
The National Security Act of 1947 was a law enacting major restructuring of the United States government's military and intelligence agencies following World War II. The majority of the provisions of the act took effect on September 18, 1947, the day after the Senate confirmed James Forrestal as the first secretary of defense.

Manuel Luis Quezon y Molina, also known by his initials MLQ, was a Filipino lawyer, statesman, soldier, and politician who was president of the Commonwealth of the Philippines from 1935 until his death in 1944. He was the first Filipino to head a government of the entire Philippines and is considered the second president of the Philippines after Emilio Aguinaldo (1899–1901), whom Quezon defeated in the 1935 presidential election.

The Lok Sabha, constitutionally the House of the People, is the lower house of India's bicameral Parliament, with the upper house being the Rajya Sabha. Members of the Lok Sabha are elected by an adult universal suffrage and a first-past-the-post system to represent their respective constituencies, and they hold their seats for five years or until the body is dissolved by the President on the advice of the council of ministers. The house meets in the Lok Sabha Chambers of the Parliament House, New Delhi.
The Congress of the Philippines is the legislature of the national government of the Philippines. It is bicameral, composed of a lower body, the House of Representatives, although colloquially the term "Congress" commonly refers to just the latter, and an upper body, the Senate. The House of Representatives meets in the Batasang Pambansa in Quezon City while the Senate meets in the GSIS Building in Pasay.

The Senate of the Philippines is the upper house of Congress of the bicameral legislature of the Philippines with the House of Representatives as the lower house. The Senate is composed of 24 senators who are elected at-large under plurality-at-large voting.
Commonwealth is a term used by two unincorporated territories of the United States in their full official names, which are the Northern Mariana Islands, whose full name is Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands, and Puerto Rico, which is named Commonwealth of Puerto Rico in English and Estado Libre Asociado de Puerto Rico in Spanish, translating to "Free Associated State of Puerto Rico." The term was also used by the Philippines during most of its period under U.S. sovereignty, when it was officially called the Commonwealth of the Philippines.
A supermajority is a requirement for a proposal to gain a specified level of support which is greater than the threshold of more than one-half used for a simple majority. Supermajority rules in a democracy can help to prevent a majority from eroding fundamental rights of a minority, but they can also hamper efforts to respond to problems and encourage corrupt compromises at times when action is taken. Changes to constitutions, especially those with entrenched clauses, commonly require supermajority support in a legislature. Parliamentary procedure requires that any action of a deliberative assembly that may alter the rights of a minority have a supermajority requirement, such as a two-thirds vote. In consensus democracy the supermajority rule is applied in most cases.

Jennings Randolph was an American politician from West Virginia. A Democrat, he was most notable for his service in the United States House of Representatives from 1933 to 1947 and the United States Senate from 1958 to 1985. He was the last living member of the United States Congress to have served during the first 100 days of Franklin D. Roosevelt's administration. Randolph retired in 1985, and was succeeded by Jay Rockefeller.
Elections in the Philippines are of several types. The president, vice-president, and the senators are elected for a six-year term, while the members of the House of Representatives, governors, vice-governors, members of the Sangguniang Panlalawigan, mayors, vice-mayors, members of the Sangguniang Panlungsod/members of the Sangguniang Bayan, barangay officials, and the members of the Sangguniang Kabataan are elected to serve for a three-year term.
The Bell Trade Act of 1946, also known as the Philippine Trade Act, was an act passed by the United States Congress specifying policy governing trade between the Philippines and the United States following independence of the Philippines from the United States. The United States Congress offered $800 million for post World War II rebuilding funds if the Bell Trade Act was ratified by the Philippine Congress. The specifics of the act required the 1935 Constitution of the Philippines be amended. The Philippine Congress approved the measure on July 2, two days before independence from the United States of America, and on September 18, 1946 approved a plebiscite to amend the Constitution of the Philippines.
Charles Ernest Chamberlain was a politician from the U.S. state of Michigan.

Richard Walker Bolling was a prominent American Democratic Congressman from Kansas City, Missouri, and Missouri's 5th congressional district from 1949 to 1983. He retired after serving for four years as the chairman of the powerful United States House Committee on Rules.
Constitutional reform in the Philippines, also known as charter change, refers to the political and legal processes needed to amend the current 1987 Constitution of the Philippines. Under the common interpretation of the Constitution, amendments can be proposed by one of three methods: a People's Initiative, a Constituent Assembly or a Constitutional Convention.
The Constitution of the Philippines is the constitution or the supreme law of the Republic of the Philippines. Its final draft was completed by the Constitutional Commission on October 12, 1986, and ratified by a nationwide plebiscite on February 2, 1987.

Election to the Senate were held on November 11, 1941 in the Philippines. The Senate was re-instituted after amendments to the constitution restored the bicameral legislature last used in 1935.

The Office for Transportation Security (OTS) is the single authority responsible for the security of the transportation systems of the Philippines, including Civil Aviation, Sea Transport and Maritime Infrastructure, Land Transportation, Rail System and Infrastructure.

Tomás Valenzuela Confesor was a Filipino politician and former Senator of the Philippines from 1946 to 1951. He was served as a governor of Iloilo and later, all of Panay Island during the Japanese occupation of the Philippines during World War II. Right after the war, he served as Mayor of Manila and secretary of the Philippine Department of the Interior under President Sergio Osmeña.

George Reginald de Silva was a Ceylonese politician.

Florida state elections in 2020 were held on Tuesday, November 3, 2020. Aside from its presidential primaries held on March 17, its primary elections were held on August 18, 2020.
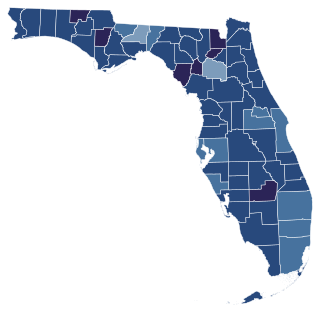
2020 Florida Amendment 1 is an amendment to the Constitution of Florida that passed on November 3, 2020 via a statewide referendum. The amendment changes the state constitution to make citizenship a requirement to vote in the state of Florida. Every county in the state voted in favor of the amendment.












