
The Canary Islands, also known informally as the Canaries, are a Spanish autonomous community and archipelago in Macaronesia in the Atlantic Ocean. At their closest point to the African mainland, they are 100 kilometres west of Morocco and the Western Sahara. The Canary Islands are part of Spanish Africa. They are the southernmost of the autonomous communities of Spain. The islands have a population of 2.2 million people and are the most populous special territory of the European Union.

The history of the Pacific Islands covers the history of the islands in the Pacific Ocean.

1595 (MDXCV) was a common year starting on Sunday of the Gregorian calendar and a common year starting on Wednesday of the Julian calendar, the 1595th year of the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the 595th year of the 2nd millennium, the 95th year of the 16th century, and the 6th year of the 1590s decade. As of the start of 1595, the Gregorian calendar was 10 days ahead of the Julian calendar, which remained in localized use until 1923.

The Vanuatu rain forests are tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests ecoregion which includes the islands of Vanuatu, as well as the Santa Cruz Islands group of the neighboring Solomon Islands. It is part of the Australasian realm, which includes neighboring New Caledonia and the Solomon Islands, as well as Australia, New Guinea, and New Zealand.
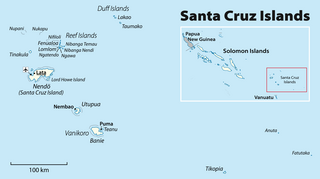
The Santa Cruz Islands are a group of islands in the Pacific Ocean, part of Temotu Province of the nation of Solomon Islands. They lie approximately 250 miles to the southeast of the Solomon Islands archipelago. The Santa Cruz Islands lie just north of the archipelago of Vanuatu, and are considered part of the Vanuatu rain forests ecoregion.

Material culture is the aspect of culture manifested by the physical objects and architecture of a society. The term is primarily used in archaeology and anthropology, but is also of interest to sociology, geography and history. The field considers artifacts in relation to their specific cultural and historic contexts, communities and belief systems. It includes the usage, consumption, creation and trade of objects as well as the behaviors, norms and rituals that the objects create or take part in.

Álvaro de Mendaña y Neira was a Spanish navigator, explorer, and cartographer, best known for two of the earliest recorded expeditions across the Pacific Ocean in 1567 and 1595. His voyages led to the discovery of the Marquesas, Cook Islands, and Solomons among other archipelagos. Born in Congosto, in El Bierzo Region (León), he was the nephew of Lope García de Castro, viceroy of Peru.

The Reef Islands are a loose collection of 16 islands in the northwestern part of the Solomon Islands province of Temotu. These islands have historically also been known by the names of Swallow Islands and Matema Islands.

A tepukei, tepuke or TePuke is a Polynesian boat type, characterized by its elaborate decking, its submerged hulls and symmetrical "crab claw" sail slender foil or radically extended tips claw sail. Tepukei boats are produced primarily by the Polynesian-speaking inhabitants of Taumako, and have been occasionally borrowed by other Polynesian and Melanesian societies.

The culture of the Solomon Islands reflects the extent of the differentiation and diversity among the groups living within the Solomon Islands archipelago, which lies within Melanesia in the Pacific Ocean, with the peoples distinguished by island, language, topography, and geography. The cultural area includes the nation state of Solomon Islands and the Bougainville Island, which is a part of Papua New Guinea.

Temotu is the easternmost province of Solomon Islands. The province was formerly known as Santa Cruz Islands Province. It consists, essentially, of two chains of islands which run parallel to each other from the northwest to the southeast. Its area is 895 square kilometres.

Tinakula is a conical stratovolcano which forms an island north of Nendo in Temotu Province, Solomon Islands. It lies at the north end of the Santa Cruz Islands. It is about 3.5 kilometres wide and rises 851 metres above sea level, rising three to four kilometres from the sea floor. The volcano was first recorded in eruption in 1595 when Álvaro de Mendaña sailed past it.

The Archdiocese of Honiara is a Latin Church ecclesiastical territory or archdiocese of the Catholic Church in the Solomon Islands. It is the successor of the apostolic prefecture of the British Solomon Islands, which was erected in 1897. The ecclesiastical province of Honiara was created in 1978, the first such creation of Pope John Paul II, and contains two suffragan sees: Gizo and Auki (1982).

Utupua is an island in the Santa Cruz Islands, located 66 km to the Southeast of the main Santa Cruz group, between Vanikoro and Santa Cruz proper (Nendö). This island belongs administratively to the Temotu Province of the Solomon Islands.

Vanikoro is an island in the Santa Cruz group, located 118 kilometres to the Southeast of the main Santa Cruz group. It is part of the Temotu Province of the Solomon Islands.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Tuvalu:
Malo is an island in the Solomon Islands; it is located in Temotu Province. The large neighbouring island is Nendö.
Isabel Barreto de Castro, was a Spanish sailor and traveler, the first known woman to hold the office of admiral in the history of navigation. She was purportedly the granddaughter of Francisco Barreto, governor of Portuguese India. Isabel Barreto married Alvaro de Mendaña, Spanish navigator, patron of several expeditions to the Pacific Ocean, and European discoverer of the Solomon Islands and the Marquesas Islands.
Gerd Koch was a German cultural anthropologist best known for his studies on the material culture of Kiribati, Tuvalu and the Santa Cruz Islands in the Pacific. He was associated with the Ethnological Museum of Berlin. His field work was directed to researching and recording the use of artefacts in their indigenous context, to begin to understand these societies.

Solomon Islands–Spain relations are the bilateral and diplomatic relations between these two countries. Solomon Islands does not have an embassy resident in Spain but maintains an honorary consulate in Madrid.


















