
Legionella pneumophila is an aerobic, pleomorphic, flagellated, non-spore-forming, Gram-negative bacterium of the genus Legionella. L. pneumophila is the primary human pathogenic bacterium in this group. In nature, L. pneumophila infects freshwater and soil amoebae of the genera Acanthamoeba and Naegleria. This pathogen is found commonly near freshwater environments and will then invade the amoebae found in these environments, using them to carry out metabolic functions.
In organic chemistry, polyketides are a class of natural products derived from a precursor molecule consisting of a chain of alternating ketone and methylene groups: [−C(=O)−CH2−]n. First studied in the early 20th century, discovery, biosynthesis, and application of polyketides has evolved. It is a large and diverse group of secondary metabolites caused by its complex biosynthesis which resembles that of fatty acid synthesis. Because of this diversity, polyketides can have various medicinal, agricultural, and industrial applications. Many polyketides are medicinal or exhibit acute toxicity. Biotechnology has enabled discovery of more naturally-occurring polyketides and evolution of new polyketides with novel or improved bioactivity.
In molecular biology, biosynthesis is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides. Biosynthesis is usually synonymous with anabolism.

Clavulanic acid is a β-lactam drug that functions as a mechanism-based β-lactamase inhibitor. While not effective by itself as an antibiotic, when combined with penicillin-group antibiotics, it can overcome antibiotic resistance in bacteria that secrete β-lactamase, which otherwise inactivates most penicillins.

The mitomycins are a family of aziridine-containing natural products isolated from Streptomyces caespitosus or Streptomyces lavendulae. They include mitomycin A, mitomycin B, and mitomycin C. When the name mitomycin occurs alone, it usually refers to mitomycin C, its international nonproprietary name. Mitomycin C is used as a medicine for treating various disorders associated with the growth and spread of cells.

Amino acid synthesis is the set of biochemical processes by which the amino acids are produced. The substrates for these processes are various compounds in the organism's diet or growth media. Not all organisms are able to synthesize all amino acids. For example, humans can synthesize 11 of the 20 standard amino acids. These 11 are called the non-essential amino acids).
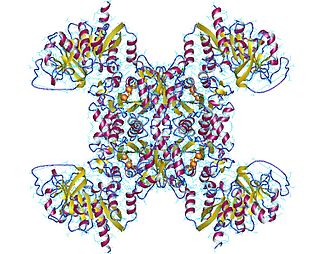
CTP synthase is an enzyme involved in pyrimidine biosynthesis that interconverts UTP and CTP.

The acetolactate synthase (ALS) enzyme is a protein found in plants and micro-organisms. ALS catalyzes the first step in the synthesis of the branched-chain amino acids.

Orotate phosphoribosyltransferase (OPRTase) or orotic acid phosphoribosyltransferase is an enzyme involved in pyrimidine biosynthesis. It catalyzes the formation of orotidine 5'-monophosphate (OMP) from orotate and phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate. In yeast and bacteria, orotate phosphoribosyltransferase is an independent enzyme with a unique gene coding for the protein, whereas in mammals and other multicellular organisms, the catalytic function is carried out by a domain of the bifunctional enzyme UMP synthase (UMPS).

Phosphatidylglycerol is a glycerophospholipid found in pulmonary surfactant and in the plasma membrane where it directly activates lipid-gated ion channels.
In enzymology, a lactosylceramide alpha-2,3-sialyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a N-acylneuraminate cytidylyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Phosphatidate cytidylyltransferase (CDS) is the enzyme that catalyzes the synthesis of CDP-diacylglycerol from cytidine triphosphate and phosphatidate.
In enzymology, a phosphatidylcholine synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Aerobactin is a bacterial iron chelating agent (siderophore) found in E. coli. It is a virulence factor enabling E. coli to sequester iron in iron-poor environments such as the urinary tract.
N,N'-diacetyllegionaminate synthase (EC 2.5.1.101, neuB (gene), legI (gene)) is an enzyme with systematic name phosphoenolpyruvate:2,4-diacetamido-2,4,6-trideoxy-alpha-D-mannopyranose 1-(2-carboxy-2-oxoethyl)transferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
UDP-4-amino-4,6-dideoxy-N-acetyl-alpha-D-glucosamine transaminase is an enzyme with systematic name UDP-4-amino-4,6-dideoxy-N-acetyl-alpha-D-glucosamine:2-oxoglutarate aminotransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
UDP-N,N'-diacetylbacillosamine 2-epimerase (hydrolysing) (EC 3.2.1.184, UDP-Bac2Ac4Ac 2-epimerase, NeuC) is an enzyme with systematic name UDP-N,N'-diacetylbacillosamine hydrolase (2-epimerising). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
2-deoxy-scyllo-Inosose synthase is an enzyme with systematic name D-glucose-6-phosphate phosphate-lyase (2-deoxy-scyllo-inosose-forming). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Legionella jordanis is a Gram-negative bacterium from the genus Legionella which was isolated from the Jordan River in Bloomington, Indiana and from the sewage in DeKalb County, Georgia. L. jordanis is a rare human pathogen and can cause respiratory tract infections.










