asia. The name derives from the white tone to the undersides of the leaves.

Malus domestica is an English cultivar of apple that is usually eaten cooked due to its sourness. The variety comes from a pip planted by Mary Ann Brailsford. The Concise Household Encyclopedia states, "Some people eat this apple raw in order to cleanse the palate, but Bramley's seedling is essentially the fruit for tart, pie, or dumpling." Once cooked, however, it has a lighter flavour. A peculiarity of the variety is that when cooked it becomes golden and fluffy.

A cooking apple or culinary apple is an apple that is used primarily for cooking, as opposed to a dessert apple, which is eaten raw. Cooking apples are generally larger, and can be tarter than dessert varieties. Some varieties have a firm flesh that does not break down much when cooked. Culinary varieties with a high acid content produce froth when cooked, which is desirable for some recipes. Britain grows a large range of apples specifically for cooking. Worldwide, dual-purpose varieties are more widely grown.

The Haralson is a cultivar of apple that is medium-sized and has a round-conic shape.

Gala is an apple cultivar with a sweet, mild flavor, a crisp but not hard texture, and a striped or mottled orange or reddish appearance. Originating from New Zealand in the 1930s, similar to most named apples, it is clonally propagated. In 2018, it surpassed Red Delicious as the apple cultivar with the highest production in the United States, according to the US Apple Association. It was the first time in over 50 years that any cultivar was produced more than Red Delicious.

Honeycrisp is an apple cultivar developed at the Minnesota Agricultural Experiment Station's Horticultural Research Center at the University of Minnesota, Twin Cities. Designated in 1974 with the MN 1711 test designation, patented in 1988, and released in 1991, the Honeycrisp, once slated to be discarded, has rapidly become a prized commercial commodity, as its sweetness, firmness, and tartness make it an ideal apple for eating raw. "...The apple wasn't bred to grow, store or ship well. It was bred for taste: crisp, with balanced sweetness and acidity." It has larger cells than most apple cultivars, a trait which is correlated with juiciness, as larger cells are more prone to rupturing instead of cleaving along the cell walls; this rupturing effect is likely what makes the apple taste juicier. The Honeycrisp also retains its pigment well and has a relatively long shelf life when stored in cool, dry conditions. Pepin Heights Orchards delivered the first Honeycrisp apples to grocery stores in 1997. The name Honeycrisp was trademarked by the University of Minnesota, but university officials were unsure of its patent status in 2007. It is now the official state fruit of Minnesota. A large-sized honeycrisp will contain about 116 kilocalories (490 kJ).

An apple is a round, edible fruit produced by an apple tree. Apple trees are cultivated worldwide and are the most widely grown species in the genus Malus. The tree originated in Central Asia, where its wild ancestor, Malus sieversii, is still found. Apples have been grown for thousands of years in Eurasia and were introduced to North America by European colonists. Apples have religious and mythological significance in many cultures, including Norse, Greek, and European Christian tradition.

The 'York Imperial', or 'York', is a cultivar of apple from which a number of other valuable strains and cultivars have arisen, including four sport varieties: Commander York, Ramey York, Red Yorking, and Yorking.

The 'Laxton's Superb' is an apple cultivar that was developed in England in 1897. It is a cross breed between 'Cellini' and 'Cox's Orange Pippin'. It is a British apple with a green color and a dull red flush. It is a firm-textured dessert apple. The fruit is well known for its sweet and aromatic taste, which is likened to the parent cultivar it is derived from, the 'Cox's Orange Pippin'.
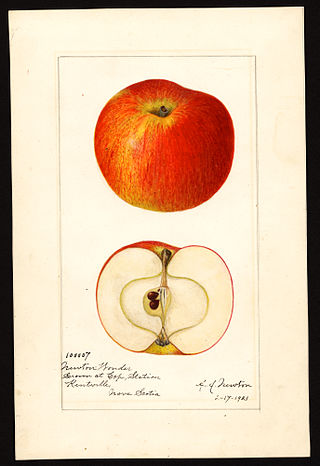
Malus domestica Newton Wonder is a cultivar of apple which is usually eaten cooked due to its sourness. The variety has a similar but slightly sweeter taste than the Bramley apple and is usually used in pies or as a preserve.

'Worcester Pearmain' is an early season English cultivar of domesticated apple, that was developed in Worcester, England, by a Mr. Hale of Swanpool in 1874. It was once the most popular cultivar in England for early autumn harvest and is still popular to keep in the garden. It has been extensively used in apple breeding.

King of the Pippins or Reine des Reinettes (French), Goldparmäne, Wintergoldparmäne (German) is an old cultivar of domesticated apple originating from France, and is still used in its original form as well as in many derivative cultivars that have been bred from it. It was also formerly known as Golden Winter Pearmain, because of its ripening period at late fall.

'Ellison's Orange' is an English cultivar of domesticated apple, it is a cross between the 'Cox's Orange Pippin' and 'Cellini', which it resembles most in looks and taste, but can develop a distinct aniseed flavor in storage. The variety is much more disease-resistant than Cox's and therefore easier to cultivate.

Winston is an English cultivar of domesticated apple which was first named Winter King because of its availability in the winter, but was renamed as Winston in 1944 or in 1945, after Winston Churchill.

Suntan is an English cultivar of domesticated apple that have earned the Award of Garden Merit by the Royal Horticultural Society in 1999.

Jupiter is a modern cultivar of domesticated apple which was developed in England, by crossing a Cox's Orange Pippin with a Starking Delicious apple. According to the Orange Pippin website, it is one of the best Cox-style apples, with somewhat a more robust flavor, but more importantly, much more disease resistant. It is a heavy cropper and has a tendency to biennial bearing if not thinned. It is also frost resistant, and earned the Award of Garden Merit by the Royal Horticultural Society in 1993.

Grenadier is an English cultivar of domesticated apple mainly used for cooking. It originated in the mid-19th century in Buckinghamshire. It was first recorded in 1862 in Maidstone, Kent, exhibited by Charles Turner of Slough, Berkshire, and then commercially introduced by Bunyard Nursery.

The Field Elm cultivar Ulmus minor 'Dicksonii', commonly known as Dickson's Golden Elm, is a yellow-leaved tree raised in Chester in 1900 by Dickson's Nursery, which distributed it from the autumn of 1907 as 'Golden Cornish Elm'. 'Cornish Elm' was the name often given in error to Guernsey or Wheatley Elm by the local authorities who planted the latter extensively, an error which may have influenced the choice of name by Dickson's nursery. 'Dicksonii' is usually listed as a variety of Guernsey Elm rather than Cornish Elm, Bean giving 'Wheatleyi Aurea' as a synonym, and Hillier 'Sarniensis Aurea' and later U. × sarniensis 'Dicksonii'. Clibrans' nursery of Altrincham, however, described it (1922) as otherwise identical "in habit and constitution" to 'type' Cornish Elm. The Späth nursery of Berlin distributed it from c.1913 as U. campestris cornubiensis Dicksonii. The nursery Messieurs Otin père et fils of Saint-Étienne sold an Ulmus Wheatleyi aurea pyramidalis, with leaves marbled yellow, in 1882, earlier than Dickson's introduction.



















