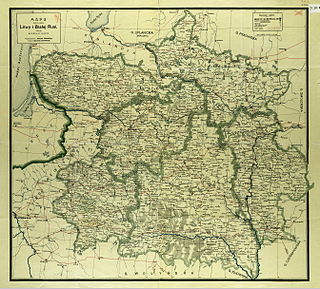
Northwestern Krai was a krai of the Russian Empire in the territories of the former Grand Duchy of Lithuania. The administrative center was in Vilna. Northwestern Krai together with the Southwestern Krai, which was composed of the territories formerly belonging to the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland, formed the Western Krai.

The Socialist Soviet Republic of Lithuania and Belorussia, alternatively referred to as the Socialist Soviet Republic of Lithuania and White Russia or simply Litbel (Lit-Bel), was a Soviet republic that existed within the parts of the territories of modern Belarus and Lithuania for approximately five months during the Lithuanian–Soviet War and the Polish–Soviet War in 1919. The Litbel republic was created in February 1919 formally through the merger of the short-lived Lithuanian Soviet Socialist Republic and the Socialist Soviet Republic of Belorussia.

Lithuania is now a country in the Baltic region of Europe.

Courland Governorate, also known as the Province of Courland or Governorate of Kurland, and known from 1795 to 1796 as the Viceroyalty of Courland, was an administrative-territorial unit (guberniya) and one of the Baltic governorates of the Russian Empire. Its area roughly corresponded to Kurzeme, Zemgale and Sēlija of modern-day Latvia.

The Vilna Governorate was a province (guberniya) of the Northwestern Krai of the Russian Empire. In 1897, the governorate covered an area of 41,907.9 square kilometres (16,180.7 sq mi) and had a population of 1,591,207 inhabitants. The governorate was defined by the Minsk Governorate to the south, the Grodno Governorate to the southwest, the Suwałki Governorate to the west, the Kovno and Courland Governorates to the north, and the Vitebsk Governorate to the east. The capital was located in Vilna (Vilnius). The city also served as the capital of Vilna Governorate-General, which existed until 1912. The area roughly corresponded to the Vilnius Region, which was later occupied by Germany, Bolsheviks, and Poland.

Grodno Governorate was an administrative-territorial unit (guberniya) of the Northwestern Krai of the Russian Empire, with its capital in Grodno. It encompassed 38,671.5 square kilometres (14,931.1 sq mi) in area and consisted of a population of 1,631,645 inhabitants by 1897. Grodno Governorate was bordered by Suwałki Governorate to the north, Vilna Governorate to the northeast, Minsk Governorate to the east, Volhynia Governorate to the south, Kholm Governorate to the west, and Łomża Governorate to the northwest. The governorate covered the areas of modern-day Grodno Region of Belarus, part of the Podlaskie Voivodeship of Poland, and a small part of Druskininkai, Lazdijai and Varėna districts of Lithuania.

Following three consecutive partitions of Poland carried out between 1772 and 1795, the sovereign state known as the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth disappeared from the map of Europe. In 1918 following the end of World War I, the territories of the former state re-emerged as the states of Poland and Lithuania among others. In the intervening period, the territory of the former Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth was split between the Austrian Empire, the Kingdom of Prussia and the Russian Empire. These powers subdivided the territories that they gained and created new toponyms for the territories conquered. The subdivisions created were complicated by changes within those empires as well as by the periodic establishment of other forms of the quasi-Polish provinces led by a foreign head of state.

Mogilev Governorate was an administrative-territorial unit (guberniya) of the Northwestern Krai of the Russian Empire. The governorate bordered the Vitebsk Governorate to the north, the Smolensk Governorate to the east, the Chernigov Governorate to the south, and the Minsk Governorate to the west. Its capital was Mogilev, also referred to as Mogilev-on-the-Dnieper, or Mogilev Gubernskiy. The area of the Mogilev Governorate covered concomitant Belarus' Vitebsk, Mogilev and Gomel Regions.

The Russian Partition, sometimes called Russian Poland, constituted the former territories of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth that were annexed by the Russian Empire in the course of late-18th-century Partitions of Poland. The Russian acquisition encompassed the largest share of Poland's population, living on 463,200 km2 of land constituting the eastern and central territory of the former commonwealth. The three partitions, which took place in 1772, 1793 and 1795, resulted in the complete loss of Poland's sovereignty, with its territory split between Russia, Prussia and Austria. The Napoleonic Wars saw significant parts of Prussia's and Austria's partitions reconstituted as the Duchy of Warsaw, most of which was then reconstituted as the Kingdom of Poland within the Russian Empire in 1815.

Lithuania Governorate was an administrative-territorial unit (guberniya) of the Russian Empire in 1796–1801.

Ethnographic Lithuania is a concept that defines Lithuanian territories as a significant part of the territories that belonged to the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and Lithuanians as all people living on them, regardless of whether those people contemporarily or currently speak the Lithuanian language and considered themselves Lithuanian. The concept was in contrast to those of "historic Lithuania", the territories of the Duchy, and the "linguistic Lithuania", the area where Lithuanian language was overwhelmingly spoken.

Veiveriai Teachers' Seminary was a seminary in Veiveriai, Suwałki Governorate, Congress Poland. It was established as teachers' courses in 1866 and reorganized into a seminary in 1872. It prepared teachers for elementary schools in the Suwałki Governorate. During World War I, the seminary was evacuated into Russia and subsequently disbanded. During its existence, the seminary prepared 1,025 teachers, some of which later became prominent figures in Lithuanian education, politics, and culture.
Governorates-General were a type of administrative-territorial division in the Russian Empire from 1775 to 1917. Governorates-General usually comprised a set of guberniyas and oblasts. The term was occasionally used to refer to krais or military guberniyas. Moscow and Saint-Petersburg Governorates were placed into a separate governorate-general.
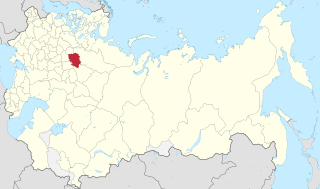
Kostroma Governorate was an administrative-territorial unit (guberniya) of the Russian Empire and the Russian SFSR, which existed from 1796 to 1929. Its administrative center was in the city of Kostroma.

Kaluga Governorate was an administrative-territorial unit (guberniya) of the Russian Empire and the Russian SFSR, which existed in 1796–1929. Its capital was Kaluga.
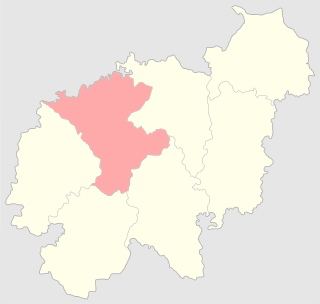
The Vilna uezd was a county (uezd) of the Vilna Governorate of the Russian Empire, with the administrative centre in Vilna. The uezd was bordered by the Sventsyany uezd to the east, the Oshmyany and Lida uezds to the south, the Troki uezd to the west, and the Vilkomir uezd of the Kovno Governorate to the north. The district covered the area of modern Vilnius County of Lithuania.

Vilna Governorate-General, known as Lithuania Governorate-General before 1830, was a Governorate-General of the Russian Empire from 1794 to 1912. It primarily encompassed the Vilna, Grodno, and Kovno Governorates. Governors General were also commanders of the Vilna Military District. According to the Russian Empire Census, the Governorate-General had 4,754,000 residents in 1897.
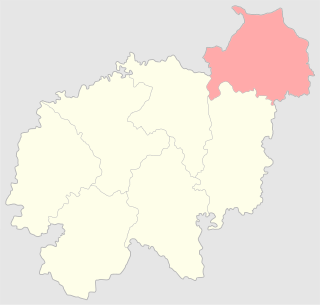
The Disna uezd was a county (uezd) of the Vilna Governorate of the Russian Empire. The uezd was bordered by the Dvinsk uezd of the Vitebsk Governorate to the north, the Minsk uezd of the Minsk Governorate to the east, the Vileyka uezd to the south, the Sventsyany uezd to the southwest, and the Novoaleksandrovsk uezd of the Kovno Governorate. The uezd was eponymously named for its administrative center, Disna, which was belonged to present-day Dizsna in Belarus. The territory of Disna uezd corresponds to a part of the present-day Miory, Hlybokaye, Sharkawshchyna, and Pastavy districts of Vitebsk Region.
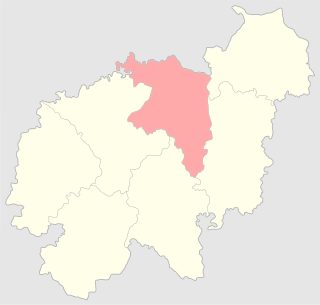
The Sventsyany uezd, known until 1842 as the Zavileisky uezd, was a county (uezd) of the Vilna Governorate of the Russian Empire.
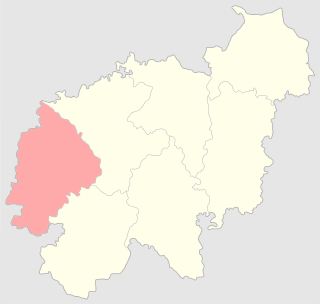
The Troki uezd was a county (uezd) of the Vilna Governorate of the Russian Empire. The uezd was bordered by the Mariampol, Kalvariya, and the Seyny uezds of the Suwałki Governorate to the west, the Lida uezd to the south, the Vilna uezd to the east, and the Kovno uezd of the Kovno Governorate to the north. The administrative centre of the county was the city of Troki. The area included most of the modern Trakai, Elektrėnai districts of Vilnius County, and Varėna, Šalčininkai districts of Alytus County, as well as part of Kaišiadorys, Alytus, and Prienai districts.



















