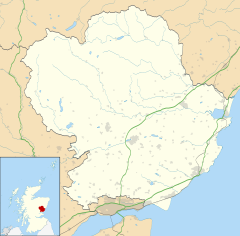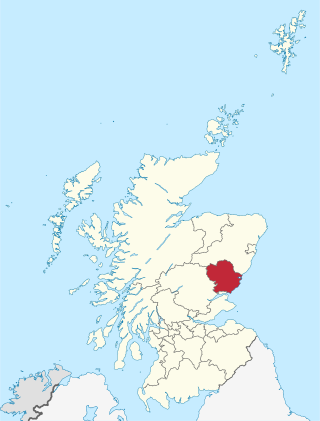
Angus is one of the 32 local government council areas of Scotland, a registration county and a lieutenancy area. The council area borders Aberdeenshire, Dundee City and Perth and Kinross. Main industries include agriculture and fishing. Global pharmaceuticals company GSK has a significant presence in Montrose in the north of the county.

Glamis Castle is situated beside the village of Glamis in Angus, Scotland. It is the home of the Earl of Strathmore and Kinghorne, and is open to the public.
Glamis is a small village in Angus, Scotland, located 4 miles (6.4 km) south of Kirriemuir and 5 miles (8.0 km) southwest of Forfar. It is the location of Glamis Castle, the childhood home of Queen Elizabeth the Queen Mother.

Strathmore is a strath in east central Scotland running from northeast to southwest between the Grampian mountains and the Sidlaws. It is approximately 50 miles (80 km) long and 10 miles (16 km) wide. Strathmore is underlain by Old Red Sandstone but this is largely obscured by glacial till, sands and gravels deposited during the ice age. Its northeast to southwest alignment is influenced by the underlying geological structure of the area which reflects the dominant Caledonian trend of both the central lowlands and the Highlands of Scotland; its northern margin reflects the presence of the Highland Boundary Fault. Strathmore is fertile and has some of Scotland's best arable farmland, producing soft fruits and cereals.
Saint Fergus was a bishop who worked in Scotland as a missionary.

Meigle is a village in Strathmore, Scotland. It lies in the council area of Perth and Kinross in the Coupar Angus and Meigle ward. It lies on the A94 road between Perth and Forfar. Other smaller settlements nearby are Balkeerie, Kirkinch and Kinloch. Meigle is accessed from the north and south via the B954 road. In 1971 it had a population of 357.

The A94 is a major road in Scotland, United Kingdom.

The Eassie Stone is a Class II Pictish stone of about the mid 8th century AD in the village of Eassie, Angus, Scotland. The stone was found in Eassie burn in the late 18th century and now resides in a purpose-built perspex building in the ruined Eassie church.

Eassie is a village located along the A94 road in Angus, Scotland. The church in Eassie is dedicated to Saint Fergus, a monk who worked at nearby Glamis. Eassie is noted for the presence of the Eassie Stone, a carved Pictish stone, which resides in the ruins of Eassie Old Church.

Hatton Castle stands on the lower part of Hatton Hill, the most easterly of the Sidlaw Hills, to the south of Newtyle in Angus, Scotland. The castle overlooks the wooded Den of Newtyle, and its views extend across Strathmore and include Ben Lawers and Schiehallion as well as the Angus and Glenshee hills. The 16th-century castle was originally built in a typical Scottish "Z plan" tower house design, as a fortified country house or château. There was an earlier castle called Balcraig Castle which stood less than half a mile from the present building, also on Hatton Hill.

Ark Hill is a mountainous landform within the Sidlaw Hills in Angus, Scotland. This location has been proposed as a windfarm for generating renewable electrical power. Approximately two kilometres to the north is the village of Eassie noted for the presence of the Eassie Stone; this carved Pictish stone is dated prior to the Early Middle Ages.

Wester Denoon is a small settlement in Angus, Scotland. Approximately one mile to the north of Wester Denoon is the village of Eassie, where the Eassie Stone is displayed in a ruined church; this carved Pictish stone is dated prior to the Early Middle Ages. Other nearby settlements are Charleston, Balkeerie and Kirkinch. Two fragments of small Pictish cross-slabs have also been found at Wester Denoon itself. One shows the stylised figure of a woman wearing a long dress or mantle fastened on the breast by a large brooch.

Charleston is a village in Angus, Scotland near Glamis.
Milton is a hamlet in Angus, Scotland situated near Glamis. Considerable early history is in the general area including Glamis Castle and the Eassie Stone, a carved Pictish stone dating prior to the Early Middle Ages.

Hatton Hill is a mountain landform in Angus, Scotland in the Sidlaw Hills. Hatton Castle stands on the flanks of Hatton Hill above the village of Newtyle. The general vicinity has elements of prehistory including presence of the Eassie Stone, a Pictish stone dating back to the Dark Ages.

The Glamis Manse Stone, also known as Glamis 2, is a Class II Pictish stone at the village of Glamis, Angus, Scotland. Dating from the 9th century, it is located outside the Manse, close to the parish church. It is inscribed on one side with a Celtic cross and on the other with a variety of Pictish symbols. It is a scheduled monument.

The Woodwrae Stone is a Class II Pictish Stone that was found in 1819 when the foundations of the old castle at Woodwrae, Angus, Scotland were cleared. It had been reused as a floor slab in the kitchen of the castle. Following its removal from the castle, it was donated to the collection of Sir Walter Scott at Abbotsford House. It is now on display at the Museum of Scotland in Edinburgh.

The Hunter's Hill Stone, otherwise known as the Glamis 1 Stone, is a Class II Pictish standing stone at Hunter's Hill to the south east of Glamis village, Angus, Scotland.

Glamis railway station served the village of Glamis, Angus, Scotland, from 1838 to 1956 on the Newtyle, Eassie and Glamiss Railway.