
Salicylic acid is an organic compound with the formula HOC6H4COOH. A colorless (or, white), bitter-tasting solid, it is a precursor to and a metabolite of acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin). It is a plant hormone, and has been listed by the EPA Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) Chemical Substance Inventory as an experimental teratogen. The name is from Latin salix for willow tree, from which it was initially identified and derived. It is an ingredient in some anti-acne products. Salts and esters of salicylic acid are known as salicylates.

Acetophenone is the organic compound with the formula C6H5C(O)CH3. It is the simplest aromatic ketone. This colorless, viscous liquid is a precursor to useful resins and fragrances.

Poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) is the synthetic polymer derived from methyl methacrylate. It is used as an engineering plastic, and it is a transparent thermoplastic. PMMA is also known as acrylic, acrylic glass, as well as by the trade names and brands Crylux, Hesalite, Plexiglas, Acrylite, Lucite, and Perspex, among several others. This plastic is often used in sheet form as a lightweight or shatter-resistant alternative to glass. It can also be used as a casting resin, in inks and coatings, and for many other purposes.

Iodoform is the organoiodine compound with the chemical formula CHI3. It is a pale yellow, crystalline, volatile substance, with a penetrating and distinctive odor and, analogous to chloroform, sweetish taste. It is occasionally used as a disinfectant.
The International Nomenclature of Cosmetic Ingredients (INCI) are the unique identifiers for cosmetic ingredients such as waxes, oils, pigments, and other chemicals that are assigned in accordance with rules established by the Personal Care Products Council (PCPC), previously the Cosmetic, Toiletry, and Fragrance Association (CTFA). INCI names often differ greatly from systematic chemical nomenclature or from more common trivial names and is a mixture of conventional scientific names, Latin and English words. INCI nomenclature conventions "are continually reviewed and modified when necessary to reflect changes in the industry, technology, and new ingredient developments".
Polyquaternium is the International Nomenclature for Cosmetic Ingredients designation for several polycationic polymers that are used in the personal care industry. Polyquaternium is a neologism used to emphasize the presence of quaternary ammonium centers in the polymer. INCI has approved at least 40 different polymers under the polyquaternium designation. Different polymers are distinguished by the numerical value that follows the word "polyquaternium". Polyquaternium-5, polyquaternium-7, and polyquaternium-47 are three examples, each a chemically different type of polymer. The numbers are assigned in the order in which they are registered rather than because of their chemical structure.

Hydroquinone, also known as benzene-1,4-diol or quinol, is an aromatic organic compound that is a type of phenol, a derivative of benzene, having the chemical formula C6H4(OH)2. It has two hydroxyl groups bonded to a benzene ring in a para position. It is a white granular solid. Substituted derivatives of this parent compound are also referred to as hydroquinones. The name "hydroquinone" was coined by Friedrich Wöhler in 1843.

Acetone is an organic compound with the formula (CH3)2CO. It is the simplest and smallest ketone. It is a colorless, highly volatile and flammable liquid with a characteristic pungent odor.

Methyl methacrylate (MMA) is an organic compound with the formula CH2=C(CH3)COOCH3. This colorless liquid, the methyl ester of methacrylic acid (MAA), is a monomer produced on a large scale for the production of poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA).

Avobenzone is an organic molecule and an oil-soluble ingredient used in sunscreen products to absorb the full spectrum of UVA rays.
Methacrylic acid, abbreviated MAA, is an organic compound with the formula CH2=C(CH3)CO2H. This colorless, viscous liquid is a carboxylic acid with an acrid unpleasant odor. It is soluble in warm water and miscible with most organic solvents. Methacrylic acid is produced industrially on a large scale as a precursor to its esters, especially methyl methacrylate (MMA), and to poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA).
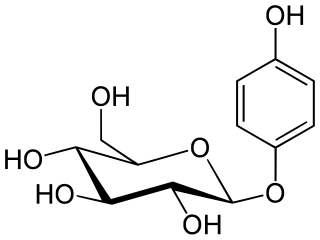
beta-Arbutin, also known as β-arbutin or by its International Nomenclature of Cosmetic Ingredients (INCI) name, arbutin, is a glycosylated derivative of hydroquinone. β-Arbutin is naturally present in the leaves and bark of a variety of plants, notably the bearberry plant, Arctostaphylos uva-ursi. Utilized as a biosynthetic active ingredient in topical treatments for skin lightening, β-arbutin is aimed at addressing hyperpigmentation issues. Its mechanism of action involves inhibiting the activity of tyrosinase, an essential enzyme for melanin synthesis in the human skin, thereby leading to a reduction in hyperpigmentation. It is important to distinguish β-arbutin from its structurally similar stereoisomer, α-arbutin, which exhibits similar effects in clinical applications.
Acetone cyanohydrin (ACH) is an organic compound used in the production of methyl methacrylate, the monomer of the transparent plastic polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), also known as acrylic. It liberates hydrogen cyanide easily, so it is used as a source of such. For this reason, this cyanohydrin is also highly toxic.

Acefylline (INN), also known as 7-theophyllineacetic acid, is a stimulant drug of the xanthine chemical class. It acts as an adenosine receptor antagonist. It is combined with diphenhydramine in the pharmaceutical preparation etanautine to help offset diphenhydramine induced drowsiness.

Glabridin is a chemical compound that is found in the root extract of licorice. Glabridin is an isoflavane, a type of isoflavonoid. This product is part of a larger family of plant-derived molecules, the natural phenols. Glabridin effectively inhibits platelet activation, so it might become therapeutic agent for thromboembolic disorders.
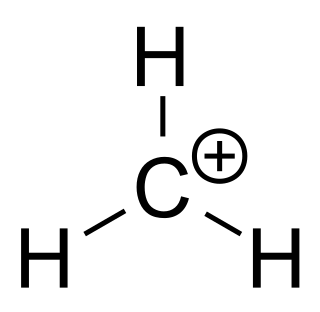
In organic chemistry, methenium is a cation with the formula CH+
3. It can be viewed as a methylene radical with an added proton, or as a methyl radical with one electron removed. It is a carbocation and an enium ion, making it the simplest of the carbenium ions.

Methyl propionate, also known as methyl propanoate, is an organic compound with the molecular formula CH3CH2CO2CH3. It is a colorless liquid with a fruity, rum-like odor.
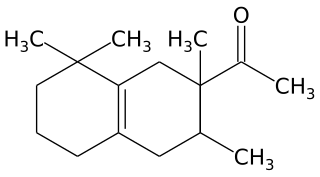
Tetramethyl acetyloctahydronaphthalenes is a synthetic ketone fragrance also known as OTNE and by other commercial trade names such as: Iso E Super, Iso Gamma Super, Anthamber, Amber Fleur, Boisvelone, Iso Ambois, Amberlan, Iso Velvetone, Orbitone, Amberonne. It is a synthetic woody odorant and is used as a fragrance ingredient in perfumes, laundry products and cosmetics.

2-Octanol is an organic compound with the chemical formula CH3CH(OH)(CH2)5CH3. It is a colorless oily liquid that is poorly soluble in water but soluble in most organic solvents. 2-Octanol is classified fatty alcohol. A secondary alcohol, it is chiral.
Poly(ethyl methacrylate) (PEMA) is a hydrophobic synthetic acrylate polymer. It has properties similar to the more common PMMA, however it produces less heat during polymerization, has a lower modulus of elasticity and has an overall softer texture. It may be vulcanized using lead oxide as a catalyst and it can be softened using ethanol.
















