In enzymology, a 3-deoxyoctulosonase (EC 3.2.1.144) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
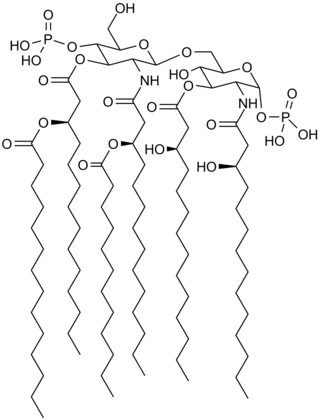
Saccharolipids are chemical compounds containing fatty acids linked directly to a sugar backbone, forming structures that are compatible with membrane bilayers. In the saccharolipids, a monosaccharide substitutes for the glycerol backbone present in glycerolipids and glycerophospholipids. The most familiar saccharolipids are the acylated glucosamine precursors of the lipid A component of the lipopolysaccharides in Gram-negative bacteria. Typical lipid A molecules are disaccharides of glucosamine, which are derivatized with as many as seven fatty-acyl chains. The minimal lipopolysaccharide required for growth in Escherichia coli is Kdo2-Lipid A, a hexa-acylated disaccharide of glucosamine (LipidA) that is glycosylated with two 3-deoxy-D-manno-octulosonic acid (Kdo) residues.

The haloacid dehydrogenase superfamily is a superfamily of enzymes that include phosphatases, phosphonatases, P-type ATPases, beta-phosphoglucomutases, phosphomannomutases, and dehalogenases, and are involved in a variety of cellular processes ranging from amino acid biosynthesis to detoxification.
In molecular biology, the lipopolysaccharide kinase (Kdo/WaaP) family is a family of lipopolysaccharide kinases that includes lipopolysaccharide core heptose(I) kinase rfaP. Lipopolysaccharide core heptose(I) kinase rfaP is required for the addition of phosphate to O-4 of the first heptose residue of the lipopolysaccharide (LPS) inner core region. It has previously been shown that it is necessary for resistance to hydrophobic and polycationic antimicrobials in E. coli and that it is required for virulence in invasive strains of Salmonella enterica. The family also includes 3-deoxy-D-manno-octulosonic acid kinase from Haemophilus influenzae, which phosphorylates Kdo-lipid IV(A), a lipopolysaccharide precursor, and is involved in virulence.
UDP-glucuronic acid dehydrogenase (UDP-4-keto-hexauronic acid decarboxylating) (EC 1.1.1.305, UDP-GlcUA decarboxylase, ArnADH) is an enzyme with systematic name UDP-glucuronate:NAD+ oxidoreductase (decarboxylating). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
UDP-4-amino-4-deoxy-L-arabinose formyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name 10-formyltetrahydrofolate:UDP-4-amino-4-deoxy-beta-L-arabinose N-formyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Lipid IVA 4-amino-4-deoxy-L-arabinosyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name 4-amino-4-deoxy-alpha-L-arabinopyranosyl ditrans, octacis-undecaprenyl phosphate:lipid IVA 4-amino-4-deoxy-L-arabinopyranosyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Lipid IVA 3-deoxy-D-manno-octulosonic acid transferase is an enzyme with systematic name CMP-3-deoxy-D-manno-oct-2-ulosonate:lipid IVA 3-deoxy-D-manno-oct-2-ulosonate transferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
KDO transferase may refer to:
WaaA (gene) may refer to:
3-deoxy-D-manno-oct-2-ulosonic acid transferase may refer to:
3-deoxy-manno-octulosonic acid transferase may refer to:
(KDO)-lipid IVA 3-deoxy-D-manno-octulosonic acid transferase is an enzyme with systematic name CMP-3-deoxy-D-manno-oct-2-ulosonate:(KDO)-lipid IVA 3-deoxy-D-manno-oct-2-ulosonate transferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
(KDO)2-lipid IVA (2-8) 3-deoxy-D-manno-octulosonic acid transferase is an enzyme with systematic name CMP-3-deoxy-D-manno-oct-2-ulosonate:(KDO)2-lipid IVA 3-deoxy-D-manno-oct-2-ulosonate transferase . This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
(KDO)3-lipid IVA (2-4) 3-deoxy-D-manno-octulosonic acid transferase is an enzyme with systematic name CMP-3-deoxy-D-manno-oct-2-ulosonate:(KDO)3-lipid IVA 3-deoxy-D-manno-oct-2-ulosonate transferase . This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Undecaprenyl-phosphate 4-deoxy-4-formamido-L-arabinose transferase is an enzyme with systematic name UDP-4-amino-4-deoxy-alpha-L-arabinose:ditrans,octacis-undecaprenyl phosphate 4-amino-4-deoxy-alpha-L-arabinosyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
UDP-2,3-diacylglucosamine diphosphatase (EC 3.6.1.54, UDP-2,3-diacylglucosamine hydrolase, UDP-2,3-diacylglucosamine pyrophosphatase, ybbF (gene), lpxH (gene)) is an enzyme with systematic name UDP-2,3-bis((3R)-3-hydroxymyristoyl)-alpha-D-glucosamine 2,3-bis((3R)-3-hydroxymyristoyl)-beta-D-glucosaminyl 1-phosphate phosphohydrolase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
N-glycosyltransferase is an enzyme in prokaryotes which transfers individual hexoses onto asparagine sidechains in substrate proteins, using a nucleotide-bound intermediary, within the cytoplasm. They are distinct from regular N-glycosylating enzymes, which are oligosaccharyltransferases that transfer pre-assembled oligosaccharides. Both enzyme families however target a shared amino acid sequence asparagine—-any amino acid except proline—serine or threonine (N–x–S/T), with some variations.


