Related Research Articles

In the United States, Social Security is the commonly used term for the federal Old-Age, Survivors, and Disability Insurance (OASDI) program and is administered by the Social Security Administration. The original Social Security Act was enacted in 1935, and the current version of the Act, as amended, encompasses several social welfare and social insurance programs.
Unemployment benefits, also called unemployment insurance, unemployment payment, unemployment compensation, or simply unemployment, are payments made by authorized bodies to unemployed people. In the United States, benefits are funded by a compulsory governmental insurance system, not taxes on individual citizens. Depending on the jurisdiction and the status of the person, those sums may be small, covering only basic needs, or may compensate the lost time proportionally to the previous earned salary.

The U.S. Railroad Retirement Board (RRB) is an independent agency in the executive branch of the United States government created in 1935 to administer a social insurance program providing retirement benefits to the country's railroad workers.
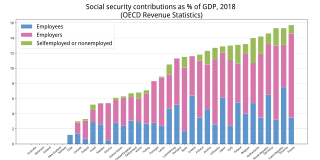
Social insurance is a form of social welfare that provides insurance against economic risks. The insurance may be provided publicly or through the subsidizing of private insurance. In contrast to other forms of social assistance, individuals' claims are partly dependent on their contributions, which can be considered insurance premiums to create a common fund out of which the individuals are then paid benefits in the future.
Trade Adjustment Assistance (TAA) is a federal program of the United States government to act as a way to reduce the damaging impact of imports felt by certain sectors of the U.S. economy. The current structure features four components of Trade Adjustment Assistance: for workers, firms, farmers, and communities. Each cabinet-level department was tasked with a different sector of the overall Trade Adjustment Assistance program. The program for workers is the largest, and administered by the U.S. Department of Labor. The program for farmers is administered by the U.S. Department of Agriculture, and the firms and communities programs are administered by the U.S. Department of Commerce.
California's Paid Family Leave (PFL) insurance program, which is also known as the Family Temporary Disability Insurance (FTDI) program, is a law enacted in 2002 that extends unemployment disability compensation to cover individuals who take time off work to care for a seriously ill family member or bond with a new minor child. If eligible, you can receive benefit payments for up to eight weeks. Payments are about 60 to 70 percent of your weekly wages earned 5 to 18 months before your claim start date. You will receive payments by debit card or check. Benefits equal approximately 70% of earnings and have a maximum per week, for a total of up to six weeks.
Social security, in Australia, refers to a system of social welfare payments provided by Australian Government to eligible Australian citizens, permanent residents, and limited international visitors. These payments are almost always administered by Centrelink, a program of Services Australia. In Australia, most payments are means tested.
The New York State Department of Labor is the department of the New York state government that enforces labor law and administers unemployment benefits.
The Defense Base Act (DBA) is an extension of the federal workers' compensation program that covers longshoremen and harbor workers, the Longshore and Harbor Workers' Compensation Act 33 U.S.C. §§ 901–950. The DBA covers persons employed at United States defense bases overseas. The DBA is designed to provide medical treatment and compensation to employees of defense contractors injured in the scope and course of employment. The DBA is administered by the United States Department of Labor.
The Ohio Department of Job and Family Services (ODJFS) is the administrative department of the Ohio state government responsible for supervising the state's public assistance, workforce development, unemployment compensation, child and adult protective services, adoption, child care, and child support programs. Prior to July 2013, ODJFS was also the state agency responsible for the administration of Ohio's Medicaid program. In July 2013, a new state agency was created, the Ohio Department of Medicaid (ODM), Ohio’s first Executive-level Medicaid agency. ODJFS employs about 2,300 full time employees and has an annual budget of $3.3 billion.

Social programs in the United States are programs designed to ensure that the basic needs of the American population are met. Federal and state social programs include cash assistance, health insurance, food assistance, housing subsidies, energy and utilities subsidies, and education and childcare assistance. Similar benefits are sometimes provided by the private sector either through policy mandates or on a voluntary basis. Employer-sponsored health insurance is an example of this.
Disability benefits are funds provided from public or private sources to a person who is ill or who has a disability.
99ers is a colloquial term for unemployed people in the United States, mostly citizens, who have exhausted all of their unemployment benefits, including all unemployment extensions. As a result of the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act passed by Congress in February 2009, many unemployed people could receive up to 99 weeks of unemployment insurance benefits, hence the name "99ers". An estimated 7 million people are affected.
The Unemployment Trust Fund (UTF) is composed of 59 accounts in the United States Treasury related to unemployment insurance program. Specifically, there are 53 state accounts, 4 federal accounts, and 2 accounts in connection with Railroad Retirement Board.
The Middle Class Tax Relief and Job Creation Act of 2012, also known as the "payroll tax cut", was an Act of the United States Congress. The bill was passed by the U.S. House of Representatives on February 17, 2012 by a vote of 293‑132, and by the Senate by a vote of 60‑36 on the same day. The bill was signed into law by President Barack Obama on February 22, 2012.

The Emergency Unemployment Compensation Extension Act is a bill that would extend the length of unemployment benefits to cover another three months, until March 31, 2014. The three-month extension would cost $6.4 billion.
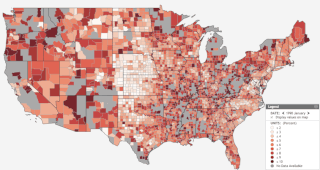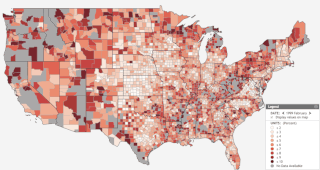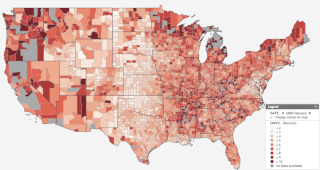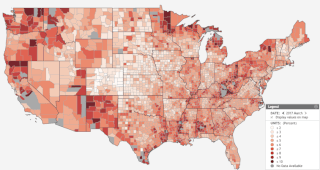
Unemployment insurance in the United States, colloquially referred to as unemployment benefits, refers to social insurance programs which replace a portion of wages for individuals during unemployment. The first unemployment insurance program in the U.S. was created in Wisconsin in 1932, and the federal Social Security Act of 1935 created programs nationwide that are administered by state governments. The constitutionality of the program was upheld by the Supreme Court in 1937.
Denmark is a Scandinavian country in Europe consisting of the Jutland Peninsula and numerous islands. Typically, Denmark has had relatively low unemployment rates. Currently, Denmark has generous unemployment benefits in the form of private insurance funds. Unemployment benefits are typically payments made by the state or other authorized actors to unemployed persons.

The Families First Coronavirus Response Act is an Act of Congress meant to respond to the economic impacts of the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic. The act provides funding for free coronavirus testing, 14-day paid leave for American workers affected by the pandemic, and increased funding for food stamps.

The Government of Canada introduced multiple temporary social security and financial aid programs in response to the economic impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic in Canada. The initial CA$82-billion aid package was announced on March 18, 2020 by Justin Trudeau.
References
- ↑ Texas Workforce Commission, Understanding Extended Unemployment Benefits PDF
- ↑ "Emergency Unemployment Compensation (EUC) Expired on January 1, 2014, Employment & Training Administration (ETA) - U.S. Department of Labor". www.workforcesecurity.doleta.gov. Retrieved 2016-07-08.
- ↑ Washington State Employment Dept., Emergency Unemployment Compensation FAQ
- ↑ U.S. Dept. of Labor, Unemployment Insurance Program Letter No. 04-10, Change 9
- ↑ U.S. Dept. of Labor, Key Dates for UI Programs Following Enactment of Middle Class Tax Relief and Job Creation Act of 2012, P.L. 112-96
- ↑ U.S. Dept. of Labor, Unemployment Insurance Extended Benefits
- ↑ U.S. Dept. of Labor, Emergency Unemployment Compensation (EUC) Program PDF