An emulsion is a mixture of two or more liquids that are normally immiscible owing to liquid-liquid phase separation. Emulsions are part of a more general class of two-phase systems of matter called colloids. Although the terms colloid and emulsion are sometimes used interchangeably, emulsion should be used when both phases, dispersed and continuous, are liquids. In an emulsion, one liquid is dispersed in the other. Examples of emulsions include vinaigrettes, homogenized milk, liquid biomolecular condensates, and some cutting fluids for metal working.

In pharmacology and toxicology, a route of administration is the way by which a drug, fluid, poison, or other substance is taken into the body.
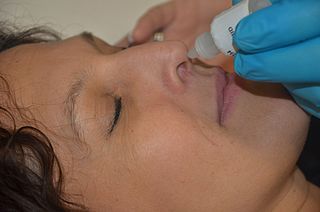
A topical medication is a medication that is applied to a particular place on or in the body. Most often topical medication means application to body surfaces such as the skin or mucous membranes to treat ailments via a large range of classes including creams, foams, gels, lotions, and ointments. Many topical medications are epicutaneous, meaning that they are applied directly to the skin. Topical medications may also be inhalational, such as asthma medications, or applied to the surface of tissues other than the skin, such as eye drops applied to the conjunctiva, or ear drops placed in the ear, or medications applied to the surface of a tooth. The word topical derives from Greek τοπικόςtopikos, "of a place".

A nanoparticle or ultrafine particle is a particle of matter 1 to 100 nanometres (nm) in diameter. The term is sometimes used for larger particles, up to 500 nm, or fibers and tubes that are less than 100 nm in only two directions. At the lowest range, metal particles smaller than 1 nm are usually called atom clusters instead.
Microencapsulation is a process in which tiny particles or droplets are surrounded by a coating to give small capsules, with useful properties. In general, it is used to incorporate food ingredients, enzymes, cells or other materials on a micro metric scale. Microencapsulation can also be used to enclose solids, liquids, or gases inside a micrometric wall made of hard or soft soluble film, in order to reduce dosing frequency and prevent the degradation of pharmaceuticals.

Enteral administration is food or drug administration via the human gastrointestinal tract. This contrasts with parenteral nutrition or drug administration, which occurs from routes outside the GI tract, such as intravenous routes. Enteral administration involves the esophagus, stomach, and small and large intestines. Methods of administration include oral, sublingual, and rectal. Parenteral administration is via a peripheral or central vein. In pharmacology, the route of drug administration is important because it affects drug metabolism, drug clearance, and thus dosage. The term is from Greek enteros 'intestine'.
Absorption is the journey of a drug travelling from the site of administration to the site of action.
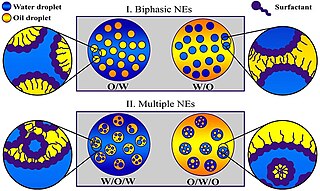
A miniemulsion is a particular type of emulsion. A miniemulsion is obtained by ultrasonicating a mixture comprising two immiscible liquid phases, one or more surfactants and, possibly, one or more co-surfactants. They usually have nanodroplets with uniform size distribution (20–500 nm) and are also known as sub-micron, mini-, and ultra-fine grain emulsions.
Dosage forms are pharmaceutical drug products presented in a specific form for use. They contain a mixture of active ingredients and inactive components (excipients), configured in a particular way and apportioned into a specific dose. For example, two products may both be amoxicillin, but one may come in 500 mg capsules, while another may be in 250 mg chewable tablets.
Pharmaceutical formulation, in pharmaceutics, is the process in which different chemical substances, including the active drug, are combined to produce a final medicinal product. The word formulation is often used in a way that includes dosage form.

Lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) are very small spherical particles composed of lipids. They are a novel pharmaceutical drug delivery system, and a novel pharmaceutical formulation. Using LNPs for drug delivery was first approved in 2018 for the siRNA drug Onpattro. LNPs became more widely known in late 2020, as some COVID-19 vaccines that use RNA vaccine technology coat the fragile mRNA strands with PEGylated lipid nanoparticles as their delivery vehicle.

Nano spray dryers refer to using spray drying to create particles in the nanometer range. Spray drying is a gentle method for producing powders with a defined particle size out of solutions, dispersions, and emulsions which is widely used for pharmaceuticals, food, biotechnology, and other industrial materials synthesis.

Pharmaceutical manufacturing is the process of industrial-scale synthesis of pharmaceutical drugs as part of the pharmaceutical industry. The process of drug manufacturing can be broken down into a series of unit operations, such as milling, granulation, coating, tablet pressing, and others.
A nanocapsule is a nanoscale shell made from a nontoxic polymer. They are vesicular systems made of a polymeric membrane which encapsulates an inner liquid core at the nanoscale. Nanocapsules have many uses, including promising medical applications for drug delivery, food enhancement, nutraceuticals, and for self-healing materials. The benefits of encapsulation methods are for protection of these substances to protect in the adverse environment, for controlled release, and for precision targeting. Nanocapsules can potentially be used as MRI-guided nanorobots or nanobots, although challenges remain.

The characterization of nanoparticles is a branch of nanometrology that deals with the characterization, or measurement, of the physical and chemical properties of nanoparticles.,. Nanoparticles measure less than 100 nanometers in at least one of their external dimensions, and are often engineered for their unique properties. Nanoparticles are unlike conventional chemicals in that their chemical composition and concentration are not sufficient metrics for a complete description, because they vary in other physical properties such as size, shape, surface properties, crystallinity, and dispersion state.
Nanoparticle drug delivery systems are engineered technologies that use nanoparticles for the targeted delivery and controlled release of therapeutic agents. The modern form of a drug delivery system should minimize side-effects and reduce both dosage and dosage frequency. Recently, nanoparticles have aroused attention due to their potential application for effective drug delivery.
Nanomaterials are materials with a size ranging from 1 to 100 nm in at least one dimension. At the nanoscale, material properties become different. These unique properties can be exploited for a variety of applications, including the use of nanoparticles in skincare and cosmetics products.

Topical cream formulation is an emulsion semisolid dosage form that is used for skin external application. Most of the topical cream formulations contain more than 20 per cent of water and volatiles and/or less than 50 per cent of hydrocarbons, waxes, or polyethylene glycols as the vehicle for external skin application. In a topical cream formulation, ingredients are dissolved or dispersed in either a water-in-oil (W/O) emulsion or an oil-in-water (O/W) emulsion. The topical cream formulation has a higher content of oily substance than gel, but a lower content of oily ingredient than ointment. Therefore, the viscosity of topical cream formulation lies between gel and ointment. The pharmacological effect of the topical cream formulation is confined to the skin surface or within the skin. Topical cream formulation penetrates through the skin by transcellular route, intercellular route, or trans-appendageal route. Topical cream formulation is used for a wide range of diseases and conditions, including atopic dermatitis (eczema), psoriasis, skin infection, acne, and wart. Excipients found in a topical cream formulation include thickeners, emulsifying agents, preservatives, antioxidants, and buffer agents. Steps required to manufacture a topical cream formulation include excipient dissolution, phase mixing, introduction of active substances, and homogenization of the product mixture.
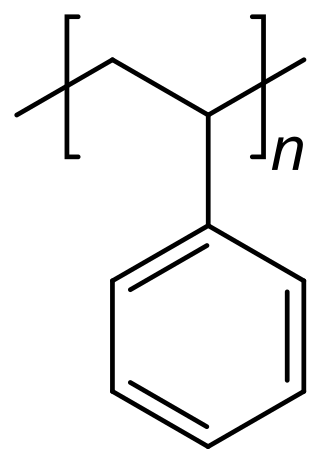
Polystyrene is a synthetic hydrocarbon polymer that is widely adaptive and can be used for a variety of purposes in drug delivery. These methods include polystyrene microspheres, nanoparticles, and solid foams. In the biomedical engineering field, these methods assist researchers in drug delivery, diagnostics, and imaging strategies.
Topical gels are a topical drug delivery dosage form commonly used in cosmetics and treatments for skin diseases because of their advantages over cream and ointment. They are formed from a mixture of gelator, solvent, active drug, and other excipients, and can be classified into organogels and hydrogels. Drug formulation and preparation methods depend on the properties of the gelators, solvents, drug and excipients used.










