
Cynodontia is a clade of eutheriodont therapsids that first appeared in the Late Permian, and extensively diversified after the Permian–Triassic extinction event. Mammals are cynodonts, as are their extinct ancestors and close relatives (Mammaliaformes), having evolved from advanced probainognathian cynodonts during the Late Triassic.

The Cynognathus Assemblage Zone is a tetrapod biozone utilized in the Karoo Basin of South Africa. It is equivalent to the Burgersdorp Formation, the youngest lithostratigraphic formation in the Beaufort Group, which is part of the fossiliferous and geologically important Karoo Supergroup. The Cynognathus Assemblage Zone is the youngest of the eight biozones found in the Beaufort Group, and is considered to be late Early Triassic (Olenekian) to early Middle Triassic (Anisian) in age. The name of the biozone refers to Cynognathus crateronotus, a large and carnivorous cynodont therapsid which occurs throughout the entire biozone.
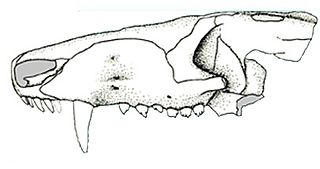
Prozostrodon is an extinct genus of probainognathian cynodonts that was closely related to mammals. The remains were found in Brazil and are dated to the Carnian age of the Late Triassic. The holotype has an estimated skull length of 6.7 centimetres (2.6 in), indicating that the whole animal may have been the size of a cat. The teeth were typical of advanced cynodonts, and the animal was probably a carnivore hunting reptiles and other small prey.

The Santa Maria Formation is a sedimentary rock formation found in Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil. It is primarily Carnian in age, and is notable for its fossils of cynodonts, "rauisuchian" pseudosuchians, and early dinosaurs and other dinosauromorphs, including the herrerasaurid Staurikosaurus, the basal sauropodomorphs Buriolestes and Saturnalia, and the lagerpetid Ixalerpeton. The formation is named after the city of Santa Maria in the central region of Rio Grande do Sul, where outcrops were first studied.
Redondasaurus is an extinct genus or subgenus of phytosaur from the Late Triassic of the southwestern United States. It was named by Hunt & Lucas in 1993, and contains two species, R. gregorii and R. bermani. It is the youngest and most evolutionarily-advanced of the phytosaurs.

Clevosaurus is an extinct genus of rhynchocephalian reptile from the Late Triassic and the Early Jurassic periods. Species of Clevosaurus were widespread across Pangaea, and have been found on all continents except Australia and Antarctica. Five species of Clevosaurus have been found in ancient fissure fill deposits in south-west England and Wales, alongside other sphenodontians, early mammals and dinosaurs. In regards to its Pangaean distribution, C. hadroprodon is the oldest record of a sphenodontian from Gondwana, though its affinity to Clevosaurus has been questioned.
The Tiki Formation is a Late Triassic geologic formation in Madhya Pradesh, northern India. Dinosaur remains are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation, although none have yet been referred to a specific genus. Phytosaur remains attributable to the genus Volcanosuchus have also been found in the Tiki Formation.
The Chinle Formation is an extensive geological unit in the southwestern United States, preserving a very diverse fauna of Late Triassic animals and plants. This is a list of fossilized organisms recovered from the formation.
Deccanodon is an extinct genus of dromatheriid cynodonts which existed in India during the Late Triassic. The type species is D. maleriensis, named in 2007. Deccanodon was one of the first Triassic cynodonts named from India and was found in the Maleri Formation in Adilabad district.

Protheriodon is an extinct genus of probainognathian cynodonts which existed in the Santa Maria Formation of the Paraná Basin in southeastern Brazil during the middle Triassic period. It contains the species Protheriodon estudianti. It was first described by Argentine palaeontologist José Bonaparte, who assigned it to the family Brasilodontidae. More recent studies have however recovered it in a more basal position than other brasilodontids, just outside Prozostrodontia.

The Manda Formation is a Middle Triassic (Anisian?) or possibly Late Triassic (Carnian?) geologic formation in Tanzania. It preserves fossils of many terrestrial vertebrates from the Triassic, including some of the earliest dinosauromorph archosaurs. The formation is often considered to be Anisian in age according to general tetrapod biochronology hypotheses and correlations to the Cynognathus Assemblage Zone of South Africa. However, some recent studies cast doubt to this age, suggesting that parts deposits may actually be younger (Carnian) in age.
The Bull Canyon Formation is a geological formation of Late Triassic (Norian) age in eastern New Mexico and the Texas Panhandle. It is one of several formations encompassed by the Dockum Group.
The Colorado City Formation is a Late Triassic geologic formation in the Dockum Group of Texas, United States. It has previously been known as the Iatan Member, Colorado City Member or 'Pre-Tecovas Horizon'.

Alemoatherium is an extinct genus of prozostrodontian cynodont which lived in the Late Triassic of Brazil. It contains a single species, A. huebneri, named in 2017 by Agustín Martinelli and colleagues. The genus is based on UFSM 11579b, a left lower jaw (dentary) found in the Alemoa Member of the Santa Maria Formation, preserving the late Carnian-age Hyperodapedon Assemblage Zone. Alemoatherium was among the smallest species of cynodonts found in the rich synapsid fauna of the Santa Maria Formation. Its blade-like four-cusped postcanine teeth show many similarities with those of dromatheriids, an obscure group of early prozostrodontians.
Oryctorhynchus is an extinct genus of rhynchosaur from the Late Triassic (Carnian-Norian)-aged Wolfville Formation of Nova Scotia, Canada that may have been the same animal as Beesiiwo. The type species, O. bairdi, was named and described in 2020. It was originally seen as a species of Hyperodapedon until 2020.
Dromatheriidae is an extinct family of prozostrodontian cynodonts, closely related to mammals. Members of the family are known from the Late Triassic of India, Europe and North America. Apart from a few jaw fragments, dromatheriids are mainly known from their sectorial (flesh-slicing) postcanine teeth. The teeth were fairly typical among early prozostrodontians, as they were labiolingually compressed, with a single root and crown hosting a longitudinal row of sharp cusps. Dromatheriids in particular have a very narrow and symmetrical crown without a prominent cingulum.
Inditherium is an extinct genus of dromatheriid cynodonts that lived in what is now India during the Late Triassic. Its type and only species is Inditherium floris, which is known from three postcanine teeth discovered at the Tiki Formation of Madhya Pradesh.
Tikiodon is an extinct genus of mammaliamorphs that lived in what is now India during the Late Triassic. Its type and only species is Tikiodon cromptoni, which is known from a single lower postcanine tooth discovered at the Tiki Formation of Madhya Pradesh.
Land vertebrate faunachrons (LVFs) are biochronological units used to correlate and date terrestrial sediments and fossils based on their tetrapod faunas. First formulated on a global scale by Spencer G. Lucas in 1998, LVFs are primarily used within the Triassic Period, though Lucas later designated LVFs for other periods as well. Eight worldwide LVFs are defined for the Triassic. The first two earliest Triassic LVFs, the Lootsbergian and Nonesian, are based on South African synapsids and faunal assemblage zones estimated to correspond to the Early Triassic. These are followed by the Perovkan and Berdyankian, based on temnospondyl amphibians and Russian assemblages estimated to be from the Middle Triassic. The youngest four Triassic LVFs, the Otischalkian, Adamanian, Revueltian, and Apachean, are based on aetosaur and phytosaur reptiles common in the Late Triassic of the southwestern United States.













