
The Pequot are a Native American people of Connecticut. The modern Pequot are members of the federally recognized Mashantucket Pequot Tribe, four other state-recognized groups in Connecticut including the Eastern Pequot Tribal Nation, or the Brothertown Indians of Wisconsin. They historically spoke Pequot, a dialect of the Mohegan-Pequot language, which became extinct by the early 20th century. Some tribal members are undertaking revival efforts.

Charlestown is a town in Washington County, Rhode Island, United States. The population was 7,997 at the 2020 census.

King Philip's War was an armed conflict in 1675–1676 between a group of indigenous peoples of the Northeastern Woodlands and the English New England Colonies and their indigenous allies. The war is named for Metacomet, the Pokanoket chief and sachem of the Wampanoag who adopted the English name Philip because of the friendly relations between his father Massasoit and the Plymouth Colony. The war continued in the most northern reaches of New England until the signing of the Treaty of Casco Bay on April 12, 1678.

The Wampanoag, also rendered Wôpanâak, are a Native American people of the Northeastern Woodlands currently based in southeastern Massachusetts and formerly parts of eastern Rhode Island. Their historical territory includes the islands of Martha's Vineyard and Nantucket.

The Pequot War was an armed conflict that took place in 1636 and ended in 1638 in New England, between the Pequot tribe and an alliance of the colonists from the Massachusetts Bay, Plymouth, and Saybrook colonies and their allies from the Narragansett and Mohegan tribes. The war concluded with the decisive defeat of the Pequot. At the end, about 700 Pequots had been killed or taken into captivity. Hundreds of prisoners were sold into slavery to colonists in Bermuda or the West Indies; other survivors were dispersed as captives to the victorious tribes.

The Narragansett people are an Algonquian American Indian tribe from Rhode Island. Today, Narragansett people are enrolled in the federally recognized Narragansett Indian Tribe. They gained federal recognition in 1983.
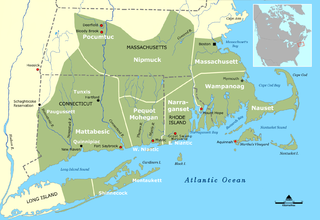
The Niantic are a tribe of Algonquian-speaking American Indians who lived in the area of Connecticut and Rhode Island during the early colonial period. They were divided into eastern and western groups due to intrusions by the more numerous and powerful Pequots. The Western Niantics were subject to the Pequots and lived just east of the mouth of the Connecticut River, while the Eastern Niantics became very close allies to the Narragansetts. It is likely that the name Nantucket is derived from the tribe's endonym, Nehantucket.

Ninigret was a sachem of the eastern Niantic Indian tribe in New England at the time of colonization, based in Rhode Island. In 1637, he allied with the colonists and the Narragansetts against the Pequot Indians.
Wyandanch (c. 1571 – 1659 was a sachem of the Montaukett Indians in the mid-17th century on eastern Long Island. Initially he was a minor chief among the Montaukett, but due to his skillful manipulation of various alliances and his accommodating stance towards the European colonists who gave him substantial military and economic support, he eventually became an influential "alliance chief" (a sachem who was responsible for maintaining friendly relations between his tribe and the settlers).

The Mystic massacre – also known as the Pequot massacre and the Battle of Mystic Fort – took place on May 26, 1637 during the Pequot War, when a force from the Connecticut Colony under Captain John Mason and their Narragansett and Mohegan allies set fire to the Pequot Fort near the Mystic River. They shot anyone who tried to escape the wooden palisade fortress and killed most of the village. There were between 400 and 700 Pequots killed during the attack; the only Pequot survivors were warriors who were away in a raiding party with their sachem Sassacus.

The Great Swamp Massacre or the Great Swamp Fight was a crucial battle fought during King Philip's War between the colonial militia of New England and the Narragansett people in December 1675. It was fought near the villages of Kingston and West Kingston in the Colony of Rhode Island and Providence Plantations. The combined force of the New England militia included 150 Pequots, and they inflicted a huge number of Narragansett casualties, including many hundred women and children. The battle has been described as "one of the most brutal and lopsided military encounters in all of New England's history." Since the 1930s, Narragansett and Wampanoag people commemorate the battle annually in a ceremony initiated by Narragansett-Wampanoag scholar Princess Red Wing.

The Indian Burial Ground is a historic Native American cemetery on Narrow Lane in Charlestown, Rhode Island. The small cemetery is believed to have been the burying ground for leaders of the Narragansett and Niantic tribes. It is now fenced off by an iron post and rail fence, erected in the late 19th century.

Ninigret is a coastal lagoon in Charlestown, Rhode Island, in the United States, located at 41°22′45″N71°38′43″W. It is the largest of the nine lagoons, or "salt ponds", in southern Rhode Island. It is utilized for recreational activities, as well as oyster and quahog harvesting. Found along its shores are "extensive" archaeological remains. Ninigret Pond, like others in the region, was "formed after the recession of the glaciers 12,000 years ago". The pond is situated on low-lying ground, and as such, it is considered particularly vulnerable to storm surge flooding. It is connected to Green Hill Pond via a small channel.

Washington County, known locally as South County, is a county located in the U.S. state of Rhode Island. As of the 2020 census, the population was 129,839. Rhode Island counties have no governmental functions other than as court administrative boundaries, which are part of the state government.

The Narragansett land claim was one of the first litigations of aboriginal title in the United States in the wake of the U.S. Supreme Court's landmark Oneida Indian Nation of New York v. County of Oneida (1974), or Oneida I, decision. The Narragansett claimed a few thousand acres of land in and around Charlestown, Rhode Island, challenging a variety of early 19th century land transfers as violations of the Nonintercourse Act, suing both the state and private land owners.

Paulla Dove Jennings is a Narragansett storyteller, educator, and children's book author.

The Treaty of Hartford was a treaty concluded between English colonists in Connecticut, the Mohegan nation and the Narragansett nation on September 21, 1638, in Hartford, Connecticut.

Harman Garrett was a Niantic sachem and then governor of the Eastern Pequots slightly east of the Pawcatuck River in what is now Westerly, Rhode Island. His chosen English name was very similar to that of Herman Garrett, a prominent colonial gunsmith from Massachusetts in the 1650s.

Quaiapen was a Narragansett-Niantic female sachem (saunkskwa) who was the last sachem captured or killed during King Philip’s War.
The Narragansett-Montaukett war was an armed conflict which began in 1653 and lasted to 1657 between the allies of the Niantic Sachem Ninigret and the Long Island tribes who were under the protection of the New England Confederation.



























