
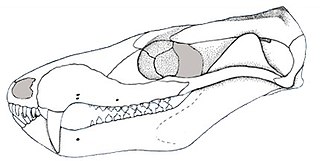
Ecteninion is an extinct genus of meat-eating cynodonts that lived during the Late Triassic (Carnian) in South America. The type species Ecteninion lunensis was named by R.N. Martinez, C.L. May, and C.A. Forster in 1996. E. lunensis is known from a nearly complete skull of about 11 centimetres (4.3 in) in length. It was found in the Cancha de Bochas Member of the Ischigualasto Formation in the Ischigualasto-Villa Unión Basin in northwestern Argentina. It has been interpreted as a basal eucynodont. The holotype is in the collection of the Universidad Nacional de San Juan.

Chiniquodon is an extinct genus of carnivorous cynodonts, which lived during the Late Triassic (Carnian) in South America and Africa. Chiniquodon was closely related to the genus Aleodon, and close to the ancestry of mammals.

Ankistrodon is an extinct genus of archosauriform known from the Early Triassic Panchet Formation of India. First thought to be a theropod dinosaur, it was later determined to be a proterosuchid. The type species is A. indicus, described by prolific British zoologist Thomas Henry Huxley in 1865. One authority in the 1970s classified Ankistrodon as a senior synonym of Proterosuchus. Ezcurra (2023) found Ankistrodon to be a nomen dubium, as the teeth are indistinguishable from those of Proterosuchus. A second Indian proterosuchid from the same formation, Samsarasuchus, was also described in the same study, making it the only known valid proterosuchid from India.

Exaeretodon is an extinct genus of fairly large, low-slung traversodontid cynodonts from the southern parts of Pangea. Four species are known, from various formations. E. argentinus is from the Carnian-age Cancha de Bochas Member of the Ischigualasto Formation in the Ischigualasto-Villa Unión Basin in northwestern Argentina. E. major and E. riograndensis are from the Carnian-age portion of the Santa Maria Formation of the Paraná Basin in southeastern Brazil. E. statisticae is from the Carnian-age Lower Maleri Formation of India.
Brasilodon is an extinct genus of small, mammal-like cynodonts that lived in what is now Brazil during the Norian age of the Late Triassic epoch, about 225.42 million years ago. While no complete skeletons have been found, the length of Brasilodon has been estimated at 12 centimetres (4.7 in). Its dentition shows that it was most likely an insectivore. The genus is monotypic, containing only the species B. quadrangularis. Brasilodon belongs to the family Brasilodontidae, whose members were some of the closest relatives of mammals, the only cynodonts alive today. Two other brasilodontid genera, Brasilitherium and Minicynodon, are now considered to be junior synonyms of Brasilodon.
Indolyrocephalus is an extinct genus of prehistoric amphibian belonging to the family Trematosauridae. It contains a single species, I. huxleyi, from the Early Triassic Panchet Formation of India. It was initially classified in Gonioglyptus, then into its own genus Indolyrocephalus, and then back into Gonioglyptus, but is presently placed in Indolyrocephalus once again.
Gonioglyptus is an extinct genus of trematosaurian temnospondyl within the family Trematosauridae. It is known from the Early Triassic Panchet Formation of India. It contains two species: G. longirostris and G. fragilis. The species G. kokeni from Pakistan has since been reclassified into Aphaneramma.
The Tiki Formation is a Late Triassic geologic formation in Madhya Pradesh, northern India. Dinosaur remains are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation, although none have yet been referred to a specific genus. Phytosaur remains attributable to the genus Volcanosuchus have also been found in the Tiki Formation.
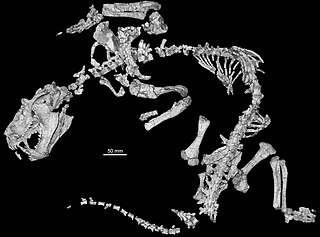
Trucidocynodon is an extinct genus of ecteniniid cynodonts from the Upper Triassic (Carnian) of Brazil. It contains a single species, Trucidocynodon riograndensis. Fossils of Trucidocynodon were discovered in outcrops of the Upper Santa Maria Formation in Paleorrota Geopark, Agudo. Trucidocynodon is one of the most completely known Triassic cynodonts, as its holotype is a nearly complete and fully articulated skeleton.
Deccanodon is an extinct genus of dromatheriid cynodonts which existed in India during the Late Triassic. The type species is D. maleriensis, named in 2007. Deccanodon was one of the first Triassic cynodonts named from India and was found in the Maleri Formation in Adilabad district.

Langbergia is an extinct genus of trirachodontid cynodont from the Early Triassic of South Africa. The type and only species L. modisei was named in 2006 after the farm where the holotype was found, Langberg 566. Langbergia was found in the Burgersdorp Formation in the Beaufort Group, a part of the Cynognathus Assemblage Zone. The closely related trirachodontids Trirachodon and Cricodon were found in the same area.
Rewaconodon is an extinct genus of dromatheriid cynodonts which existed in India during the upper Triassic period. It is known from two species: R. tikiensis and R. indicus, both of which were found in the Tiki Formation. Other, undescribed species may have lived in North America.

Madysaurus is an extinct genus of cynodonts which existed in Kyrgyzstan. It was first named by Leonid Petrovich Tatarinov in 2005. Madysaurus is known from the Madygen Formation, a Triassic Lagerstätte that also includes well-preserved remains of insects and small reptiles like Sharovipteryx and Longisquama. Madysaurus is one of the most primitive cynodonts and is placed in its own family, Madysauridae.
Scalenodon is an extinct genus of traversodontid cynodonts from the Middle Triassic of Africa and possibly Russia. The type species S. angustifrons was named in 1946 and several other species were named in the following years. Most of the species from Africa are now thought to belong to different genera than Scalenodon.
Ecteniniidae is an extinct family of probainognathian cynodonts from the Triassic of South America. They are notable for their large size, as well as for being among the first synapsids with specializations towards cursoriality.
Ruberodon is an extinct genus of traversodontid cynodonts known from the type and only species Ruberodon roychowdhurii from the Late Triassic of India. Ruberodon was named in 2015 on the basis of several isolated lower jaws found in the Tiki Formation. The lower jaw of Ruberodon has three pairs of incisors, one pair of canines, and 9 pairs of postcanine teeth. The first pair of incisors is enlarged and protrudes forward from the tip of the jaw and there is a gap called a diastema between the canines and postcanines. Phylogenetic analysis indicates that among traversodontids, R. roychowdhurii is most closely related to Exaeretodon statisticae, which is also from India.

Manubrantlia was a genus of lapillopsid temnospondyls from the Early Triassic Panchet Formation of India. This genus is only known from a single holotype left jaw, given the designation ISI A 57. Despite the paucity of remains, the jaw is still identifiable as belonging to a relative of Lapillopsis. For example, all three of its coronoid bones possessed teeth, the articular bone is partially visible in lateral (outer) view, and its postsplenial does not contact the posterior meckelian foramen. However, the jaw also possesses certain unique features which justify the erection of a new genus separate from Lapillopsis. For example, the mandible is twice the size of any jaws referred to other lapillopsids. The most notable unique feature is an enlarged "pump-handle" shaped arcadian process at the back of the jaw. This structure is responsible for the generic name of this genus, as "Manubrantlia" translates from Latin to the English expression "pump-handle". The type and only known species of this genus is Manubrantlia khaki. The specific name refers to the greenish-brown mudstones of the Panchet Formation, with a color that had been described as "khaki" by the first British geologists who studied the formation.
Capulomala is an extinct genus of stereospondyl temnospondyl known from the Early Triassic. Separate species are recognised, C. panchetensis found in the Panchet Formation of India and C. arcadiaensis from the Arcadia Formation of Australia.
Inditherium is an extinct genus of dromatheriid cynodonts that lived in what is now India during the Late Triassic. Its type and only species is Inditherium floris, which is known from three postcanine teeth discovered at the Tiki Formation of Madhya Pradesh.
Tikiodon is an extinct genus of mammaliamorphs that lived in what is now India during the Late Triassic. Its type and only species is Tikiodon cromptoni, which is known from a single lower postcanine tooth discovered at the Tiki Formation of Madhya Pradesh.















