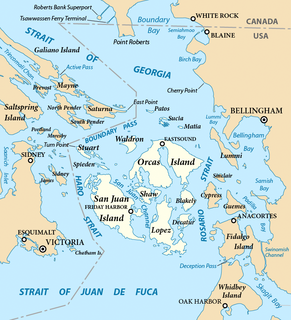
Whatcom County is a county located in the U.S. state of Washington. As of the 2010 census, the population was 201,140. It is bordered by Canada on the north, Okanogan County on the east, Skagit County on the south, and the Strait of Georgia on the west. The county seat and largest city is Bellingham.

The Lummi, governed by the Lummi Nation, are a Native American tribe of the Coast Salish ethnolinguistic group in western Washington state in the United States. The federally recognized tribe primarily resides on and around the Lummi Indian Reservation to the west of Bellingham in western Whatcom County, 20 miles (32 km) south of the border with Canada.

King Street Station is a train station in Seattle, Washington, United States. Located between South King and South Jackson streets and Second and Fourth Avenues South in the Pioneer Square neighborhood of Seattle, the station is just south of downtown. Built between 1904 and 1906, it served the Great Northern Railway and Northern Pacific Railway from its grand opening on May 10, 1906, until the creation and start of Amtrak on May 1, 1971. The station was designed by the St. Paul, Minnesota architectural firm of Charles A. Reed and Allen H. Stem, who were later associate designers for the New York Central Railroad's Grand Central Terminal in New York City. King Street Station was Seattle's primary train terminal until the construction of the adjacent Oregon & Washington Depot, later named Union Station, in 1911. King Street Station was added to the National Register of Historic Places and the Washington Heritage Register in 1973.

Bellingham International Airport is three miles (5 km) northwest of Bellingham, in Whatcom County, Washington, and the third-largest commercial airport in Washington. BLI covers 2,190 acres of land.

Pacific Central Station in Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada is a railway station which acts as the western terminus of Via Rail's cross-country The Canadian to Toronto and the northern terminus of Amtrak’s Cascades to Seattle and Portland. The station also provides intercity coach service, being the head office and bus depot of Pacific Coach Lines and the main Vancouver terminal for Greyhound Bus Lines. The station is wheelchair-accessible and is staffed with full Via services.

Bellingham School District No. 501 is a public school district in Whatcom County, Washington, United States that serves the city of Bellingham.

State Route 11 (SR 11) is a 21.28-mile (34.25 km) long state highway that serves Skagit and Whatcom counties in the U.S. state of Washington. SR 11, known as Chuckanut Drive, begins at an interchange with Interstate 5 (I-5) north of Burlington and continues northwest through several small towns and the Chuckanut Mountains to the Fairhaven district of Bellingham, where the highway turns east and ends again at I-5.

The Bellingham Herald is a daily newspaper published in Bellingham, Washington, in the United States. It is currently owned by The McClatchy Company.

NOAA Ship John N. Cobb was a National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration research vessel in commission from 1970 to 2008. She was named for John Nathan Cobb and was the oldest commissioned ship in the NOAA fleet when she was decommissioned, having previously served in the United States Department of the Interior′s Fish and Wildlife Service from 1950 to 1956 and in the United States Fish and Wildlife Service′s Bureau of Commercial Fisheries from 1956 to 1970 as R/V John N. Cobb.

Fairhaven Station, also called Bellingham, is a train station serving Amtrak's Cascades route, as well as a bus station serving Greyhound Lines and local Whatcom Transportation Authority buses, in Bellingham, Washington, United States. Built in 1995, the station is located near the Bellingham Cruise Terminal, the southern connection for the Alaska Marine Highway. Water Taxi services and seasonal whale watching excursions also provide connections from the Bellingham Cruise Terminal to the San Juan Islands.
The Bellingham Public Library is a public library system serving Bellingham, Washington, US. It maintains three libraries, one in the Civic Center of downtown Bellingham, one in Fairhaven, and one in Barkley Village. The system is independent of the Whatcom County Library System, serving the entire county, but has a reciprocal borrowing agreement.
The history of Bellingham, Washington, as it is now known, begins with the settling of Whatcom County in the mid-to-late 19th century.

The Whatcom Museum was originally built in 1892 as the city hall for the former town of New Whatcom, before it was joined with surrounding towns to form Bellingham, Washington. The building was designed in a Late Victorian style by Alfred Lee, a local architect, who used red brick and Chuckanut Sandstone for its construction. The design itself was an almost exact replica of the second Saginaw County Courthouse in Saginaw, Michigan, Designed by Fred W. Hollister.

The Fairhaven and Southern Railroad was a railroad located in the northwest part of Washington State built by the Fairhaven Land Co., founded by E. M. Wilson, E. L. Cowgill, Nelson Bennett, C. X. Larrabee, and Samuel E. Larrabee.

The Whatcom Chief is a ferry in Washington State, United States. The ferry carries both pedestrians and vehicles to Lummi Island from Gooseberry Point west of Bellingham, Washington.

MV Plover is an 11-ton, 17-passenger ferry in Whatcom County, Washington, built in 1944, listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1997. She is owned by the City of Blaine, Washington and operated by the nonprofit Drayton Harbor Maritime. She originally ferried workers from Blaine to the Alaska Packers' Association cannery at Semiahmoo Spit, carrying out this function until 1964. She was restored by volunteers of Whatcom Maritime Historical Society, and now carries passengers during the summer months from the Blaine harbor dock across Drayton Harbor to the resort dock. At approximately 1 kilometer, this is claimed to be the shortest ferry run in Washington. She is the second oldest operating foot passenger ferry in Washington, next to Kitsap Transit's Carlisle II which was built in Bellingham 27 years earlier, in 1917.
The Interurban Trail is a rail trail in Whatcom County, Washington. It runs 6.6 miles (10.6 km) between Fairhaven and Larrabee State Park (48°38′52″N122°29′12″W) in the Bellingham area. Popular with hikers and bicycles, the trail runs parallel to Chuckanut Drive though the Chuckanut Mountains. The trail follows the shoreline of the Salish Sea and Puget Sound, with ample views of Bellingham Bay, the Lummi Peninsula, Portage Island, Lummi Island, Chuckanut Bay and the distant San Juan Islands.