NGC 1 is an intermediate spiral galaxy of the morphological type Sbc, located in the constellation of Pegasus. It was discovered on 30 September 1861 by Heinrich d'Arrest.

IC 1101 is a class S0 supergiant (cD) lenticular galaxy at the center of the Abell 2029 galaxy cluster. It has an isophotal diameter at about 123.65 to 169.61 kiloparsecs. It possesses a diffuse core which is the largest known core of any galaxy to date, and contains a supermassive black hole, one of the largest discovered. IC 1101 is located at 354.0 megaparsecs from Earth. It was discovered on 19 June 1790, by the British astronomer William Herschel.

NGC 5144 is an unbarred spiral galaxy located in the constellation of Ursa Minor. It has a velocity of 3,202 ± 9 km/s corresponding to a Hubble Distance of 47.2 ± 3.3 megaparsecs. It was discovered by William Herschel in May 1791.

NGC 3862 is an elliptical galaxy located 300 million light-years away in the constellation Leo. Discovered by astronomer William Herschel on April 27, 1785, NGC 3862 is an outlying member of the Leo Cluster.

NGC 7016 is an elliptical galaxy located about 480 million light-years away from Earth in the constellation Capricornus. NGC 7016's calculated velocity is 11,046 km/s. The galaxy has an estimated diameter of about 160 thousand light years and was discovered by American astronomer Francis Preserved Leavenworth on July 8, 1885. It is also host to a supermassive black hole with an estimated mass of 1.4 × 109M☉.

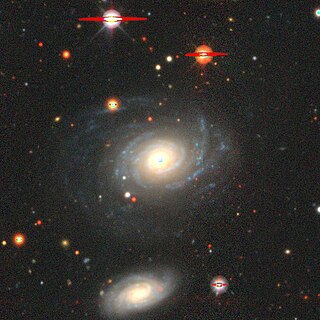
NGC 485, also commonly referred to as PGC 4921 or GC 270, is a spiral galaxy in the constellation Pisces. It is located approximately 86 million light-years from Earth and was discovered on January 8, 1828 by astronomer William Herschel. It was later also observed by Heinrich d'Arrest and Herman Schultz. When NGC 485 was originally categorized in the New General Catalogue by John Louis Eil Dreyer in 1888, it was incorrectly described as a "considerably faint, pretty large, round, 8th magnitude star 3 1/2 arcmin to southwest".

NGC 4598 is a barred lenticular galaxy located in the constellation Virgo. NGC 4598 was discovered by astronomer William Herschel on April 15, 1784. The distance to NGC 4598 has not been accurately determined; measurements vary from 64 to 102 million light-years. According to the NASA/IPAC Extragalactic Database, its redshift based distance is 102 Mly (31.3 Mpc) while its redshift independent based distance is 88.71 Mly (27.200 Mpc). Also, according to SIMBAD, its distance is 63.7 Mly (19.54 Mpc). NGC 4598's average distance is 84.8 Mly (26.0 Mpc). NGC 4598 is usually considered to be a member of the Virgo Cluster. However, P. Fouqu´e et al. suggests it may be a background galaxy independent of the main cluster.

NGC 6047 is an elliptical galaxy located about 430 million light-years away in the constellation Hercules. It was discovered by astronomer Lewis Swift on June 27, 1886. NGC 6047 is a member of the Hercules Cluster.

NGC 918 is a barred spiral galaxy in the constellation Aries, about 67 million light years from the Milky Way. It was discovered by John Herschel on Jan 11, 1831.

NGC 5555 is a distant spiral galaxy located in the constellation Virgo. Its velocity in respect to the cosmic microwave background is 11,200 ± 20 km/s, corresponding to a Hubble Distance of 165 ± 12 Mpc. It was discovered by Ormond Stone in 1886 who described it as "very faint, small, irregularly round with a bright middle nucleus."

NGC 5850 is a barred spiral galaxy in the constellation Virgo. Its speed relative to the cosmic microwave background is 2,735 ± 13 km/s, which corresponds to a Hubble distance of 40.3 ± 2.8 Mpc. NGC 5850 was discovered by German-British astronomer William Herschel in 1786.

NGC 3800 is an intermediate spiral galaxy located in the constellation Leo. Its speed relative to the cosmic microwave background is 3,653 ± 24 km/s, which corresponds to a Hubble distance of 53.9 ± 3.8 Mpc. NGC 3800 was discovered by German-British astronomer William Herschel in 1784.

NGC 3799 is a barred spiral galaxy located in the constellation Leo. Its speed relative to the cosmic microwave background is 3,659 ± 24 km/s, which corresponds to a Hubble distance of 54.0 ± 3.8 Mpc. NGC 3799 was discovered by British astronomer John Herschel in 1832.

NGC 5885 is an intermediate barred spiral galaxy located in the constellation Libra. Its speed relative to the cosmic microwave background is 2,185 ± 13 km/s, which corresponds to a Hubble distance of 32.3 ± 2.3 Mpc. NGC 5885 was discovered by German-British astronomer William Herschel in 1784.

NGC 4017 is an intermediate spiral radio galaxy located in the constellation Coma Berenices. Its speed relative to the cosmic microwave background is 3,748 ± 21 km/s, which corresponds to a Hubble distance of 55.3 ± 3.9 Mpc. NGC 4017 was discovered by German-British astronomer William Herschel in 1785.

NGC 5416 is a spiral galaxy and radio galaxy located in the constellation Boötes. Its speed relative to the cosmic microwave background is 6,499 ± 18 km/s, which corresponds to a Hubble distance of 95.9 ± 6.7 Mpc. NGC 5416 was discovered by German-British astronomer William Herschel in 1784.

NGC 638 is a barred spiral galaxy located in the constellation of Pisces. Its velocity speed to the cosmic microwave background is 2,864± 21 km/s, which corresponds to a Hubble's law of 42.2 ± 3.0 Mpc. NGC 638 was discovered by American astronomer Lewis A. Swift in 1886.

NGC 5377 is an intermediate barred spiral galaxy located in the constellation Canes Venatici. Its speed relative to the cosmic microwave background is 1,951 ± 11 km/s, which corresponds to a Hubble distance of 28.8 ± 2.0 Mpc. NGC 5377 was discovered by German-British astronomer William Herschel in 1787.

NGC 5394 is a barred spiral galaxy located in the constellation Canes Venatici. Its speed relative to the cosmic microwave background is 3,639 ± 14 km/s, which corresponds to a Hubble distance of 53.7 ± 3.8 Mpc. NGC 5394 was discovered by German-British astronomer William Herschel in 1787.

NGC 5508 is a very large and distant spiral galaxy located in the constellation Boötes. Its velocity relative to the cosmic microwave background is 11,615 ± 15 km/s, which corresponds to a Hubble's law of 171 ± 12 Mpc. It was discovered by French astronomer Édouard Stephan in 1882.




















