
Probainognathus meaning “progressive jaw” is an extinct genus of cynodonts that lived around 235 to 221.5 million years ago, during the Late Triassic in what is now Argentina. Together with the genus Bonacynodon from Brazil, Probainognathus forms the family Probainognathidae. Probainognathus was a relatively small, carnivorous or insectivorous cynodont. Like all cynodonts, it was a relative of mammals, and it possessed several mammal-like features. Like some other cynodonts, Probainognathus had a double jaw joint, which not only included the quadrate and articular bones like in more basal synapsids, but also the squamosal and surangular bones. A joint between the dentary and squamosal bones, as seen in modern mammals, was however absent in Probainognathus.
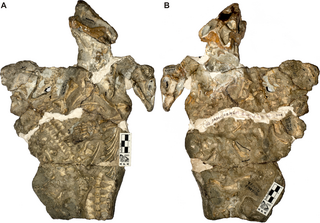
Galesaurus is an extinct genus of carnivorous cynodont therapsid that lived between the Induan and the Olenekian stages of the Early Triassic in what is now South Africa. It was incorrectly classified as a dinosaur by Sir Richard Owen in 1859.

Ericiolacerta is an extinct genus of small therocephalian therapsids from the early Triassic of South Africa and Antarctica. Ericiolacerta, meaning "hedgehog lizard", was named by D.M.S. Watson in 1931. The species E. parva is known from the holotype specimen which consists of a nearly complete skeleton found in the Lystrosaurus Assemblage Zone within the Katberg Formation of the Beaufort Group in South Africa, and from a partial jaw found in the Lower Triassic Fremouw Formation in Antarctica. Ericiolacerta was around 20 centimetres (7.9 in) in length, with long limbs and relatively small teeth. It probably ate insects and other small invertebrates. The therocephalians – therapsids with mammal-like heads – were abundant in Permian times, but only a few made it into the Triassic. Ericiolacerta was one of those. It is possible that they gave rise to the cynodonts, the only therapsid group to survive into post-Triassic times. Cynodonts gave rise to mammals.
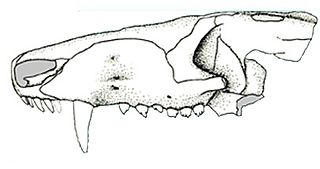
Prozostrodon is an extinct genus of probainognathian cynodonts that was closely related to mammals. The remains were found in Brazil and are dated to the Carnian age of the Late Triassic. The holotype has an estimated skull length of 6.7 centimetres (2.6 in), indicating that the whole animal may have been the size of a cat. The teeth were typical of advanced cynodonts, and the animal was probably a carnivore hunting reptiles and other small prey.

Moschorhinus is an extinct genus of therocephalian synapsid in the family Akidnognathidae with only one species: M. kitchingi, which has been found in the Late Permian to Early Triassic of the South African Karoo Supergroup. It was a large carnivorous therapsid, reaching 1.1–1.5 metres (3.6–4.9 ft) in total body length with the largest skull comparable to that of a lion in size, and had a broad, blunt snout which bore long, straight canines.

Viatkogorgon is a genus of gorgonopsian that lived during the Permian period in what is now Russia. The first fossil was found at the Kotelnich locality near the Vyatka River and was made the holotype of the new genus and species V. ivachnenkoi in 1999. The generic name refers to the river and the related genus Gorgonops—the gorgons of Greek mythology are often referenced in the names of the group. The specific name honors the paleontologist Mikhail F. Ivakhnenko. The holotype skeleton is one of the most complete gorgonopsian specimens known and includes rarely preserved elements such as gastralia and a sclerotic ring. A larger, but poorly preserved specimen has also been assigned to the species.

Theriognathus is an extinct genus of therocephalian therapsid belonging to the family Whaitsiidae, known from fossils from South Africa, Zambia, and Tanzania. Theriognathus has been dated as existing during the Late Permian. Although Theriognathus means mammal jaw, the lower jaw is actually made up of several bones as seen in modern reptiles, in contrast to mammals. Theriognathus displayed many different reptilian and mammalian characteristics. For example, Theriognathus had canine teeth like mammals, and a secondary palate, multiple bones in the mandible, and a typical reptilian jaw joint, all characteristics of reptiles. It is speculated that Theriognathus was either carnivorous or omnivorous based on its teeth, and was suited to hunting small prey in undergrowth. This synapsid adopted a sleek profile of a mammalian predator, with a narrow snout and around 1 meter long. Theriognathus is represented by 56 specimens in the fossil record.

Labidosaurikos is a genus of extinct captorhinid tetrapods that lived around 279 to 272 million years ago during Kungurian age of the lower Permian. The American paleontologist John Willis Stovall first described Labidosaurikos in 1950, naming it "Labidosaurus like" for the striking similarity of the holotype skull of his specimen to the cranial anatomy of another captorhinid Labidosaurus hamatus.
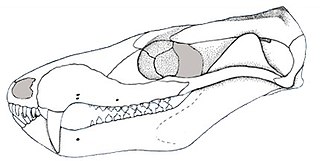
Brasilodon is an extinct genus of small, mammal-like cynodonts that lived in what is now Brazil during the Norian age of the Late Triassic epoch, about 225.42 million years ago. While no complete skeletons have been found, the length of Brasilodon has been estimated at 12 centimetres (4.7 in). Its dentition shows that it was most likely an insectivore. The genus is monotypic, containing only the species B. quadrangularis. Brasilodon belongs to the family Brasilodontidae, whose members were some of the closest relatives of mammals, the only cynodonts alive today. Two other brasilodontid genera, Brasilitherium and Minicynodon, are now considered to be junior synonyms of Brasilodon.

Aerosaurus is an extinct genus within Varanopidae, a family of non-mammalian synapsids. It lived between 252-299 million years ago during the Early Permian in North America. The name comes from Latin aes (aeris) “copper” and Greek sauros “lizard,” for El Cobre Canyon in northern New Mexico, where the type fossil was found and the site of former copper mines. Aerosaurus was a small to medium-bodied carnivorous synapsid characterized by its recurved teeth, triangular lateral temporal fenestra, and extended teeth row. Two species are recognized: A. greenleeorum (1937) and A. wellesi (1981).

Biseridens is an extinct genus of anomodont therapsid, and one of the most basal anomodont genera known. Originally known from a partial skull misidentified as an eotitanosuchian in 1997, another well-preserved skull was found in the Qingtoushan Formation in the Qilian Mountains of Gansu, China, in 2009 that clarified its relationships to anomodonts, such as the dicynodonts.
Cynosaurus is an extinct genus of cynodonts. Remains have been found from the Dicynodon Assemblage Zone in South Africa. Cynosaurus was first described by Richard Owen in 1876 as Cynosuchus suppostus. Cynosaurus has been found in the late Permian period. Cyno- is derived from the Greek word kyon for dog and –sauros in Greek meaning lizard.
Platycraniellus is an extinct genus of carnivorous cynodonts from the Early Triassic. It is known from the Lystrosaurus Assemblage Zone of the Normandien Formation in South Africa. P. elegans is the only species in this genus based on the holotype specimen from the Ditsong National Museum of Natural History in Pretoria, South Africa. Due to limited fossil records for study, Platycraniellus has only been briefly described a handful of times.
"Dixeya" nasuta is a extinct species of gorgonopsian that lived during the Late Permian of East Africa, known from fossils found in what is now Tanzania. The species has a complicated taxonomic history, it was originally named as a second species of the genus Dixeya which is now considered a junior synonym of Aelurognathus. "D." nasuta itself, however, was not moved to Aelurognathus, and although it was instead tentatively referred to Arctognathus at first it has since been recognised to not belong to this genus either. This situation leaves "Dixeya" nasuta without a formal genus name. It was proposed to belong to a new distinct genus, named "Njalila", that was informally proposed for the species in a PhD thesis, but this name has not yet been formally published and is currently a nomen nudum. "D." nasuta has been characterised from other gorgonopsians by a combination of its straight snout profile, upturned and "pinched" nose, and curved jaw margin. The fossil record of the Usili Formation shows that the taxon was contemporary with many other gorgonopsians, even alongside large representatives such as Inostrancevia and rubidgeines.

Bulbasaurus is an extinct genus of dicynodont that is known from the Lopingian epoch of the Late Permian period of what is now South Africa, containing the type and only species B. phylloxyron. It was formerly considered as belonging to Tropidostoma; however, due to numerous differences from Tropidostoma in terms of skull morphology and size, it has been reclassified the earliest known member of the family Geikiidae, and the only member of the group known from the Tropidostoma Assemblage Zone. Within the Geikiidae, it has been placed close to Aulacephalodon, although a more basal position is not implausible.

Abdalodon is an extinct genus of late Permian cynodonts, known by its only species A. diastematicus.Abdalodon together with the genus Charassognathus, form the clade Charassognathidae. This clade represents the earliest known cynodonts, and is the first known radiation of Permian cynodonts.
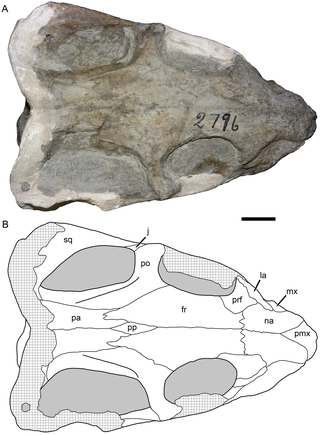
Thliptosaurus is an extinct genus of small kingoriid dicynodont from the latest Permian period of the Karoo Basin in KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. It contains the type and only known species T. imperforatus. Thliptosaurus is from the upper Daptocephalus Assemblage Zone, making it one of the youngest Permian dicynodonts known, living just prior to the Permian mass extinction. It also represents one of the few small bodied dicynodonts to exist at this time, when most other dicynodonts had large body sizes and many small dicynodonts had gone extinct. The unexpected discovery of Thliptosaurus in a region of the Karoo outside of the historically sampled localities suggests that it may have been part of an endemic local fauna not found in these historic sites. Such under-sampled localities may contain 'hidden diversities' of Permian faunas that are unknown from traditional samples. Thliptosaurus is also unusual for dicynodonts as it lacks a pineal foramen, suggesting that it played a much less important role in thermoregulation than it did for other dicynodonts.
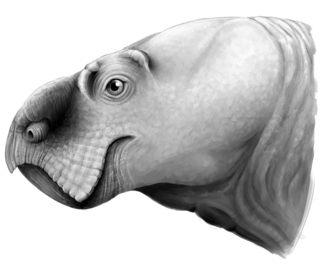
Ufudocyclops is an extinct genus of stahleckeriid dicynodont from the Middle Triassic of South Africa. It was found in the Burgersdorp Formation, part of the uppermost Cynognathus Assemblage Zone of the Beaufort Group in the Karoo Basin. The type and only known species is U. mukanelai. It was a large, beaked herbivore like other Triassic dicynodonts, lacking tusks, and is mostly characterised by unique features of the skull. It is known from three specimens, two of which were previously referred to the Tanzanian dicynodont Angonisaurus. The separation of Ufudocyclops from Angonisaurus indicates that the Middle Triassic fauna of the Beaufort Group in South Africa was not part of a larger shared fauna with those of the Manda Beds in Tanzania, as was previously supposed, and suggests that they were separated as more localised faunas, possibly by geographic barriers or in time. Ufudocyclops then would have been a unique part of the uppermost Cynognathus Assemblage Zone in South Africa. It is also the oldest known member of the family Stahleckeriidae, and implies that the family was already diversifying in the Middle Triassic alongside other kannemeyeriiforms, not just in the Late Triassic after other families died out.
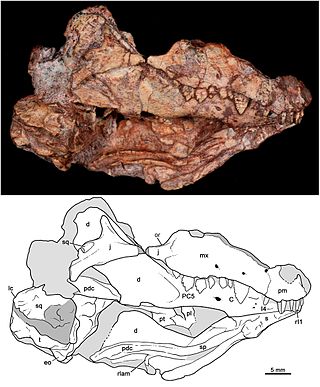
Bonacynodon is an extinct genus of cynodonts that lived in what is now southern Brazil during the Triassic period. The genus is monotypic, containing only the type species Bonacynodon schultzi. B. schultzi is known from two specimens, consisting of two partial skulls and some badly preserved parts of the postcranium. Both specimens were recovered from the Pinheiros-Chiniquá Sequence, part of the Santa Maria Supersequence of the Paraná Basin. This sequence preserves a faunal association known as the Dinodontosaurus Assemblage Zone, which contains numerous other species of cynodonts, dicynodonts and reptiles. Bonacynodon was a small, likely insectivorous cynodont, whose length has been estimated at around 30 centimetres (12 in). It can be distinguished from other cynodonts by its large, serrated (saw-like) canine teeth. Together with the genus Probainognathus of Argentina, it made up the family Probainognathidae, one of the earliest-diverging lineages of the clade Probainognathia. It was a fairly close relative of mammals, the only group of cynodonts alive today.
Vetusodon is an extinct genus of cynodonts belonging to the clade Epicynodontia. It contains one species, Vetusodon elikhulu, which is known from four specimens found in the Late Permian Daptocephalus Assemblage Zone of South Africa. With a skull length of about 18 centimetres (7.1 in), Vetusodon is the largest known cynodont from the Permian. Through convergent evolution, it possessed several unusual features reminiscent of the contemporary therocephalian Moschorhinus, including broad, robust jaws, large incisors and canines, and small, single-cusped postcanine teeth.






















