
A diacritic is a glyph added to a letter or to a basic glyph. The term derives from the Ancient Greek διακριτικός, from διακρίνω. The word diacritic is a noun, though it is sometimes used in an attributive sense, whereas diacritical is only an adjective. Some diacritics, such as the acute ⟨ó⟩, grave ⟨ò⟩, and circumflex ⟨ô⟩, are often called accents. Diacritics may appear above or below a letter or in some other position such as within the letter or between two letters.

Y, or y, is the twenty-fifth and penultimate letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. According to some authorities, it is the sixth vowel letter of the English alphabet. Its name in English is wye, plural wyes.
The circumflex is a diacritic in the Latin and Greek scripts that is also used in the written forms of many languages and in various romanization and transcription schemes. It received its English name from Latin: circumflexus "bent around"—a translation of the ‹See Tfd›Greek: περισπωμένη.

A breve is the diacritic mark ◌̆, shaped like the bottom half of a circle. As used in Ancient Greek, it is also called brachy, βραχύ. It resembles the caron but is rounded, in contrast to the angular tip of the caron. In many forms of Latin, ◌̆ is used for a shorter, softer variant of a vowel, such as "Ĭ", where the sound is nearly identical to the English /i/.

Á, á (a-acute) is a letter of the Chinese (Pinyin), Blackfoot, Czech, Dobrujan Tatar, Dutch, Faroese, Filipino, Galician, Hungarian, Icelandic, Irish, Karakalpak, Lakota, Navajo, Occitan, Portuguese, Sámi, Slovak, Spanish, Vietnamese, Welsh and Western Apache languages as a variant of the letter a. It is sometimes confused with à; e.g. "5 pommes á €1", which is supposed to be written as "5 pommes à €1".

The Russian alphabet is the script used to write the Russian language. It is derived from the Cyrillic script, which was modified in the 9th century to capture accurately the phonology of the first Slavic literary language, Old Slavonic. Initially an old variant of the Bulgarian alphabet, it was used in Kievan Rus' from the 10th century onward to write what would become the modern Russian language.

The Romanian alphabet is a variant of the Latin alphabet used for writing the Romanian language. It is a modification of the classical Latin alphabet and consists of 31 letters, five of which have been modified from their Latin originals for the phonetic requirements of the language.
A yer is either of two letters in Cyrillic alphabets, ъ and ь. The Glagolitic alphabet used, as respective counterparts, the letters (Ⱏ) and (Ⱐ). They originally represented phonemically the "ultra-short" vowels in Slavic languages, including Old Church Slavonic, and are collectively known as the yers.

The Bulgarian Cyrillic alphabet is used to write the Bulgarian language. The Cyrillic alphabet was originally developed in the First Bulgarian Empire during the 9th – 10th century AD at the Preslav Literary School.

The soft sign is a letter in the Cyrillic script that is used in various Slavic languages. In Old Church Slavonic, it represented a short or reduced front vowel. However, over time, the specific vowel sound it denoted was largely eliminated and merged with other vowel sounds.

Yeru or Eru, usually called Y in modern Russian or Yery or Ery historically and in modern Church Slavonic, is a letter in the Cyrillic script. It represents the close central unrounded vowel after non-palatalised (hard) consonants in the Belarusian and Russian alphabets.
In phonetics, vowel reduction is any of various changes in the acoustic quality of vowels as a result of changes in stress, sonority, duration, loudness, articulation, or position in the word, and which are perceived as "weakening". It most often makes the vowels shorter as well.

The letter Ъ ъ of the Cyrillic script is known as er golyam in the Bulgarian alphabet, as the hard sign in the modern Russian and Rusyn alphabets, as the debelo jer in pre-reform Serbian orthography, and as ayirish belgisi in the Uzbek Cyrillic alphabet. The letter is called back yer or back jer and yor or jor in the pre-reform Russian orthography, in Old East Slavic, and in Old Church Slavonic.

Three alphabets are used to write Kazakh: the Cyrillic, Latin and Arabic scripts. The Cyrillic script is used in Kazakhstan, Russia, and Mongolia. An October 2017 Presidential Decree in Kazakhstan ordered that the transition from Cyrillic to a Latin script be completed by 2031. The Arabic script is used in Saudi Arabia, Iran, Afghanistan, and parts of China.
The grave accent is a diacritical mark used to varying degrees in French, Dutch, Portuguese, Italian, Catalan and many other western European languages as well as for a few unusual uses in English. It is also used in other languages using the Latin alphabet, such as Mohawk and Yoruba, and with non-Latin writing systems such as the Greek and Cyrillic alphabets and the Bopomofo or Zhuyin Fuhao semi-syllabary. It has no single meaning, but can indicate pitch, stress, or other features.

A with breve is a letter of the Cyrillic script. It may be a homoglyph of the Latin letter A with breve unless the typeface distinguishes between the Latin and Cyrillic breve.
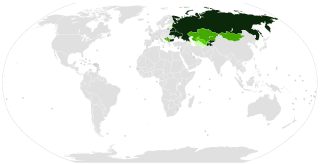
Numerous Cyrillic alphabets are based on the Cyrillic script. The early Cyrillic alphabet was developed in the 9th century AD and replaced the earlier Glagolitic script developed by the theologians Cyril and Methodius. It is the basis of alphabets used in various languages, past and present, Slavic origin, and non-Slavic languages influenced by Russian. As of 2011, around 252 million people in Eurasia use it as the official alphabet for their national languages. About half of them are in Russia. Cyrillic is one of the most-used writing systems in the world. The creator is Saint Clement of Ohrid from the Preslav literary school in the First Bulgarian Empire.
Inverted breve or arch is a diacritical mark, shaped like the top half of a circle ( ̑ ), that is, like an upside-down breve (˘). It looks similar to the circumflex (ˆ), which has a sharp tip, while the inverted breve is rounded:.
Ge with breve is a letter of the Cyrillic script. It may be a homoglyph of the Latin letter A with breve unless the typeface distinguishes between the Latin and Cyrillic breve.













