Mont Blanc is the highest mountain in the Alps and Western Europe, and the highest mountain in Europe outside the Caucasus Mountains, rising 4,805.59 m (15,766 ft) above sea level, located on the Franco-Italian border. It is the second-most prominent mountain in Europe, after Mount Elbrus, and the 11th most prominent mountain in the world.

Chamonix-Mont-Blanc, more commonly known simply as Chamonix (Chamôni), is a commune in the Haute-Savoie department in the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes region in Southeastern France. It was the site of the first Winter Olympics, held in 1924.

The Aiguille du Midi is a 3,842-metre-tall (12,605 ft) mountain in the Mont Blanc massif within the French Alps. It is a popular tourist destination and can be directly accessed by cable car from Chamonix that takes visitors close to Mont Blanc.

The Montenvers Railway or Chemin de fer du Montenvers is a rack railway line in the Haute-Savoie department of France. The line runs from a connection with the SNCF, in Chamonix, to the Hotel de Montenvers station, at the Mer de Glace, at an altitude of 1,913 m (6,276 ft).

The Arve is a river in France, and Switzerland. A left tributary of the Rhône, it is 108 km (67 mi) long, of which 9 km in Switzerland. Its catchment area is 1,976 km2 (763 sq mi), of which 80 km2 in Switzerland. Its average discharge in Geneva is 79 m3/s (2,800 cu ft/s).

The Mont Blanc massif is a mountain range in the Alps, located mostly in France and Italy, but also straddling Switzerland at its northeastern end. It contains eleven major independent summits, each over 4,000 metres (13,123 ft) in height. It is named after Mont Blanc, the highest point in western Europe and the European Union. Because of its considerable overall altitude, a large proportion of the massif is covered by glaciers, which include the Mer de Glace and the Miage Glacier – the longest glaciers in France and Italy, respectively.

The Bossons Glacier is one of the larger glaciers of the Mont Blanc massif of the Alps, found in the Chamonix valley of Haute-Savoie département, south-eastern France. It is fed from icefields lying on the northern side of Mont Blanc, and descends down close to the Aiguille du Midi and ends on the southern side of the Arve valley, close to the town of Chamonix. It has the largest altitudinal drop of all the alpine glaciers in Europe, and formerly extended much further down the valley than it does today. It is now approximately 7.5 km long, with a surface area of approximately 10 km2.

Pointe Helbronner is a mountain in the Mont Blanc massif in the Graian Alps on the watershed between France and Italy.

The Cosmiques Hut is a mountain hut in the Mont Blanc massif in the French Alps at an altitude of 3,613 m. It is a large structure capable of accommodating 148 mountaineers. It was constructed in 1990 on a rock promontory situated between the Col du Midi and the base of the Cosmiques Arête which descends southwards from the Aiguille du Midi. It gives access to a number of classic alpine mountaineering routes, and has proved to be extremely popular with mountaineers, so much so that in the summer months prior booking a few days beforehand is essential in order to secure a bed. The Hut is wardened between mid-February and mid-October. In winter the nearby Abri Simond Hut is left unlocked, although this has no cooking facilities, heating or water.

The Torino Hut is a high mountain refuge in the Alps in northwestern Italy. Located near the border with France, it is about 15 km (10 mi) southwest of Mont Dolent, the tripoint with Switzerland. The refuge is in the Mont Blanc massif above the town of Courmayeur in the Aosta Valley, Italy. It can be most easily accessed from the Italian side by the Skyway Monte Bianco cable car from La Palud in Courmayeur, with a change at the Pavilion du Mont Fréty. It can also be reached from Chamonix via the Aiguille du Midi, either by cable car which crosses the massif, or by a long crossing of the Glacier du Gèant. The refuge lies nearly directly above the 11.6 km (7.2 mi) Mont Blanc Tunnel, which passes deep underground, and connects Courmayeur to Chamonix.

The Tête Rousse Glacier is a small but significant glacier located in the Mont Blanc massif within the French Alps whose collapse in 1892 killed 200 people in the town of Saint-Gervais-les-Bains.

Jean-Marc Boivin was a French mountaineer, extreme skier, hang glider and paraglider pilot, speleologist, BASE jumper, film maker and author. The holder of several altitude records for hang gliding and paragliding, the creator of numerous first ascents and first ski descents in the Alps, a member of the team that broke the record for a sub-glacial dive and the first person to paraglide from the summit of Mount Everest, Boivin was a pioneer of extreme sports. He died from injuries incurred after BASE jumping off Angel Falls in Venezuela, the highest waterfall in the world.
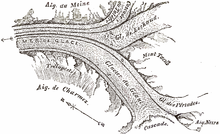
Glacier Montanvert was the common name in the 18th century for a portion of the Alps glacier, now known as Mer de Glace, on the northern slopes of the Mont Blanc massif. Alternative spellings of Montanvert include Montainvert and Montvers. The Glacier Montanvert was a popular tourist destination of European travellers and is referenced in numerous travel writings and novels of the time.

The Tour Ronde is a mountain in the Mont Blanc massif of the Alps, situated on the border between France and Italy. It is a prominent mountain, some 3.5 km north-east of Mont Blanc, but is effectively part of a continuation of the south eastern spur of Mont Maudit which forms a frontier ridge between the two countries. It is easily accessible to mountaineers and provides not only a very good viewpoint from its summit of the Brenva face and the major peaks on the southern side of Mont Blanc, but it also offers a popular introduction to alpine climbing of all grades, including a north face ascent.
Venance Payot was a naturalist, glaciologist, alpine mountain-guide, scholar, author, and two-time mayor of Chamonix, France. He published a wide range of early scientific literature relating to the mountains of the Mont Blanc massif and undertook some of the earliest continued measurements of the movement of glaciers within that mountain range. He has been posthumously credited in mountaineering literature with being the youngest person to have climbed Mont Blanc, and would have been sixteen years old at the time; other sources have challenged this.

The Géant Glacier is a large glacier on the French side of the Mont Blanc massif in the Alps. It is the main supplier of ice to the Mer de Glace which flows down towards Montenvers. It gets its name from the nearby Dent du Géant.

The Aiguille de Toule is a mountain peak in the Mont Blanc massif of the Alps. Its summit is one of a number which form part of the mountainous frontier ridge between France and Italy which descends eastwards from Mont Blanc and continues towards the Grandes Jorasses and Mont Dolent.

The Aiguille de la Brenva is a remote rocky mountain peak in the Mont Blanc massif of the Alps. It lies wholly within Italy on a ridge descending south-east from the Tour Ronde. It has been described as "a spectacular fin with a fine E face". It stands on a ridge separating the Entrèves glacier from the Brenva glacier, yet is somewhat overshadowed by its larger neighbours, such as the Aiguille Blanche and the Aiguille Noire de Peuterey. Nevertheless, it is a distinctive peak, offering a number of very challenging climbs, especially on its east face which consists of vertical granite flakes and cracks. On its northern side stands a distinctive, slender rock pinnacle about 60 metres high, known as the Père Eternel.

The Brenva Glacier is a valley glacier, located on the southern side of the Mont Blanc massif in the Alps. It is the second longest and eighth largest glacier in Italy, and descends down into Val Veny, close to Entrèves, near Courmayeur. Over the centuries it has experienced a number of major rock avalanches which have shaped the glacier and influenced its movement.

The Mer de Glace ice cave is an artificial ice cave in the French department of Haute-Savoie, on the Mont Blanc massif of the French Alps. The cave, which is situated within the Chamonix valley, on the Mer de Glace glacier, has been dug out every year since the middle of the 19th century. This annual renewal is made necessary by the flow of the glacier it sits on. Mer de Glace welcomes approximately 350,000 visitors per year.