
The Great Western Railway 4000 or Star were a class of 4-cylinder 4-6-0 passenger steam locomotives designed by George Jackson Churchward for the Great Western Railway (GWR) in 1906 and introduced from early 1907. The prototype was built as a 4-4-2 Atlantic. They proved to be a successful design which handled the heaviest long-distance express trains, reaching top speeds of 90 mph (145 km/h), and established the design principles for GWR 4-cylinder classes over the next twenty-five years.

The Great Western Railway 3700 Class, or City Class, locomotives were a series of twenty 4-4-0 steam locomotives, designed for hauling express passenger trains.

George Jackson Churchward was an English railway engineer, and was chief mechanical engineer of the Great Western Railway (GWR) in the United Kingdom from 1902 to 1922.

The first Locomotives of the Great Western Railway (GWR) were specified by Isambard Kingdom Brunel but Daniel Gooch was soon appointed as the railway's Locomotive Superintendent. He designed several different 7 ft 1⁄4 in broad gauge types for the growing railway, such as the Firefly and later Iron Duke Class 2-2-2s. In 1864 Gooch was succeeded by Joseph Armstrong who brought his standard gauge experience to the workshops at Swindon. To replace some of the earlier locomotives, he put broad gauge wheels on his standard gauge locomotives and from this time on all locomotives were given numbers, including the broad gauge ones that had previously carried just names.

The Great Western Railway 2900 Class or Saint Class, which was built by the Great Western Railway's Swindon Works, incorporated several series of 2-cylinder passenger steam locomotives designed by George Jackson Churchward and built between 1902 and 1913 with differences in the dimensions. The majority of these were built as 4-6-0 locomotives; but thirteen examples were built as 4-4-2. They proved to be a highly successful class which established the design principles for GWR 2-cylinder classes over the next fifty years, and influenced similar classes on other British railways.

The Great Western Railway (GWR) Star Class of 2-2-2 broad gauge steam locomotives were used for passenger train work. Designed by Robert Stephenson, the class was introduced into service between November 1838 and November 1841, and withdrawn between April 1864 and September 1871.

The Great Western Railway (GWR) Ariadne Class and Caliph Class were broad gauge 0-6-0 steam locomotives designed for goods train work by Daniel Gooch and are often referred to as his Standard Goods locomotives.
The Great Western Railway (GWR) Bogie Class4-4-0ST were broad gauge steam locomotives for passenger train work. The first two locomotives of this class were introduced into service in August/September 1849, with the remainder following between June 1854 and March 1855. All but one were withdrawn between October 1871 and 1873, with the final locomotive being withdrawn in December 1880.

The Great Western Railway Iron Duke Class 4-2-2 was a class of 7 ft 1⁄4 in broad gauge steam locomotives for express passenger train work.

The Great Western Railway Sir Watkin Class were 0-6-0T broad gauge steam locomotives. They were designed for working goods trains through to the underground Metropolitan Railway in London. This class was introduced into service between December 1865 and the last was withdrawn at the end of the GWR broad gauge in May 1892. They were all named after directors and senior officers of the railway.

The GWR 1400 Class is a class of steam locomotive designed by the Great Western Railway for branch line passenger work. It was originally classified as the 4800 Class when introduced in 1932, and renumbered in 1946.

The Dean Single, 3031 Class, or Achilles Class was a type of steam locomotive built by the British Great Western Railway between 1891 and 1899. They were designed by William Dean for passenger work. The first 30 members of the class were built as 2-2-2s of the 3001 Class.

Joseph Armstrong was an English locomotive engineer and the second locomotive superintendent of the Great Western Railway. His younger brother George and one of his sons also became outstanding engineers in the employment of the GWR.

The South Devon Railway 2-4-0 locomotives were small 2-4-0T broad gauge locomotives operated on the South Devon Railway, mainly on its branch lines such as that to Ashburton.
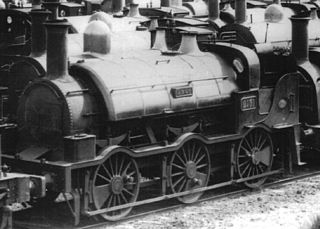
The eight Dido class locomotives were 0-6-0ST broad gauge locomotives operated on the South Devon Railway and Cornwall Railway and associated other adjacent railways. They were designed for goods trains but were also used on passenger trains when required.

The GWR Hercules Class were four broad gauge steam locomotives for the Great Western Railway. They were its first 0-6-0 locomotives, being built in 1842 by Nasmyth, Gaskell and Company stemming from the company's need for goods locomotives. This resulted in the last four Firefly Class locomotives being modified while still in production. From about 1865, the Hercules Class locomotives became part of the Fury Class, along with the Premier Class locomotives. They were withdrawn between 1870 and 1871.

The first 19 locomotives ordered by Isambard Kingdom Brunel for the Great Western Railway included two unusual Haigh Foundry locomotives.
Hurricane was the second of a pair of steam locomotives built for the Great Western Railway (GWR) by R. & W. Hawthorn & Co. whose design was very different from other locomotives. In order to meet Isambard Kingdom Brunel's strict specifications, a 2-2-2 frame carried the 'engine', while the boiler was on a separate six-wheeled frame.
During the 1880s and 1890s, William Dean constructed a series of experimental locomotives to test various new ideas in locomotive construction for the Great Western Railway.
The Daniel Gooch standard gauge locomotives comprise several classes of locomotives designed by Daniel Gooch, Superintendent of Locomotive Engines for the Great Western Railway (GWR) from 1837 to 1864.















