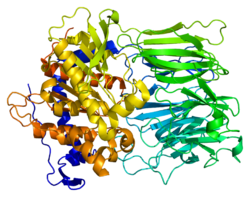
1e5t: PROLYL OLIGOPEPTIDASE FROM PORCINE BRAIN, MUTANT
1e8m: PROLYL OLIGOPEPTIDASE FROM PORCINE BRAIN, MUTANT, COMPLEXED WITH INHIBITOR
1e8n: PROLYL OLIGOPEPTIDASE FROM PORCINE BRAIN, MUTANT, COMPLEXED WITH PEPTIDE
1h2w: PROLYL OLIGOPEPTIDASE FROM PORCINE BRAIN
1h2x: PROLYL OLIGOPEPTIDASE FROM PORCINE BRAIN, Y473F MUTANT
1h2y: PROLYL OLIGOPEPTIDASE FROM PORCINE BRAIN, Y473F MUTANT WITH COVALENTLY BOUND INHIBITOR Z-PRO-PROLINAL
1h2z: PROLYL OLIGOPEPTIDASE FROM PORCINE BRAIN, S554A MUTANT WITH BOUND PEPTIDE LIGAND SUC-GLY-PRO
1o6f: PROLYL OLIGOPEPTIDASE FROM PORCINE BRAIN, D641A MUTANT WITH BOUND PEPTIDE LIGAND SUC-GLY-PRO
1o6g: PROLYL OLIGOPEPTIDASE FROM PORCINE BRAIN, D641N MUTANT WITH BOUND PEPTIDE LIGAND SUC-GLY-PRO
1qfm: PROLYL OLIGOPEPTIDASE FROM PORCINE MUSCLE
1qfs: PROLYL OLIGOPEPTIDASE FROM PORCINE MUSCLE WITH COVALENTLY BOUND INHIBITOR Z-PRO-PROLINAL
1uoo: PROLYL OLIGOPEPTIDASE FROM PORCINE BRAIN, S554A MUTANT WITH BOUND PEPTIDE LIGAND GLY-PHE-ARG-PRO
1uop: PROLYL OLIGOPEPTIDASE FROM PORCINE BRAIN, S554A MUTANT WITH BOUND PEPTIDE LIGAND GLY-PHE-GLU-PRO
1uoq: PROLYL OLIGOPEPTIDASE FROM PORCINE BRAIN, S554A MUTANT WITH BOUND PEPTIDE LIGAND GLU-PHE-SER-PRO
1vz2: PROLYL OLIGOPEPTIDASE FROM PORCINE BRAIN, Y73C/V427C/C255T MUTANT
1vz3: PROLYL OLIGOPEPTIDASE FROM PORCINE BRAIN, T597C MUTANT