
Xenarthra is a major clade of placental mammals native to the Americas. There are 31 living species: the anteaters, tree sloths, and armadillos. Extinct xenarthrans include the glyptodonts, pampatheres and ground sloths. Xenarthrans originated in South America during the late Paleocene about 60 million years ago. They evolved and diversified extensively in South America during the continent's long period of isolation in the early to mid Cenozoic Era. They spread to the Antilles by the early Miocene and, starting about 3 million years ago, spread to Central and North America as part of the Great American Interchange. Nearly all of the formerly abundant megafaunal xenarthrans became extinct at the end of the Pleistocene.

Synapsids are one of the two major clades of vertebrate animals in the group Amniota, the other being the sauropsids. The synapsids were the dominant land animals in the late Paleozoic and early Mesozoic, but the only group that survived into the Cenozoic are mammals. Unlike other amniotes, synapsids have a single temporal fenestra, an opening low in the skull roof behind each eye orbit, leaving a bony arch beneath each; this accounts for their name. The distinctive temporal fenestra developed about 318 million years ago during the Late Carboniferous period, when synapsids and sauropsids diverged, but was subsequently merged with the orbit in early mammals.

Maotherium is a genus extinct symmetrodont mammal that was discovered in Early Cretaceous rocks in Liaoning Province, China, in 2003. Its scientific name directly translates to "fur beast", in reference to the impressions of fur around the fossil. Maotherium belongs to an extinct group of Mesozoic mammals called symmetrodonts. Though little is known about this group, the symmetrodonts have several similarities - specifically their teeth. They have tall pointed, but simple molars in a triangular arrangement. Originally symmetrodonts were known since the 1920s. Now a vast majority have been restored, such as Zhangheotherium and Akidolestes, during the early 21st century. One of the fossils of Maotherium preserved the imprints of fur, like the mammals Eomaia and Sinodelphys.

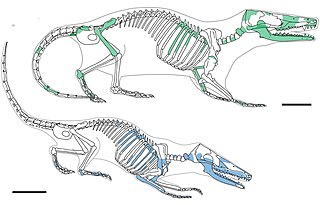
Zhangheotherium is an extinct genus of "symmetrodont" mammal from the Early Cretaceous of China. A single species is known, Zhangheotherium quinquecuspidens from Jianshangou Beds of the Yixian Formation. Zhangheotherium was the first "symmetrodont" known from a nearly complete skeleton, expanding knowledge of the group beyond isolated teeth and jaws. The genus name honors Zhang He, who collected the holotype fossil from Liaoning Province prior to its 1997 description. The specific name is Latin for "five-cusped teeth".

Symmetrodonta is a group of Mesozoic mammals and mammal-like synapsids characterized by the triangular aspect of the molars when viewed from above, and the absence of a well-developed talonid. The traditional group of 'symmetrodonts' ranges in age from the latest Triassic to the Late Cretaceous, but most research in the last 20-30 years has concluded that they are not a true taxonomic group, but include several unrelated branches of the mammal tree. Despite this, the name is still used informally by some researchers for convenience, usually restricted to the spalacotheriids and zhangheotheriids.

Akidolestes is an extinct genus of mammals of the family Spalacotheriidae, a group of mammals related to therians.
Docodonta is an order of extinct Mesozoic mammaliaforms. They were among the most common mammaliaforms of their time, persisting from the Middle Jurassic to the Early Cretaceous across the continent of Laurasia. They are distinguished from other early mammaliaforms by their relatively complex molar teeth. Docodont teeth have been described as "pseudotribosphenic": a cusp on the inner half of the upper molar grinds into a basin on the front half of the lower molar, like a mortar-and-pestle. This is a case of convergent evolution with the tribosphenic teeth of therian mammals. There is much uncertainty for how docodont teeth developed from their simpler ancestors. Their closest relatives may have been certain Triassic "symmetrodonts", namely Woutersia, Delsatia, and Tikitherium.

Mammaliaformes is a clade that contains the crown group mammals and their closest extinct relatives; the group radiated from earlier probainognathian cynodonts. It is defined as the clade originating from the most recent common ancestor of Morganucodonta and the crown group mammals; the latter is the clade originating with the most recent common ancestor of extant Monotremata, Marsupialia, and Placentalia. Besides Morganucodonta and the crown group mammals, Mammaliaformes includes Docodonta and Hadrocodium as well as the Triassic Tikitherium, the earliest known member of the group.

Volaticotherium antiquum is an extinct, gliding, insectivorous mammal that lived in Asia during the Jurassic period, around 164 mya. It is the only member of the genus Volaticotherium.

The evolution of mammals has passed through many stages since the first appearance of their synapsid ancestors in the Pennsylvanian sub-period of the late Carboniferous period. By the mid-Triassic, there were many synapsid species that looked like mammals. The lineage leading to today's mammals split up in the Jurassic; synapsids from this period include Dryolestes, more closely related to extant placentals and marsupials than to monotremes, as well as Ambondro, more closely related to monotremes. Later on, the eutherian and metatherian lineages separated; the metatherians are the animals more closely related to the marsupials, while the eutherians are those more closely related to the placentals. Since Juramaia, the earliest known eutherian, lived 160 million years ago in the Jurassic, this divergence must have occurred in the same period.

Eutriconodonta is an order of early mammals. Eutriconodonts existed in Asia, Africa, Europe, North and South America during the Jurassic and the Cretaceous periods. The order was named by Kermack et al. in 1973 as a replacement name for the paraphyletic Triconodonta.

Dryolestida is an extinct order of mammals, known from the Jurassic and Cretaceous. They are considered basal members of the clade Cladotheria, close to the ancestry of therian mammals. It is also believed that they developed a fully mammalian jaw and also had the three middle ear bones. Most members of the group, as with most Mesozoic mammals, are only known from fragmentary tooth and jaw remains.

Morganucodonta is an extinct order of basal Mammaliaformes, a group including crown-group mammals (Mammalia) and their close relatives. Their remains have been found in Southern Africa, Western Europe, North America, India and China. The morganucodontans were probably insectivorous and nocturnal, though like eutriconodonts some species attained large sizes and were carnivorous. Nocturnality is believed to have evolved in the earliest mammals in the Triassic as a specialisation that allowed them to exploit a safer, night-time niche, while most larger predators were likely to have been active during the day.
Chronoperates is an extinct genus of mammal whose remains have been found in a late Paleocene deposit in Alberta, Canada. It is represented by the type species Chronoperates paradoxus and known only from a partial left lower jaw. It was first identified in 1992 as a non-mammalian cynodont, implying a ghost lineage of over 100 million years since the previously youngest known record of non-mammalian cynodonts, which at that time was in the Jurassic period. Subsequent authors have challenged this interpretation, particularly as the teeth do not resemble any known non-mammalian cynodonts. Chronoperates is now generally considered to be more likely to be a late-surviving symmetrodont mammal. This would still infer a ghost lineage for symmetrodonts, but a more plausible one, as symmetrodonts persisted into the Late Cretaceous.

Cladotheria is a clade of mammals. It contains modern therian mammals and several extinct groups, such as the "dryolestoids", amphitheriids and peramurids. The clade was named in 1975 by Malcolm McKenna. In 2002, it was defined as a node-based taxon containing "the common ancestor of dryolestids and living therians, plus all its descendants". A different, stem-based definition was given in 2013, in which Cladotheria contains all taxa that are closer to Mus musculus than to the "symmetrodont" Spalacotherium tricuspidens.

Kuehneotherium is an early mammaliaform genus, previously considered a holothere, that lived during the Late Triassic-Early Jurassic Epochs and is characterized by reversed-triangle pattern of molar cusps. Although many fossils have been found, the fossils are limited to teeth, dental fragments, and mandible fragments. The genus includes Kuehneotherium praecursoris and all related species. It was first named and described by Doris M. Kermack, K. A. Kermack, and Frances Mussett in November 1967. The family Kuehneotheriidae and the genus Kuehneotherium were created to house the single species Kuehneotherium praecursoris. Modeling based upon a comparison of the Kuehneotherium jaw with other mammaliaforms indicates it was about the size of a modern-day shrew between 4 and 5.5 g at adulthood.

Ambondro mahabo is a mammal from the Middle Jurassic (Bathonian) Isalo III Formation of Madagascar. The only described species of the genus Ambondro, it is known from a fragmentary lower jaw with three teeth, interpreted as the last premolar and the first two molars. The premolar consists of a central cusp with one or two smaller cusps and a cingulum (shelf) on the inner, or lingual, side of the tooth. The molars also have such a lingual cingulum. They consist of two groups of cusps: a trigonid of three cusps at the front and a talonid with a main cusp, a smaller cusp, and a crest at the back. Features of the talonid suggest that Ambondro had tribosphenic molars, the basic arrangement of molar features also present in marsupial and placental mammals. It is the oldest known mammal with putatively tribosphenic teeth; at the time of its discovery it antedated the second oldest example by about 25 million years.

Meridiolestida is an extinct clade of mammals known from the Cretaceous and Cenozoic of South America and possibly Antarctica. They represented the dominant group of mammals in South America during the Late Cretaceous. Meridiolestidans were morphologically diverse, containing both small insectivores such as the "sabretooth-squirrel" Cronopio, as well as the clade Mesungulatoidea/Mesungulatomorpha, which ranged in size from the shrew-sized Reigitherium to the dog-sized Peligrotherium. Mesungulatoideans had highly modified dentition with bunodont teeth, and were likely herbivores/omnivores. Meridiolestidans are generally classified within Cladotheria, more closely related to living marsupials and placental mammals (Theria) than to monotremes, barring one study recovering them as the sister taxa to spalacotheriid "symmetrodonts". However, more recent studies have stuck to the cladotherian interpretation. Within Cladotheria, they have often been placed in a group called Dryolestoidea together with Dryolestida, a group of mammals primarily known from the Jurassic and Early Cretaceous of the Northern Hemisphere. However, some analyses have found this group to be paraphyletic, with the meridiolestidans being more or less closely related to therian mammals than dryolestidans are. Meridiolestidans differ from dryolestidans in the absence of a parastylar hook on the molariform teeth and the lack of a Meckelian groove.
Wareolestes rex is a mammaliaform from the Middle Jurassic (Bathonian) rocks of England and Scotland. It was originally known from isolated teeth from England, before a more complete jaw with teeth was found in the Kilmaluag Formation of Skye, Scotland.
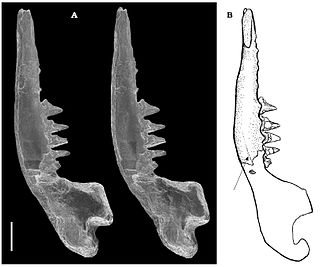
Symmetrolestes is an extinct genus of small spalacotheriid mammal from the Early Cretaceous period of Japan. The genus contains one species known as S. parvus, the type fossil is from fluvial deposits located in the Dinosaur Quarry in the Kitadani Formation, near the city of Katsuyama which lies alongside valley of the Sugiyamagawa River. It was described by Tsubamoto and Rougier in 2004 keeping the holotype at the National Science Museum, Tokyo, Japan.





















