
Presidential elections were held in the United States from October 31 to December 3, 1800. In what is sometimes called the "Revolution of 1800", the Democratic-Republican Party candidate, Vice President Thomas Jefferson, defeated the Federalist Party candidate and incumbent, President John Adams. The election was a political realignment that ushered in a generation of Democratic-Republican leadership. This was the first presidential election in American history to be a rematch. It was also the first election in American history where an incumbent president did not win re-election.

The 6th United States Congress was the 6th meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, consisting of the Senate and the House of Representatives. It initially met at Congress Hall in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania and then was the first congress to meet in the new Capitol Building in Washington, D.C.. Its term was from March 4, 1799, to March 4, 1801, during the last two years of John Adams's presidency. It was the last Congress of the 18th century and the first to convene in the 19th. The apportionment of seats in House of Representatives was based on the 1790 United States census. Both chambers had a Federalist majority. This was the last Congress in which the Federalist Party controlled the presidency or either chamber of Congress.

The 7th United States Congress was a meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, consisting of the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives. It met in Washington, D.C. from March 4, 1801, to March 4, 1803, during the first two years of Thomas Jefferson's presidency. The apportionment of seats in the House of Representatives was based on the 1790 United States census. Both chambers had a Democratic-Republican majority, except when the Senate held a two-day Special Senate session in order to provide advice to the new President Thomas Jefferson, when there was still a Federalist majority in the Senate.

The 1806–07 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between April 29, 1806 and August 4, 1807. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 10th United States Congress convened on October 26, 1807. They occurred during Thomas Jefferson's second term. Elections were held for all 142 seats, representing 17 states.

The 1800–01 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between April 29, 1800, and August 1, 1801. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 7th United States Congress convened on December 7, 1801. They were held at the same time as the 1800 presidential election, in which Vice President Thomas Jefferson, a Democratic Republican, defeated incumbent President John Adams, a Federalist. Elections were held for all 106 seats, representing 15 states.

The 1798–99 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between April 24, 1798 in New York and August 1, 1799 in Tennessee. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives, with some after the official start of the 6th United States Congress on March 4, 1799, but before the start of the first session of this Congress in Philadelphia on December 2, 1799. These elections were held during President John Adams term. It was the last congressional session before the move to the new capital at Washington, D.C. Elections were held for all 106 seats, representing 16 states.

The 1792–93 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between August 27, 1792, and September 6, 1793. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 3rd United States Congress convened on December 2, 1793. With the addition of the new state of Kentucky's representatives, and the congressional reapportionment based on the 1790 United States census, the size of the House increased to 105 seats.

The 1788–89 United States House of Representatives elections were the first U.S. House of Representatives elections following the adoption of the Constitution of the United States. Each state set its own date for its congressional elections, ranging from November 24, 1788, to March 5, 1789, before or after the first session of the 1st United States Congress convened on March 4, 1789. They coincided with the election of George Washington as the first president of the United States.

The 2008 congressional elections in Rhode Island were held on November 4, 2008 to determine who will represent Rhode Island in the United States House of Representatives, coinciding with the presidential and senatorial elections. Representatives are elected for two-year terms; those elected will serve in the 111th Congress from January 3, 2009 until January 3, 2011.

The 2010 congressional elections in Rhode Island were held on November 2, 2010, and determined who would represent Rhode Island in the United States House of Representatives. Representatives are elected for two-year terms; the elected served in the 112th Congress from January 3, 2011, until January 3, 2013.
The second 1800 United States Senate special election in New York was held on November 6, 1800, by the New York State Legislature to elect a U.S. Senator to represent the State of New York in the United States Senate.
The 1801 United States Senate election in New York was held on January 27, 1801, by the New York State Legislature to elect a U.S. Senator to represent the State of New York in the United States Senate.

Of the 6 South Carolina incumbents, only 3 were re-elected.

Rhode Island elected its members August 26, 1806. Rhode Island law required a majority of votes to win. In this election, only one candidate won a majority on the first ballot, and so a run-off election was required to choose the second seat.

Only 1 of the 2 Vermont incumbents were re-elected.

The 2016 United States House of Representatives elections in Rhode Island were held on November 8, 2016, to elect the two U.S. representatives from the state of Rhode Island, one from each of the state's 2 congressional districts. The elections coincided with the 2016 U.S. presidential election, as well as other elections to the House of Representatives, elections to the United States Senate and various state and local elections. The primaries took place on September 13.

The 2018 United States House of Representatives elections in Rhode Island were held on November 6, 2018, to elect the two U.S. representatives from the state of Rhode Island, one from each of the state's two congressional districts. The election coincided with the 2018 U.S. mid-term elections, as well as other elections to the House of Representatives, elections to the United States Senate and various state and local elections. The primaries took place on September 12.

Rhode Island elected its members August 30, 1825 after the term began but before the new Congress convened. Rhode Island law required a candidate receive votes from a majority of voters for election, as only one candidate received a majority in this election, a second election was held for the remaining seat.
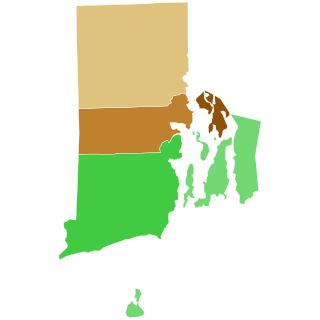
The 1800 United States presidential election in Rhode Island took place as part of the 1800 United States presidential election. Voters chose 4 representatives, or electors to the Electoral College who voted for president and vice president.
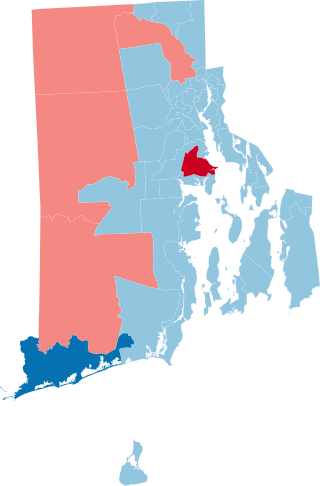
The 2022 Rhode Island State Senate elections took place on November 8, 2022. Primary elections were held on September 13, 2022. Rhode Island voters elected state senators in all 38 seats of the Senate. State senators serve two-year terms in the Rhode Island Senate.














