Related Research Articles

Ammonium hydrosulfide is the chemical compound with the formula [NH4]SH.

Erbium(III) chloride is a violet solid with the formula ErCl3. It is used in the preparation of erbium metal.
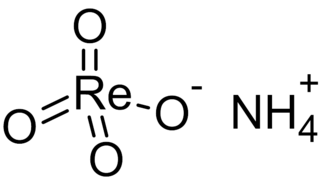
Ammonium perrhenate (APR) is the ammonium salt of perrhenic acid, NH4ReO4. It is the most common form in which rhenium is traded. It is a white salt; soluble in ethanol and water, and mildly soluble in NH4Cl. It was first described soon after the discovery of rhenium.

Ytterbium(III) chloride (YbCl3) is an inorganic chemical compound. It reacts with NiCl2 to form a very effective catalyst for the reductive dehalogenation of aryl halides. It is poisonous if injected, and mildly toxic by ingestion. It is an experimental teratogen, known to irritate the skin and eyes.
Indium(III) sulfate (In2(SO4)3) is a sulfate salt of the metal indium. It is a sesquisulfate, meaning that the sulfate group occurs 11/2 times as much as the metal. It may be formed by the reaction of indium, its oxide, or its carbonate with sulfuric acid. An excess of strong acid is required, otherwise insoluble basic salts are formed. As a solid indium sulfate can be anhydrous, or take the form of a pentahydrate with five water molecules or a nonahydrate with nine molecules of water. Indium sulfate is used in the production of indium or indium containing substances. Indium sulfate also can be found in basic salts, acidic salts or double salts including indium alum.

Lanthanum chloride is the inorganic compound with the formula LaCl3. It is a common salt of lanthanum which is mainly used in research. It is a white solid that is highly soluble in water and alcohols.
Selenium trioxide is the inorganic compound with the formula SeO3. It is white, hygroscopic solid. It is also an oxidizing agent and a Lewis acid. It is of academic interest as a precursor to Se(VI) compounds.

Ammonium dichromate is an inorganic compound with the formula (NH4)2Cr2O7. In this compound, as in all chromates and dichromates, chromium is in a +6 oxidation state, commonly known as hexavalent chromium. It is a salt consisting of ammonium ions and dichromate ions.
Ammonium fluorosilicate (also known as ammonium hexafluorosilicate, ammonium fluosilicate or ammonium silicofluoride) has the formula (NH4)2SiF6. It is a toxic chemical, like all salts of fluorosilicic acid. It is made of white crystals, which have at least three polymorphs and appears in nature as rare minerals cryptohalite or bararite.

Sodium hexachloroplatinate(IV), the sodium salt of chloroplatinic acid, is an inorganic compound with the formula Na2[PtCl6], consisting of the sodium cation and the hexachloroplatinate anion. As explained by Cox and Peters, anhydrous sodium hexachloroplatinate, which is yellow, tends to form the orange hexahydrate upon storage in humid air. The latter can be dehydrated upon heating at 110 °C.
Langbeinites are a family of crystalline substances based on the structure of langbeinite with general formula M2M'2(SO4)3, where M is a large univalent cation, and M' is a small divalent cation. The sulfate group, SO2−4, can be substituted by other tetrahedral anions with a double negative charge such as tetrafluoroberyllate, selenate, chromate, molybdate, or tungstates. Although monofluorophosphates are predicted, they have not been described. By redistributing charges other anions with the same shape such as phosphate also form langbeinite structures. In these the M' atom must have a greater charge to balance the extra three negative charges.

Monofluorophosphate is an anion with the formula PO3F2−, which is a phosphate group with one oxygen atom substituted with a fluoride atom. The charge of the ion is −2. The ion resembles sulfate in size, shape and charge, and can thus form compounds with the same structure as sulfates. These include Tutton's salts and langbeinites. The most well-known compound of monofluorophosphate is sodium monofluorophosphate, commonly used in toothpaste.

Ammonium hexachlorotellurate is an inorganic chemical compound with the chemical formula [NH4]2[TeCl6].
Ammonium hexafluoroindate is an inorganic chemical compound with the chemical formula (NH4)3InF6.
Ammonium hexachlororhenate is an inorganic chemical compound with the chemical formula (NH4)2ReCl6.
Ammonium hexachloroplumbate is an inorganic chemical compound with the chemical formula (NH4)2PbCl6.
Ammonium hexachloropalladate is an inorganic chemical compound with the chemical formula (NH4)2PdCl6.
Ammonium hexachlororhodate(III) is an inorganic chemical compound with the chemical formula (NH4)3RhCl6.
Ammonium hexachloroosmate(IV) is an inorganic chemical compound with the chemical formula (NH4)2OsCl6.
Ammonium hexabromostannate(IV) is an inorganic chemical compound with the chemical formula (NH4)2SnBr6.
References
- ↑ Macintyre, Jane E. (23 July 1992). Dictionary of Inorganic Compounds. CRC Press. p. 2993. ISBN 978-0-412-30120-9 . Retrieved 7 October 2024.
- ↑ Kume, Yoshio; Muraoka, Hiroki; Matsuo, Takasuke; Suga, Hiroshi (1 February 1994). "Low-temperature heat capacities of ammonium hexachloroselenate and of its deuterated analogue". The Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics . 26 (2): 211–222. Bibcode:1994JChTh..26..211K. doi:10.1006/jcht.1994.1041. ISSN 0021-9614 . Retrieved 7 October 2024.
- ↑ Kudri︠a︡vt︠s︡ev, Aleksandr Andreevich (1974). The Chemistry & Technology of Selenium and Tellurium. Collet's. p. 105. ISBN 978-0-569-08009-5 . Retrieved 7 October 2024.
- ↑ Donnay, Joseph Désiré Hubert (1973). Crystal Data: Inorganic compounds. National Bureau of Standards . Retrieved 7 October 2024.
- ↑ Prager, M; Raaen, A M; Svare, I (28 February 1983). "Tunnel splittings in ammonium hexachlorides". Journal of Physics C: Solid State Physics . 16 (6): L181–L186. Bibcode:1983JPhC...16L.181P. doi:10.1088/0022-3719/16/6/002 . Retrieved 7 October 2024.
- ↑ Pelzl, J.; Dimitropoulos, C. (1 February 1994). "Effect of Deuteration on the Phase Transitions and on the Critical Dynamics in Ammonium Hexachlorometallates". Zeitschrift für Naturforschung A . 49 (1–2): 232–246. Bibcode:1994ZNatA..49..232P. doi:10.1515/zna-1994-1-235.