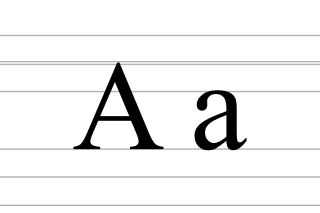
A, or a, is the first letter and the first vowel letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, and others worldwide. Its name in English is a, plural aes.

D, or d, is the fourth letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is dee, plural dees.

R, or r, is the eighteenth letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ar, plural ars, or in Ireland or.

Esh is a character used in phonology to represent the voiceless postalveolar fricative.

ʔ⟨Majuscule: Ɂ, Minuscule: ɂ⟩, called glottal stop, is an alphabetic letter in some Latin alphabets, most notably in several languages of Canada where it indicates a glottal stop sound. Such usage derives from phonetic transcription, for example the International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA), that use this letter for the glottal stop sound. The letter derives graphically from use of the apostrophe ⟨ʼ⟩ or the symbol ʾ for glottal stop.

Ou is a ligature of the Greek letters ο and υ which was frequently used in Byzantine manuscripts. This omicron-upsilon ligature is still seen today on icon artwork in Greek Orthodox churches, and sometimes in graffiti or other forms of informal or decorative writing.
Ə, or ə, also called schwa, is an additional letter of the Latin alphabet. In the International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA), minuscule ə is used to represent the mid central vowel or a schwa.
A unicase or unicameral alphabet has just one case for its letters. Arabic, Brahmic scripts like Telugu, Kannada, Malayalam, Tamil and Devanagari, Hebrew, Iberian, Georgian, Chinese, Syriac, Thai and Hangul are unicase writing systems, while modern Latin, Greek, Cyrillic, and Armenian are bicameral, as they have two cases for each letter, e.g. B and b, Β and β, or Բ and բ. Individual characters can also be called unicameral if they are used as letters with a generally bicameral alphabet but have only one form for both cases; for example, the ʻokina as used in Polynesian languages and the glottal stop as used in Nuu-chah-nulth are unicameral.

Latin epsilon or open E is a letter of the extended Latin alphabet, based on the lowercase of the Greek letter epsilon (ε). It was introduced in the 16th century by Gian Giorgio Trissino to represent the pronunciation of the "open e" in the Italian language; this use of the letter has since become the standard in IPA notation. Since the 20th century, the letter also occurs in the orthographies of many Niger–Congo and Nilo-Saharan languages, such as Ewe, Akan, Lingala, Dinka and Maasai, for the vowel or, and is included in the African reference alphabet.

ẗ is a modified letter of the Latin alphabet, derived from the letter T with a double dot on it. It is used in the ISO 233 transliteration of Arabic to represent tāʼ marbūṭa, and also in the Uralic Phonetic Alphabet to represent a tenuis interdental stop. It is also used in the Ixtlán Zapotec language.

⟨Ɓ⟩, called "B-hook" or "B with a hook", is a letter of the Latin alphabet and the International African Alphabet. Its lower-case form, ⟨⟩, represents a voiced bilabial implosive in the International Phonetic Alphabet. It is used to spell that sound in various languages, notably Fula, Hausa, and Giziga. It was also formerly used in, or at least proposed for, Xhosa and Zulu.

G with hook is a letter of the extended Latin alphabet. In the International Phonetic Alphabet, its small caps form represents the voiced uvular implosive and its lowercase form represents the voiced velar implosive. Because it occurs in the orthographies of some African languages, including some unofficial orthographies of Fula, it is included in the African reference alphabet.

Ᵽ or "P with stroke" is a letter of the Latin alphabet, formed from P with the addition of a stroke, usually through the bowl but sometimes through the descender. It is used in some phonetic transcription systems, such as the Americanist phonetic notation, to represent a fricative.
Ȼ is a letter of the Latin alphabet, formed from C with the addition of a stroke through the letter. Its minuscule form represents the sound in certain phonetic transcription systems for the indigenous languages of Mexico, and the Saanich alphabet uses its majuscule form for, and in Unifon, a phonemic transcription for American English; where it represents the sound of Ч.
The Latin-1 Supplement is the second Unicode block in the Unicode standard. It encodes the upper range of ISO 8859-1: 80 (U+0080) - FF (U+00FF). C1 Controls (0080–009F) are not graphic. This block ranges from U+0080 to U+00FF, contains 128 characters and includes the C1 controls, Latin-1 punctuation and symbols, 30 pairs of majuscule and minuscule accented Latin characters and 2 mathematical operators.

The letter Ƥ, called P with hook, is a letter of the Latin alphabet based on the letter p. It is used in some alphabets of African languages such as Serer.

The letter Ƭ, called T with hook, is a letter of the Latin alphabet based on the letter t. It is used in the Serer language.

The null sign (∅) is often used in mathematics for denoting the empty set. The same letter in linguistics represents zero, the lack of an element. It is commonly used in phonology, morphology, and syntax.

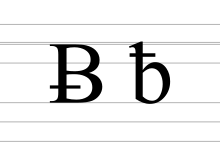
B, or b, is the second letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is bee, plural bees.

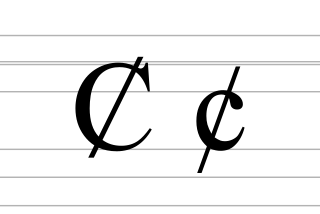
The C with bar, also known as barred C, is a modified letter of the Latin alphabet, formed from C with the addition of a bar. It was used in the final version of the Unified Northern Alphabet, approved in 1932, for Saami, Selkup, Khanty, Evenki, Even, Nanai, Udege, Chukchi, Koryak and Nivkh languages to denote the sound, although in some of these languages in practice, several other alphabets were used. Also, this letter was used in the Latinized Shugnan alphabet (1931-1939) to denote the sound.