This article needs additional citations for verification .(October 2011) |

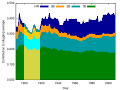
A chart (sometimes known as a graph) is a graphical representation for data visualization, in which "the data is represented by symbols, such as bars in a bar chart, lines in a line chart, or slices in a pie chart". [1] A chart can represent tabular numeric data, functions or some kinds of quality structure and provides different info.
Contents
- Features
- Types
- Common charts
- Less-common charts
- Field-specific charts
- Well-known named charts
- Other charts
- Common plots
- Chart software
- See also
- References
- Further reading
The term "chart" as a graphical representation of data has multiple meanings:
- A data chart is a type of diagram or graph, that organizes and represents a set of numerical or qualitative data.
- Maps that are adorned with extra information (map surround) for a specific purpose are often known as charts, such as a nautical chart or aeronautical chart, typically spread over several map sheets.
- Other domain-specific constructs are sometimes called charts, such as the chord chart in music notation or a record chart for album popularity.
Charts are often used to ease understanding of large quantities of data and the relationships between parts of the data. Charts can usually be read more quickly than the raw data. They are used in a wide variety of fields, and can be created by hand (often on graph paper) or by computer using a charting application. Certain types of charts are more useful for presenting a given data set than others. For example, data that presents percentages in different groups (such as "satisfied, not satisfied, unsure") are often displayed in a pie chart, but maybe more easily understood when presented in a horizontal bar chart. [2] On the other hand, data that represents numbers that change over a period of time (such as "annual revenue from 1990 to 2000") might be best shown as a line chart.