
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is an organic compound that provides energy to drive and support many processes in living cells, such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, condensate dissolution, and chemical synthesis. Found in all known forms of life, ATP is often referred to as the "molecular unit of currency" of intracellular energy transfer. When consumed in metabolic processes, it converts either to adenosine diphosphate (ADP) or to adenosine monophosphate (AMP). Other processes regenerate ATP. The human body recycles its own body weight equivalent in ATP each day. It is also a precursor to DNA and RNA, and is used as a coenzyme.

Adenosine diphosphate (ADP), also known as adenosine pyrophosphate (APP), is an important organic compound in metabolism and is essential to the flow of energy in living cells. ADP consists of three important structural components: a sugar backbone attached to adenine and two phosphate groups bonded to the 5 carbon atom of ribose. The diphosphate group of ADP is attached to the 5’ carbon of the sugar backbone, while the adenine attaches to the 1’ carbon.
Adenosine thiamine triphosphate (AThTP), or thiaminylated adenosine triphosphate, is a natural thiamine adenine nucleotide. It was discovered in Escherichia coli where it may account for up to 15 - 20% of total thiamine under carbon starvation. AThTP also exists in eukaryotic organisms such as yeast, roots of higher plants and animal tissues, albeit at a much lower concentration. It was found to exist in small amounts in the muscle, heart, brain, kidneys and liver of mice.
Translocase is a general term for a protein that assists in moving another molecule, usually across a cell membrane. These enzymes catalyze the movement of ions or molecules across membranes or their separation within membranes. The reaction is designated as a transfer from “side 1” to “side 2” because the designations “in” and “out”, which had previously been used, can be ambiguous. Translocases are the most common secretion system in Gram positive bacteria.
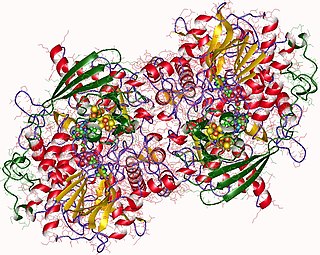
Adenylyl-sulfate reductase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction of the reduction of adenylyl-sulfate/adenosine-5'-phosphosulfate (APS) to sulfite through the use of an electron donor cofactor. The products of the reaction are AMP and sulfite, as well as an oxidized electron donor cofactor.
In enzymology, an adenylylsulfatase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme ADP-phosphoglycerate phosphatase (EC 3.1.3.28) catalyzes the reaction
In enzymology, an adenylylsulfate-ammonia adenylyltransferase (EC 2.7.7.51) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction adenylyl sulfate + NH3 adenosine 5'-phosphoramidate + sulfate.

In enzymology, an adenylyl-sulfate kinase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an ADP—thymidine kinase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an aldose-1-phosphate adenylyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a FMN adenylyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a glucose-1-phosphate adenylyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a [glutamate—ammonia-ligase] adenylyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a nucleoside-triphosphate-adenylate kinase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a phenylalanine adenylyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a ribose-5-phosphate adenylyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a sulfate adenylyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

The prokaryotic riboflavin biosynthesis protein is a bifunctional enzyme found in bacteria that catalyzes the phosphorylation of riboflavin into flavin mononucleotide (FMN) and the adenylylation of FMN into flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD). It consists of a C-terminal riboflavin kinase and an N-terminal FMN-adenylyltransferase. This bacterial protein is functionally similar to the monofunctional riboflavin kinases and FMN-adenylyltransferases of eukaryotic organisms, but only the riboflavin kinases are structurally homologous.

Dissimilatory sulfate reduction is a form of anaerobic respiration that uses sulfate as the terminal electron acceptor to produce hydrogen sulfide. This metabolism is found in some types of bacteria and archaea which are often termed sulfate-reducing organisms. The term "dissimilatory" is used when hydrogen sulfide is produced in an anaerobic respiration process. By contrast, the term "assimilatory" would be used in relation to the biosynthesis of organosulfur compounds, even though hydrogen sulfide may be an intermediate.







