
Tortoises are reptiles of the family Testudinidae of the order Testudines. Like other turtles, tortoises have a shell to protect from predation and other threats. The shell in tortoises is generally hard, and like other members of the suborder Cryptodira, they retract their necks and heads directly backward into the shell to protect them.

Aldabra is the world's second-largest coral atoll, lying southeast of the continent of Africa. It is part of the Aldabra Group of islands in the Indian Ocean that are part of the Outer Islands of the Seychelles, with a distance of 1,120 km (700 mi) southwest of the capital, Victoria on Mahé Island. Initially named by Arab seafarers for its harsh environment, Aldabra became a French colony dependency in the 18th century, leading to the exploitation of its natural resources, particularly giant tortoises. After passing through British hands, Aldabra faced potential military use in the 1960s, but international protests resulted in its protection. The atoll boasts unique geography, featuring the world's largest raised coral reef and a large shallow lagoon. Aldabra's history involves human impact, including failed agricultural ventures. Post-World War II, conservation efforts increased, leading to its inclusion in the British Indian Ocean Territory and eventual independence for Seychelles. Following an international protest by scientists known as the 'Aldabra Affair,' the Royal Society of London and later the Seychelles Islands Foundation conducted research, leading to Aldabra's declaration as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1982. The atoll's flora and fauna, notably the giant tortoises, comprise an 'ecological wonder', with Aldabra serving as a critical breeding ground for various species. Conservation challenges, such as invasive species and plastic pollution, persist, but protective measures, including UNESCO designation, underscore Aldabra's significance as a natural vital scientific research site. Aldabra receives limited tourism to safeguard its delicate ecosystem and is accessible primarily through guided tours.

Giant tortoises are any of several species of various large land tortoises, which include a number of extinct species, as well as two extant species with multiple subspecies formerly common on the islands of the western Indian Ocean and on the Galápagos Islands.

Adansonia is a genus made up of eight species of medium-to-large deciduous trees known as baobabs. They are placed in the Malvaceae family, subfamily Bombacoideae. They are native to Madagascar, mainland Africa, and Australia. The trees have also been introduced to other regions such as Asia. The generic name honours Michel Adanson, the French naturalist and explorer who described Adansonia digitata. The baobab is also known as the "upside down tree", a name that originates from several myths. They are among the most long-lived of vascular plants and have large flowers that are reproductive for a maximum of 15 hours. The flowers open around dusk, opening so quickly that movement can be detected by the naked eye, and are faded by the next morning. The fruits are large, oval to round and berry-like and hold kidney-shaped seeds in a dry, pulpy matrix.

The Aldabra giant tortoise is a species of tortoise in the family Testudinidae. The species is endemic to the Seychelles, with the nominate subspecies, A. g. gigantea native to Aldabra atoll. It is one of the largest tortoises in the world. Historically, giant tortoises were found on many of the western Indian Ocean islands, as well as Madagascar, and the fossil record indicates giant tortoises once occurred on every continent and many islands with the exception of Australia and Antarctica.

Island gigantism, or insular gigantism, is a biological phenomenon in which the size of an animal species isolated on an island increases dramatically in comparison to its mainland relatives. Island gigantism is one aspect of the more general "island effect" or "Foster's rule", which posits that when mainland animals colonize islands, small species tend to evolve larger bodies, and large species tend to evolve smaller bodies. This is itself one aspect of the more general phenomenon of island syndrome which describes the differences in morphology, ecology, physiology and behaviour of insular species compared to their continental counterparts. Following the arrival of humans and associated introduced predators, many giant as well as other island endemics have become extinct. A similar size increase, as well as increased woodiness, has been observed in some insular plants such as the Mapou tree in Mauritius which is also known as the "Mauritian baobab" although it is member of the grape family (Vitaceae).

Aldabrachelys is genus of giant tortoises, including the Aldabra giant tortoise native to the Seychelles, as well as two extinct species, Aldabrachelys abrupta and Aldabrachelys grandidieri known from Madagascar.

Adansonia rubrostipa, commonly known as fony baobab, is a deciduous tree in the Malvaceae family. Of eight species of baobab currently recognized, six are indigenous to Madagascar, including fony baobab. It is endemic to western Madagascar, found in Baie de Baly National Park, south. It is associated with well-drained soils and is found in dry and spiny forests. It occurs in the following protected areas: Amoron'i Onilahy, Baie de Baly, Menabe Antimena, Mikea, Namoroka, Ranobe PK 32, Tsimanampesotse, Tsimembo Manambolomaty, Tsinjoriake.

Adansonia grandidieri is the biggest and most famous of Madagascar's six species of baobabs. It is sometimes known as Grandidier's baobab or the giant baobab. In French it is called Baobab malgache. The local name is renala or reniala. This tree is endemic to the island of Madagascar, where it is an endangered species threatened by the encroachment of agricultural land. This is the tree found at the Avenue of the Baobabs.

Cylindraspis is a genus of recently extinct giant tortoises. All of its species lived in the Mascarene Islands in the Indian Ocean and all are now extinct due to hunting and introduction of non-native predators.

The domed Rodrigues giant tortoise is an extinct species of giant tortoise in the family Testudinidae. It was endemic to Rodrigues. It appears to have become extinct around 1800, as a result of human exploitation.

The saddle-backed Rodrigues giant tortoise is an extinct species of giant tortoise in the family Testudinidae. The species was endemic to Rodrigues. Human exploitation caused the extinction of this species around 1800.

Tsimanampetsotsa National Park also spelt Tsimanampetsotse, and known as Tsimanampetsotsa Nature Reserve is a 432 km2 national park on the south-west coast of Madagascar in the region Atsimo-Andrefana. The park is 90 kilometres (56 mi) south of Toliara and 950 kilometres (590 mi) south of the capital, Antananarivo. Route Nationales (RN) 10 to Faux Cap passes the park and the nearest airport is at Toliara. The national park contains and is named after Lake Tsimanampetsotsa.

Aldabrachelys abrupta, the abrupt giant tortoise, is an extinct species of giant tortoise that was endemic to Madagascar.

The Kirindy Forest is a private nature reserve situated in western Madagascar, about 50 km northeast of the town of Morondava, near Ambivy. The forest reserve falls within the boundaries of the Kirindy Mitea National Park, which spreads further to the south.

Arnold's giant tortoise, also known as the Seychelles saddle-backed giant tortoise, is a tortoise subspecies in the genus Aldabrachelys.
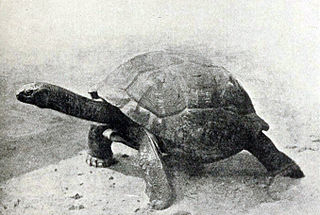
The Seychelles giant tortoise, also known as the Seychelles domed giant tortoise, is a tortoise subspecies in the genus Aldabrachelys.

François Leguat Giant Tortoise and Cave Reserve is a park and nature reserve on the island of Rodrigues, dedicated to protecting the fauna and flora of the island. The reserve first opened in August 2007, part of the same project as La Vanille Reserve in Mauritius. It is named after the 18th century Huguenot settler François Leguat, who recorded much of the island's natural flora and fauna before it went extinct. The reserve includes a museum, several education centres and information areas, and a restaurant.
Giant tortoises are any of various large land tortoises
Astrochelys rogerbouri is an extinct tortoise species in the family Testudinidae which formerly lived in Madagascar.



















