You can help expand this article with text translated from the corresponding article in Russian. (January 2021)Click [show] for important translation instructions.
|
| Nizhny Novgorod Governorate Нижегородская губерния | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Governorate of the Russian Empire (1714–1917), Russian Republic, and RSFSR (1917–1929) | |||||||||||
| 1714–1929 | |||||||||||
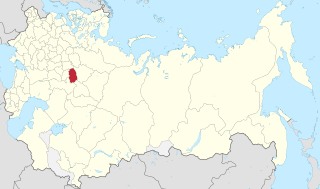
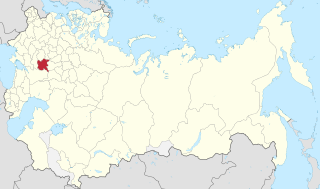
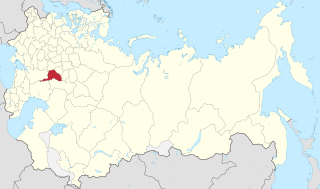
 Location in the Russian Empire | |||||||||||
| Capital | Nizhny Novgorod | ||||||||||
| Area | |||||||||||
• | 51,252 km2 (19,789 sq mi) | ||||||||||
| Population | |||||||||||
• 1897 | 1,584,774 | ||||||||||
| History | |||||||||||
• Established | January 1714 | ||||||||||
• Disestablished | 14 January 1929 | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||

Nizhny Novgorod Governorate [lower-alpha 1] was an administrative-territorial unit ( guberniya ) of the Russian Empire, Russian Republic, and the Russian SFSR, roughly corresponding to the Upper and Middle Volga region and what is now most of the Nizhny Novgorod Oblast. In the early 20th Century, Nizhny Novgorod Governorate bordered Kostroma and Vyatka governorates to the north, Vladimir Governorate to the west, Kazan and Simbirsk governorates to the east, and Penza with Tambov governorates to the south.
Contents
- Geography
- History
- Nizhny Novgorod Land in pre-Peter periods
- Formation of the Governorate
- Subdivisions
- References
In the early 18th Century, Nizhny Novgorod Governorate was included in Kazan Governorate, from 1708–1714, and 1717–1719. The Reform of Peter the Great formed the newly governorate from 1714 to 1779. in the Reign of Catherine the Great, the governorate was reorganized to the Viceroyalty until 1796. In 1929 the governorate was disestablished, as a result of the new administrative reform, where the governorate was again reorganized to the Oblast. The governorate's administrative center was seated in Nizhny Novgorod and consisted of eleven uezds.