
Pyruvate carboxylase (PC) encoded by the gene PC is an enzyme of the ligase class that catalyzes the physiologically irreversible carboxylation of pyruvate to form oxaloacetate (OAA).
Pyruvate dehydrogenase (NADP+) EC 1.2.1.51 is an enzyme that should not be confused with Pyruvate dehydrogenase (acetyltransferase) EC 1.2.4.1.
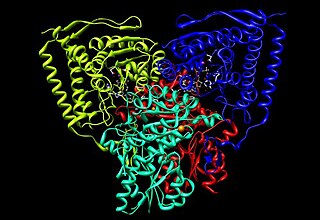
Pyruvate dehydrogenase is an enzyme that catalyzes the reaction of pyruvate and a lipoamide to give the acetylated dihydrolipoamide and carbon dioxide. The conversion requires the coenzyme thiamine pyrophosphate.
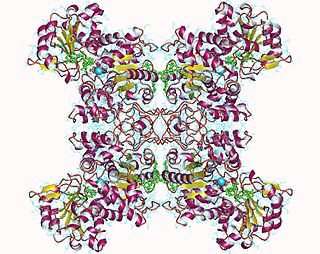
Malate dehydrogenase (decarboxylating) (EC 1.1.1.39) or NAD-malic enzyme (NAD-ME) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Malate dehydrogenase (oxaloacetate-decarboxylating) (NADP+) (EC 1.1.1.40) or NADP-malic enzyme (NADP-ME) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction in the presence of a bivalent metal ion:
In enzymology, a deacetoxycephalosporin-C hydroxylase (EC 1.14.11.26) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a deacetoxycephalosporin-C synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an indolepyruvate ferredoxin oxidoreductase (EC 1.2.7.8) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a pyruvate synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the interconversion of pyruvate and acetyl-CoA. It is also called pyruvate:ferredoxin oxidoreductase (PFOR).

Isocitrate lyase, or ICL, is an enzyme in the glyoxylate cycle that catalyzes the cleavage of isocitrate to succinate and glyoxylate. Together with malate synthase, it bypasses the two decarboxylation steps of the tricarboxylic acid cycle and is used by bacteria, fungi, and plants.
In enzymology, a 1-deoxy-d-xylulose-5-phosphate synthase (EC 2.2.1.7) is an enzyme in the non-mevalonate pathway that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 3-deoxy-8-phosphooctulonate synthase (EC 2.5.1.55) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
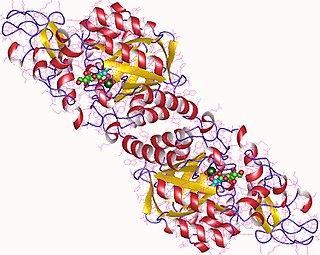
In enzymology, a N-acetylneuraminate synthase (EC 2.5.1.56) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, an UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 1-carboxyvinyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the first committed step in peptidoglycan biosynthesis of bacteria:
In enzymology, a hygromycin-B kinase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Pyruvate, phosphate dikinase, or PPDK is an enzyme in the family of transferases that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Pyruvate dehydrogenase (lipoamide) alpha 2, also known as pyruvate dehydrogenase E1 component subunit alpha, testis-specific form, mitochondrial or PDHE1-A type II, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PDHA2 gene.
Isocitrate lyase family is a family of evolutionarily related proteins.

Streptomyces hygroscopicus is a bacterial species in the genus Streptomyces. It was first described by Hans Laurits Jensen in 1931.
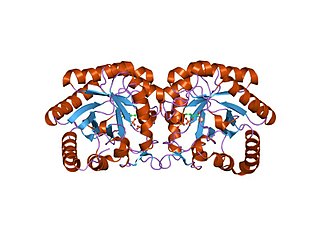
3-Deoxy-D-arabinoheptulosonate 7-phosphate (DAHP) synthase is the first enzyme in a series of metabolic reactions known as the shikimate pathway, which is responsible for the biosynthesis of the amino acids phenylalanine, tyrosine, and tryptophan. Since it is the first enzyme in the shikimate pathway, it controls the amount of carbon entering the pathway. Enzyme inhibition is the primary method of regulating the amount of carbon entering the pathway. Forms of this enzyme differ between organisms, but can be considered DAHP synthase based upon the reaction that is catalyzed by this enzyme.












