
A safety valve is a valve that acts as a fail-safe. An example of safety valve is a pressure relief valve (PRV), which automatically releases a substance from a boiler, pressure vessel, or other system, when the pressure or temperature exceeds preset limits. Pilot-operated relief valves are a specialized type of pressure safety valve. A leak tight, lower cost, single emergency use option would be a rupture disk.

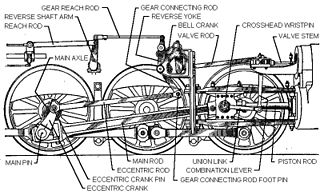
The valve gear of a steam engine is the mechanism that operates the inlet and exhaust valves to admit steam into the cylinder and allow exhaust steam to escape, respectively, at the correct points in the cycle. It can also serve as a reversing gear. It is sometimes referred to as the "motion".

The Walschaerts valve gear is a type of valve gear invented by Belgian railway mechanical engineer Egide Walschaerts in 1844 used to regulate the flow of steam to the pistons in Steam locomotives. The gear is sometimes named without the final "s", since it was incorrectly patented under that name. It was extensively used in steam locomotives from the late 19th century until the end of the steam era.
A tappet is most commonly a component in an internal combustion engine which converts the rotating motion of the camshaft into linear motion of the valves, either directly or indirectly.

Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 4-12-2 represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels, twelve coupled driving wheels, and two trailing wheels. This arrangement was named the Union Pacific type, after the only railroad to use it, the Union Pacific Railroad.

The Scotch Yoke is a reciprocating motion mechanism, converting the linear motion of a slider into rotational motion, or vice versa. The piston or other reciprocating part is directly coupled to a sliding yoke with a slot that engages a pin on the rotating part. The location of the piston versus time is simple harmonic motion, i.e., a sine wave having constant amplitude and constant frequency, given a constant rotational speed.

Matthew Murray was an English steam engine and machine tool manufacturer, who designed and built the first commercially viable steam locomotive, the twin cylinder Salamanca in 1812. He was an innovative designer in many fields, including steam engines, machine tools and machinery for the textile industry.
After about 1910, the Baker valve gear was the main competitor to Walschaerts valve gear for steam locomotives in the United States. Strictly speaking it was not a valve gear but a variable expansion mechanism adapted to the Walschaerts layout replacing the expansion link and sliding die block. The Baker arrangement used more pivot bearings or pin joints, but avoided the die slip inherent to the expansion link, with the aim of lessening wear and the need for service; it could also facilitate longer valve travel.

The Stephenson valve gear or Stephenson link or shifting link is a simple design of valve gear that was widely used throughout the world for various kinds of steam engines. It is named after Robert Stephenson but was invented by his employees.

A Corliss steam engine is a steam engine, fitted with rotary valves and with variable valve timing patented in 1849, invented by and named after the American engineer George Henry Corliss of Providence, Rhode Island.

Joy valve gear is a type of steam locomotive valve gear, designed by David Joy, Locomotive and Marine engineer, and patented on 8 March 1879. The British patent has not been found but the US patent has. Joy's gear is similar to Hackworth valve gear but has a compensating mechanism which corrects for "the slight inequality in the motion of the valve arising from the arc of the lever".

Southern valve gear was briefly popular on steam locomotives in the United States. It combines elements of the Walschaerts and Baker patterns.

The cylinder is the power-producing element of the steam engine powering a steam locomotive. The cylinder is made pressure-tight with end covers and a piston; a valve distributes the steam to the ends of the cylinder. Cylinders were cast in iron and later made of steel. The cylinder casting includes other features such as valve ports and mounting feet. The last big American locomotives incorporated the cylinders as part of huge one-piece steel castings that were the main frame of the locomotive. Renewable wearing surfaces were needed inside the cylinders and provided by cast-iron bushings.

An expansion valve is a device in steam engine valve gear that improves engine efficiency. It operates by closing off the supply of steam early, before the piston has travelled through its full stroke. This cut-off allows the steam to then expand within the cylinder. This expanding steam is still sufficient to drive the piston, even though its pressure decreases as it expands. As less steam is supplied in the shorter time for which the valve is open, use of the expansion valve reduces the steam consumed and thus the fuel required. The engine may deliver two-thirds of the work, for only one-third of the steam.

James Thompson Marshall was an English railway and mechanical engineer known for inventing the 'Marshall valve gear' for steam locomotive use. James Marshall began his engineering career at the Leeds-based Steam Plough Company, and later moved to the city's Boyne Engine Works.

The Holcroft valve gear was a type of conjugated valve gear designed and patented by Harold Holcroft and used on three-cylinder steam locomotives of the South Eastern & Chatham Railway (SECR). It bore many similarities to the Gresley conjugated valve gear, which it predated, as eventually used on all Gresley's three cylinder designs. It varied from the Gresley method of operation by using the combination lever assembly instead of the valve spindles to drive the middle cylinder of a three-cylinder design. This had operational advantages over Gresley's design, namely eliminating the problems of flexure, bush wear and the influence of heat in the valve spindles.

Musgrave's non-dead-centre engine was a stationary steam engine of unusual design, intended to solve the problem of stopping on dead centre. It was designed in 1887 to serve as a marine engine. It used a pair of linked cylinders to prevent the engine from stopping in a position where no turning force can be applied. At least one engine is known to survive.
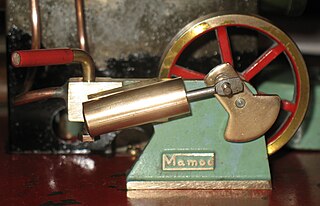
An oscillating cylinder steam engine is a simple steam-engine design that requires no valve gear. Instead the cylinder rocks, or oscillates, as the crank moves the piston, pivoting in the mounting trunnion so that ports in the cylinder line up with ports in a fixed port face alternately to direct steam into or out of the cylinder.

Gab valve gear was an early form of valve gear used on steam engines. Its simplest form allowed an engine to be stopped and started. A double form, mostly used on steam locomotives, allowed easy reversing.
Stuart Turner Ltd is a British engineering company, based in Henley-on-Thames, Oxfordshire, England, founded by engineer Sidney Marmaduke Stuart Turner in 1906.





















