A special election was held in Connecticut's at-large congressional district on December 16, 1790 to fill a vacancy left when Representative-elect Pierpont Edwards (P) declined to serve.
| Elections in Connecticut |
|---|
 |
A special election was held in Connecticut's at-large congressional district on December 16, 1790 to fill a vacancy left when Representative-elect Pierpont Edwards (P) declined to serve.
| Candidate | Party | Votes [1] | Percent |
|---|---|---|---|
| Jeremiah Wadsworth | Pro-Administration | 1,222 | 48.6% |
| Amasa Learned | Pro-Administration | 800 | 23.9% |
| Benjamin Huntington | Pro-Administration | 333 | 13.2% |
| Tapping Reeve | [2] | 203 | 8.1% |
| Stephen M. Mitchell | [2] | 103 | 4.1% |
| James Davenport | [2] | 37 | 1.5% |
| John Chester | [2] | 17 | 0.7% |
A by-election, also known as a special election in the United States and the Philippines, and a bye-election or a bypoll in India, is an election used to fill an office that has become vacant between general elections.

The 1926 United States Senate elections were elections for the United States Senate that occurred in the middle of Republican President Calvin Coolidge's second term. The 32 seats of Class 3 were contested in regular elections, and special elections were held to fill vacancies. The Republican majority was reduced by seven seats.

The 1998 United States House of Representatives elections were held on November 3, 1998, to elect U.S. Representatives to serve in the 106th United States Congress. They were part of the midterm elections held during President Bill Clinton's second term. They were a major disappointment for the Republicans, who were expecting to gain seats due to the embarrassment Clinton suffered during the Monica Lewinsky scandal and the "six-year itch" effect observed in most second-term midterm elections. However, the Republicans lost five seats to the Democrats, although they retained a narrow majority in the House. A wave of Republican discontent with Speaker Newt Gingrich prompted him to resign shortly after the election; he was replaced by Congressman Dennis Hastert of Illinois.
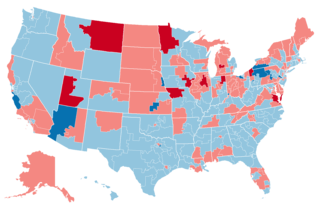
The 1976 United States House of Representatives elections were elections for the United States House of Representatives on November 2, 1976, to elect members to serve in the 95th United States Congress. They coincided with Jimmy Carter's election as president. Carter's narrow victory over Gerald Ford had limited coattails, and his Democratic Party gained a net of only one seat from the Republican Party in the House. The result was nevertheless disappointing to the Republicans, who were hoping to win back some of the seats they lost in the wake of the Watergate scandal two years earlier.

The 1974 United States House of Representatives elections were elections for the United States House of Representatives on November 5, 1974, to elect members to serve in the 94th United States Congress. They occurred in the wake of the Watergate scandal, which had forced President Richard Nixon to resign in favor of Gerald Ford. This scandal, along with high inflation, allowed the Democrats to make large gains in the midterm elections, taking 48 seats from the Republicans, and increasing their majority above the two-thirds mark. Altogether, there were 93 freshmen representatives in the 94th Congress when it convened on January 3, 1975. Those elected to office that year later came to be known collectively as "Watergate Babies." The gain of 49 Democratic seats was the largest pickup by the party since 1958. Only four Democratic incumbents lost their seats.

The 1956 United States House of Representatives elections was an election for the United States House of Representatives to elect members to serve in the 85th United States Congress. They were held for the most part on November 6, 1956, while Maine held theirs on September 10. They coincided with the re-election of President Dwight D. Eisenhower.

The 1950 United States House of Representatives elections was an election for the United States House of Representatives to elect members to serve in the 82nd United States Congress. They were held for the most part on November 7, 1950, while Maine held theirs on September 11. These elections occurred in the middle of President Harry Truman's second term.

The 1948 United States House of Representatives elections were elections for the United States House of Representatives to elect members to serve in the 81st United States Congress. They were held for the most part on November 2, 1948, while Maine held theirs on September 13. These elections coincided with President Harry S. Truman's election to a full term. Truman had campaigned against a "do-nothing"' Republican Party Congress that had opposed his initiatives and was seen as counterproductive. The Democratic Party regained control of both the House and Senate in this election. For Democrats, this was their largest gain since 1932. These were the last elections until 1980 when a member of a political party other than the Democrats, Republicans, or an independent had one or more seats in the chamber. As of 2023, this is the last time the Democrats gained more than 50 seats in a U.S. House election.

The 1940 United States House of Representatives elections were elections for the United States House of Representatives to elect members to serve in the 77th United States Congress. They were held for the most part on November 5, 1940, while Maine held theirs on September 9. They coincided with President Franklin D. Roosevelt's re-election to an unprecedented third term. His Democratic Party narrowly gained seats from the opposition Republican Party, cementing their majority. However, the election gave firm control of the US House of Representatives and Senate to the New Dealers once again, as Progressives dominated the election.
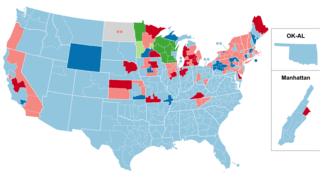
The 1934 United States House of Representatives elections were elections for the United States House of Representatives to elect members to serve in the 74th United States Congress. They were held for the most part on November 6, 1934, while Maine held theirs on September 10. They occurred in the middle of President Franklin D. Roosevelt's first term. The Democratic Party continued its progress, gaining another 9 net seats from the opposition Republican Party, who also lost seats to the Progressive Party. The Republicans were reduced below one-fourth of the chamber for the first time since the creation of the party. The Wisconsin Progressive Party, a liberal group which allied with the Democrats, also became a force in Wisconsin politics.

The 1920 United States House of Representatives elections were elections for the United States House of Representatives to elect members to serve in the 67th United States Congress. They were held for the most part on November 2, 1920, while Maine held its on September 13. They coincided with the election of President Warren G. Harding, the first time that women in all states were allowed to vote in federal elections after the passage of the 19th Amendment.

1914 United States House of Representatives elections were elections for the United States House of Representatives to elect members to serve in the 64th United States Congress. They were held for the most part on November 3, 1914, while Maine held theirs on September 14. They were held in the middle of President Woodrow Wilson's first term.
The 1836–37 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between July 4, 1836, and November 7, 1837. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives, either before or after the first session of the 25th United States Congress convened on September 4, 1837. With Arkansas and Michigan officially achieving statehood in 1836 and 1837, respectively, the size of the House was set at 242 seats.

The 2024 United States elections are scheduled to be held on Tuesday, November 5, 2024. During this presidential election year, the president and vice president will be elected. In addition, all 435 seats in the United States House of Representatives and 34 of the 100 seats in the United States Senate will be contested to determine the membership of the 119th United States Congress. Thirteen state and territorial governorships and numerous other state and local elections will also be contested.

The Robert Mueller special counsel investigation was an investigation into 45th U.S. president Donald Trump regarding Russian interference in the 2016 United States elections and was conducted by special prosecutor Robert Mueller from May 2017 to March 2019. It was also called the Russia investigation, Mueller probe, and Mueller investigation. The investigation focused on three points:
There were twelve special elections in 1947 to the United States House of Representatives during the 80th United States Congress. Each party held all of its seats elected in 1947, with the majority Republican Party keeping its seven seats, and President Harry Truman's Democratic Party keeping its five. Therefore, no party lost or gained U.S House seats in 1947.
There were several special elections to the United States House of Representatives in 1923, spanning the 67th United States Congress and 68th United States Congress.
There were elections in 1929 to the United States House of Representatives:

The 2024 United States House of Representatives elections will be held on November 5, 2024, as part of the 2024 United States elections, to elect representatives from all 435 congressional districts across each of the 50 U.S. states, as well as 6 non-voting delegates from the District of Columbia and the inhabited U.S. territories to the United States House of Representatives. Special elections have also been held on various dates in 2024. Numerous other federal, state, and local elections, including the U.S. presidential election and elections to the Senate, will also be held on this date. The winners of this election will serve in the 119th United States Congress, with seats apportioned among the states based on the 2020 United States census.