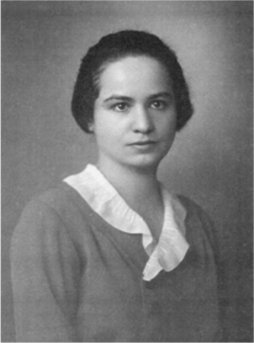Erwin Rudolf Josef Alexander Schrödinger, sometimes written as Schroedinger or Schrodinger, was a Nobel Prize–winning Austrian and naturalized Irish physicist who developed fundamental results in quantum theory. In particular, he is recognized for postulating the Schrödinger equation, an equation that provides a way to calculate the wave function of a system and how it changes dynamically in time. Schrödinger coined the term "quantum entanglement", and was the earliest to discuss it, doing so in 1932. He also anticipated the many-worlds interpretation of quantum mechanics.

Wolfgang Ernst Pauli was an Austrian theoretical physicist and a pioneer of quantum physics. In 1945, after having been nominated by Albert Einstein, Pauli received the Nobel Prize in Physics for his "decisive contribution through his discovery of a new law of Nature, the exclusion principle or Pauli principle". The discovery involved spin theory, which is the basis of a theory of the structure of matter.

Max Ludwig Henning Delbrück was a German–American biophysicist who participated in launching the molecular biology research program in the late 1930s. He stimulated physical scientists' interest into biology, especially as to basic research to physically explain genes, mysterious at the time. Formed in 1945 and led by Delbrück along with Salvador Luria and Alfred Hershey, the Phage Group made substantial headway unraveling important aspects of genetics. The three shared the 1969 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine "for their discoveries concerning the replication mechanism and the genetic structure of viruses". He was the first physicist to predict what is now called Delbrück scattering.

Gerty Theresa Cori was a Bohemian-Austrian and American biochemist who in 1947 was the third woman to win a Nobel Prize in science, and the first woman to be awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine, for her role in the "discovery of the course of the catalytic conversion of glycogen".

The University of Graz is a public research university located in Graz, Austria. It is the largest and oldest university in Styria, as well as the second-largest and second-oldest university in Austria. The university is associated with numerous Nobel prize laureates and is highly regarded.
The year 1930 in science and technology involved some significant events, listed below.
The year 1929 in science and technology involved some significant events, listed below.
Walter Eduard Thirring was an Austrian physicist after whom the Thirring model in quantum field theory is named. He was the son of the physicist Hans Thirring.

Franz Serafin Exner Jnr was an Austrian physicist and professor at the University of Vienna. He is known for pioneering physical chemistry education in Austria. The early introduction to university curricula of subjects such as radioactivity, spectroscopy, electrochemistry electricity in the atmosphere, and color theory in Austria are often credited to him.
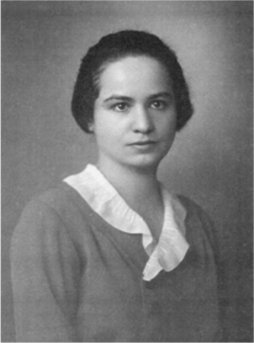
Marietta Blau was an Austrian physicist credited with developing photographic nuclear emulsions that were usefully able to image and accurately measure high-energy nuclear particles and events, significantly advancing the field of particle physics in her time. For this, she was awarded the Lieben Prize by the Austrian Academy of Sciences. As a Jew, she was forced to flee Austria when Nazi Germany annexed it in 1938, eventually making her way to the United States. She was nominated for Nobel Prizes in both physics and chemistry for her work, but did not win. After her return to Austria, she won the Erwin Schrödinger Prize from the Austrian Academy of Sciences.

The Austrian Academy of Sciences is a legal entity under the special protection of the Republic of Austria. According to the statutes of the Academy its mission is to promote the sciences and humanities in every respect and in every field, particularly in fundamental research.

Karl Landsteiner was an Austrian-American biologist, physician, and immunologist. He emigrated with his family to New York in 1923 at the age of 55 for professional opportunities, working for the Rockefeller Institute.
Gesellschaft der Ärzte in Wien is a medical society with a long-standing tradition in Austria. Its principal task is the continuing education of medical practitioners. The society's headquarter is the Billrothhaus in the 9th district of Vienna.
The Haitinger Prize of the Austrian Academy of Sciences was founded in 1904 by the chemist and factory director, Ludwig Camillo Haitinger (1860–1945), who created the award in honor of his father, Karl Ludwig Haitinger. From 1905 to 1943 it was awarded every year, for "studies in chemistry and physics that proved to be of great practical use for industrial applications". The prize was awarded for the last time in the year 1954.