Related Research Articles
Aspergillopepsin I is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Microbial collagenase is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

Actinidain is a type of cysteine protease enzyme found in fruits including kiwifruit, pineapple, mango, banana, figs, and papaya. This enzyme is part of the peptidase C1 family of papain-like proteases.
Kexin is a prohormone-processing protease, specifically a yeast serine peptidase, found in the budding yeast. It catalyzes the cleavage of -Lys-Arg- and -Arg-Arg- bonds to process yeast alpha-factor pheromone and killer toxin precursors. The human homolog is PCSK4. It is a family of subtilisin-like peptidases. Even though there are a few prokaryote kexin-like peptidases, all kexins are eukaryotes. The enzyme is encoded by the yeast gene KEX2, and usually referred to in the scientific community as Kex2p. It shares structural similarities with the bacterial protease subtilisin. The first mammalian homologue of this protein to be identified was furin. In the mammal, kexin-like peptidases function in creating and regulating many differing proproteins.

Dipeptidyl peptidase I is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Cathepsin X is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

Signal peptidases are enzymes that convert secretory and some membrane proteins to their mature or pro forms by cleaving their signal peptides from their N-termini.
Diacylglycerol diphosphate phosphatase (EC 3.1.3.81, DGPP phosphatase, DGPP phosphohydrolase, DPP1, DPPL1, DPPL2, PAP2, pyrophosphate phosphatase) is an enzyme with systematic name 1,2-diacyl-sn-glycerol 3-phosphate phosphohydrolase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Gly-Xaa carboxypeptidase is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Lysyl endopeptidase is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Oryzin is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Glycyl endopeptidase is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Ulp1 peptidase is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Candidapepsin is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Saccharopepsin is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Serralysin is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Low-specificity L-threonine aldolase is an enzyme with systematic name L-threonine/L-allo-threonine acetaldehyde-lyase (glycine-forming). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

The sedolisin family of peptidases are a family of serine proteases structurally related to the subtilisin (S8) family. Well-known members of this family include sedolisin ("pseudomonalisin") found in Pseudomonas bacteria, xanthomonalisin ("sedolisin-B"), physarolisin as well as animal tripeptidyl peptidase I. It is also known as sedolysin or serine-carboxyl peptidase. This group of enzymes contains a variation on the catalytic triad: unlike S8 which uses Ser-His-Asp, this group runs on Ser-Glu-Asp, with an additional acidic residue Asp in the oxyanion hole.
ERG5 or Sterol 22-desaturase is a cytochrome P450 enzyme in the ergosterol biosynthesis pathway of fungi Saccharomyces cerevisiae, with the CYP Symbol CYP61A1. CYP61A1 is one of only three P450 enzyme found in baker's yeast, the other two are CYP51F1 and CYP56A1. The ortholog in Schizosaccharomyces pombe, was named CYP61A3 for historical reasons, and is only one of two P450 enzyme found with CYP51F1. ERG5 catalyzes the C22-C23 double bond formation on the sterol side chain of ergostatrienol to convert it into ergostatetraenol, then the C24 double bond of ergostatetrenol will be hydrogenation reduced into ergosterol by ERG4.
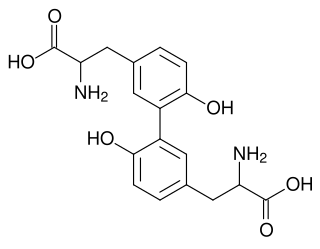
Cytochrome P450-DIT2 or CYP56A1 is one of the only three P450 enzyme found in fungi baker's yeast, the other two are CYP51F1(ERG11) and CYP61A1(ERG5) in the ergosterol biosynthesis pathway. CYP56A1 thought to catalyze the oxidation of tyrosine residues in the formation of L,L-dityrosine, a precursor of the spore wall.
References
- ↑ Félix F, Brouillet N (July 1966). "[Purification and properties of 2 peptidases from baker's yeast]". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta. 122 (1): 127–44. doi:10.1016/0926-6593(66)90096-8. PMID 4961236.
- ↑ Kominami E, Hoffschulte H, Leuschel L, Maier K, Holzer H (September 1981). "The substrate specificity of proteinase B from baker's yeast". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Enzymology. 661 (1): 136–41. doi:10.1016/0005-2744(81)90092-9. PMID 7028121.
- ↑ Farley PC, Shepherd MG, Sullivan PA (May 1986). "The purification and properties of yeast proteinase B from Candida albicans". The Biochemical Journal. 236 (1): 177–84. doi:10.1042/bj2360177. PMC 1146803 . PMID 3539100.
- ↑ Moehle CM, Tizard R, Lemmon SK, Smart J, Jones EW (December 1987). "Protease B of the lysosomelike vacuole of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae is homologous to the subtilisin family of serine proteases". Molecular and Cellular Biology. 7 (12): 4390–9. doi:10.1128/mcb.7.12.4390. PMC 368122 . PMID 3325823.