In earth science, erosion is the action of surface processes that removes soil, rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust, and then transports it to another location. Erosion is distinct from weathering which involves no movement. Removal of rock or soil as clastic sediment is referred to as physical or mechanical erosion; this contrasts with chemical erosion, where soil or rock material is removed from an area by dissolution. Eroded sediment or solutes may be transported just a few millimetres, or for thousands of kilometres.

In geology, a fjord or fiord is a long, narrow inlet with steep sides or cliffs, created by a glacier. There are many fjords on the coasts of Alaska, Antarctica, British Columbia, Chile, Denmark, Greenland, the Faroe Islands, Iceland, Ireland, Kamchatka, the Kerguelen Islands, New Zealand, Norway, Novaya Zemlya, Labrador, Nunavut, Newfoundland, Quebec, Scotland, South Georgia Island, Isla de los Estados, and Washington state. Norway's coastline is estimated at 29,000 kilometres (18,000 mi) with nearly 1,200 fjords, but only 2,500 kilometres (1,600 mi) when fjords are excluded.
Landforms are categorized by characteristic physical attributes such as their creating process, shape, elevation, slope, orientation, rock exposure, and soil type.

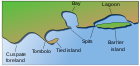
Submergent coastlines or drowned coastlines are stretches along the coast that have been inundated by the sea by a relative rise in sea levels from either isostacy or eustacy.

A raised beach, coastal terrace, or perched coastline is a relatively flat, horizontal or gently inclined surface of marine origin, mostly an old abrasion platform which has been lifted out of the sphere of wave activity. Thus, it lies above or under the current sea level, depending on the time of its formation. It is bounded by a steeper ascending slope on the landward side and a steeper descending slope on the seaward side. Due to its generally flat shape it is often used for anthropogenic structures such as settlements and infrastructure.

Post-glacial rebound is the rise of land masses after the removal of the huge weight of ice sheets during the last glacial period, which had caused isostatic depression. Post-glacial rebound and isostatic depression are phases of glacial isostasy, the deformation of the Earth's crust in response to changes in ice mass distribution. The direct raising effects of post-glacial rebound are readily apparent in parts of Northern Eurasia, Northern America, Patagonia, and Antarctica. However, through the processes of ocean siphoning and continental levering, the effects of post-glacial rebound on sea level are felt globally far from the locations of current and former ice sheets.

A skerry is a small rocky island, or islet, usually too small for human habitation. It may simply be a rocky reef. A skerry can also be called a low sea stack.

The Cordilleran ice sheet was a major ice sheet that periodically covered large parts of North America during glacial periods over the last ~2.6 million years. This included the following areas:

In geology, a depression is a landform sunken or depressed below the surrounding area. Depressions form by various mechanisms.

A terminal moraine, also called end moraine, is a type of moraine that forms at the terminal (edge) of a glacier, marking its maximum advance. At this point, debris that has accumulated by plucking and abrasion, has been pushed by the front edge of the ice, is driven no further and instead is deposited in an unsorted pile of sediment. Because the glacier acts very much like a conveyor belt, the longer it stays in one place, the greater the amount of material that will be deposited. The moraine is left as the marking point of the terminal extent of the ice.

The geology of England is mainly sedimentary. The youngest rocks are in the south east around London, progressing in age in a north westerly direction. The Tees-Exe line marks the division between younger, softer and low-lying rocks in the south east and the generally older and harder rocks of the north and west which give rise to higher relief in those regions. The geology of England is recognisable in the landscape of its counties, the building materials of its towns and its regional extractive industries.
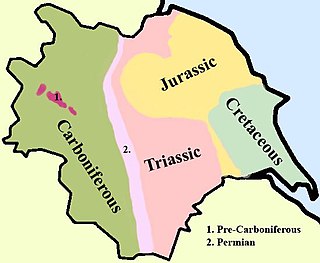
The Geology of Yorkshire in northern England shows a very close relationship between the major topographical areas and the geological period in which their rocks were formed. The rocks of the Pennine chain of hills in the west are of Carboniferous origin whilst those of the central vale are Permo-Triassic. The North York Moors in the north-east of the county are Jurassic in age while the Yorkshire Wolds to the south east are Cretaceous chalk uplands. The plain of Holderness and the Humberhead levels both owe their present form to the Quaternary ice ages. The strata become gradually younger from west to east.
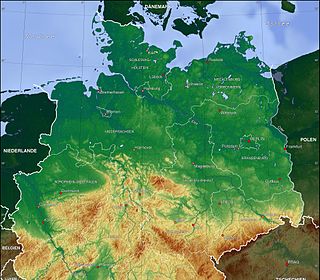
The North German Plain or Northern Lowland is one of the major geographical regions of Germany. It is the German part of the North European Plain. The region is bounded by the coasts of the North Sea and the Baltic Sea to the north, Germany's Central Uplands to the south, by the Netherlands to the west and Poland to the east.

Weichselian glaciation refers to the last glacial period and its associated glaciation in northern parts of Europe. In the Alpine region it corresponds to the Würm glaciation. It was characterized by a large ice sheet that spread out from the Scandinavian Mountains and extended as far as the east coast of Schleswig-Holstein, the March of Brandenburg and Northwest Russia.

A fjard is a large open space of water between groups of islands or mainland in archipelagos. Fjards can be found along sea coasts, in freshwater lakes or rivers. Fjard and Fjord are originally the same word with the general meaning of sailable waterway. In Scandinavia, fjords dominate along the North Sea coast while fjards dominate the Baltic Sea coast.

The Champlain Sea was a temporary inlet of the Atlantic Ocean, created by the retreating glaciers during the close of the last glacial period. The Sea once included lands in what are now the Canadian provinces of Quebec and Ontario, as well as parts of the American states of New York and Vermont.

A steep coast is a stretch of coastline where the mainland descends abruptly into the sea. There is a sharp transition from the land to sea as opposed to that on a flat coast where the land descends gradually seawards. The height of the land on a steep coast is well above sea level.

Strandflat is a landform typical of the Norwegian coast consisting of a flattish erosion surface on the coast and near-coast seabed. In Norway, strandflats provide room for settlements and agriculture, constituting important cultural landscapes. The shallow and protected waters of strandflats are valued fishing grounds that provide sustenance to traditional fishing settlements. Outside Norway proper, strandflats can be found in other high-latitude areas, such as Antarctica, Alaska, the Canadian Arctic, the Russian Far North, Greenland, Svalbard, Sweden and Scotland.

The Central Swedish lowland is a large region of low relief and altitude in Sweden spanning from the Swedish West Coast at Bohuslän to Stockholm archipelago and Roslagen at the Baltic Sea. The Central Swedish lowland forms a broad east-west trending belt north of the South Swedish highlands and south of the Norrland terrain. Traditionally the heartland of Sweden due to its large population and agricultural resources the region benefits additionally from the proximity of hydropower, forest and mineral resources. The lowland is also at a good position for trade with the Baltic region. These advantages are reflected in the location of Sweden's capital, Stockholm, at the eastern end of the lowlands. Most of Sweden's manufacturing industries lies in this region.

The Skanderbeg Mountains are a mountain range in Albania, Southern Europe.