Related Research Articles

A protease is an enzyme that catalyzes proteolysis, breaking down proteins into smaller polypeptides or single amino acids, and spurring the formation of new protein products. They do this by cleaving the peptide bonds within proteins by hydrolysis, a reaction where water breaks bonds. Proteases are involved in many biological functions, including digestion of ingested proteins, protein catabolism, and cell signaling.
Serine proteases are enzymes that cleave peptide bonds in proteins. Serine serves as the nucleophilic amino acid at the (enzyme's) active site. They are found ubiquitously in both eukaryotes and prokaryotes. Serine proteases fall into two broad categories based on their structure: chymotrypsin-like (trypsin-like) or subtilisin-like.
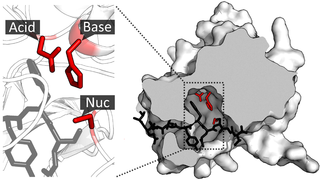
A catalytic triad is a set of three coordinated amino acids that can be found in the active site of some enzymes. Catalytic triads are most commonly found in hydrolase and transferase enzymes. An acid-base-nucleophile triad is a common motif for generating a nucleophilic residue for covalent catalysis. The residues form a charge-relay network to polarise and activate the nucleophile, which attacks the substrate, forming a covalent intermediate which is then hydrolysed to release the product and regenerate free enzyme. The nucleophile is most commonly a serine or cysteine amino acid, but occasionally threonine or even selenocysteine. The 3D structure of the enzyme brings together the triad residues in a precise orientation, even though they may be far apart in the sequence.
Kallikreins are a subgroup of serine proteases, enzymes capable of cleaving peptide bonds in proteins. In humans, plasma kallikrein has no known paralogue, while tissue kallikrein-related peptidases (KLKs) encode a family of fifteen closely related serine proteases. These genes are localised to chromosome 19q13, forming the largest contiguous cluster of proteases within the human genome. Kallikreins are responsible for the coordination of various physiological functions including blood pressure, semen liquefaction and skin desquamation.
Aspartic proteases are a catalytic type of protease enzymes that use an activated water molecule bound to one or more aspartate residues for catalysis of their peptide substrates. In general, they have two highly conserved aspartates in the active site and are optimally active at acidic pH. Nearly all known aspartyl proteases are inhibited by pepstatin.

Serine protease HTRA2, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the HTRA2 gene. This protein is involved in caspase-dependent apoptosis and in Parkinson's disease.

Kallikrein-6 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KLK6 gene. Kallikrein-6 is also referred to as neurosin, protease M, hK6, or zyme. It is a 223 amino acid sequence, derived from its 244 original form, which contains a 16 residue presignal and 5 residue activation peptide.
Kallikrein-related peptidase 7 (KLK7) is a serine protease that in humans is encoded by the KLK7 gene. KLK7 was initially purified from the epidermis and characterised as stratum corneum chymotryptic enzyme (SCCE). It was later identified as the seventh member of the human kallikrein family, which includes fifteen homologous serine proteases located on chromosome 19 (19q13).

Kallikrein-14 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KLK14 gene.

Prostasin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PRSS8 gene.

Lon protease homolog, mitochondrial is a protease, an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the LONP1 gene.

Corin, also called atrial natriuretic peptide-converting enzyme, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CORIN gene.
Signal peptidase I is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Mannan-binding lectin-associated serine protease-2 is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
HtrA2 peptidase is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Matriptases are an enzyme family. This enzyme cleaves various synthetic substrates with Arg or Lys at the P1 position and prefers small side-chain amino acids, such as Ala and Gly, at the P2 position

The 3C-like protease (3CLpro) or main protease (Mpro), formally known as C30 endopeptidase or 3-chymotrypsin-like protease, is the main protease found in coronaviruses. It cleaves the coronavirus polyprotein at eleven conserved sites. It is a cysteine protease and a member of the PA clan of proteases. It has a cysteine-histidine catalytic dyad at its active site and cleaves a Gln–(Ser/Ala/Gly) peptide bond.

The PA clan is the largest group of proteases with common ancestry as identified by structural homology. Members have a chymotrypsin-like fold and similar proteolysis mechanisms but can have identity of <10%. The clan contains both cysteine and serine proteases. PA clan proteases can be found in plants, animals, fungi, eubacteria, archaea and viruses.
ORF1ab refers collectively to two open reading frames (ORFs), ORF1a and ORF1b, that are conserved in the genomes of nidoviruses, a group of viruses that includes coronaviruses. The genes express large polyproteins that undergo proteolysis to form several nonstructural proteins with various functions in the viral life cycle, including proteases and the components of the replicase-transcriptase complex (RTC). Together the two ORFs are sometimes referred to as the replicase gene. They are related by a programmed ribosomal frameshift that allows the ribosome to continue translating past the stop codon at the end of ORF1a, in a -1 reading frame. The resulting polyproteins are known as pp1a and pp1ab.

The nidoviral papain-like protease is a papain-like protease protein domain encoded in the genomes of nidoviruses. It is expressed as part of a large polyprotein from the ORF1a gene and has cysteine protease enzymatic activity responsible for proteolytic cleavage of some of the N-terminal viral nonstructural proteins within the polyprotein. A second protease also encoded by ORF1a, called the 3C-like protease or main protease, is responsible for the majority of further cleavages. Coronaviruses have one or two papain-like protease domains; in SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2, one PLPro domain is located in coronavirus nonstructural protein 3 (nsp3). Arteriviruses have two to three PLP domains. In addition to their protease activity, PLP domains function as deubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs) that can cleave the isopeptide bond found in ubiquitin chains. They are also "deISGylating" enzymes that remove the ubiquitin-like domain interferon-stimulated gene 15 (ISG15) from cellular proteins. These activities are likely responsible for antagonizing the activity of the host innate immune system. Because they are essential for viral replication, papain-like protease domains are considered drug targets for the development of antiviral drugs against human pathogens such as MERS-CoV, SARS-CoV, and SARS-CoV-2.
References
- ↑ Snijder EJ, Wassenaar AL, van Dinten LC, Spaan WJ, Gorbalenya AE (March 1996). "The arterivirus nsp4 protease is the prototype of a novel group of chymotrypsin-like enzymes, the 3C-like serine proteases". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 271 (9): 4864–71. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.9.4864 . PMID 8617757.
- ↑ van Dinten LC, Rensen S, Gorbalenya AE, Snijder EJ (March 1999). "Proteolytic processing of the open reading frame 1b-encoded part of arterivirus replicase is mediated by nsp4 serine protease and Is essential for virus replication". Journal of Virology. 73 (3): 2027–37. doi:10.1128/JVI.73.3.2027-2037.1999. PMC 104445 . PMID 9971783.
- ↑ Barrette-Ng IH, Ng KK, Mark BL, Van Aken D, Cherney MM, Garen C, Kolodenko Y, Gorbalenya AE, Snijder EJ, James MN (October 2002). "Structure of arterivirus nsp4. The smallest chymotrypsin-like proteinase with an alpha/beta C-terminal extension and alternate conformations of the oxyanion hole". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 277 (42): 39960–6. doi: 10.1074/jbc.m206978200 . PMID 12163505.