
Local government is a generic term for the lowest tiers of public administration within a particular sovereign state. This particular usage of the word government refers specifically to a level of administration that is both geographically localised and has limited powers. While in some countries, "government" is normally reserved purely for a national administration (government), the term local government is always used specifically in contrast to national government – as well as, in many cases, the activities of sub-national, first-level administrative divisions. Local governments generally act only within powers specifically delegated to them by law and/or directives of a higher level of government. In federal states, local government generally comprises a third or fourth tier of government, whereas in unitary states, local government usually occupies the second or third tier of government.
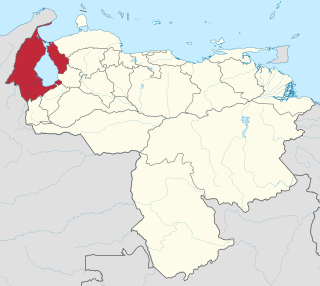
Zulia State is one of the 23 states of Venezuela. The state capital is Maracaibo. As of the 2011 census, it has a population of 3,704,404, the largest population among Venezuela's states. It is also one of the few states in Venezuela in which voseo is widespread. The state is coterminous with the eponymous region of Zulia.

Colombia is a unitary republic made up of thirty-two departments and a Capital District. Each department has a governor (gobernador) and an Assembly, elected by popular vote for a four-year period. The governor cannot be re-elected in consecutive periods. Departments are country subdivisions and are granted a certain degree of autonomy.

Barinas State is one of the 23 states of Venezuela. The state capital is Barinas.

The State of Mérida commonly known simply as Mérida is one of the 23 states of Venezuela. The state capital is Mérida, in the Libertador Municipality.

Táchira State is one of the 23 states of Venezuela. The state capital is San Cristóbal.

La Guaira State, officially La Guaira, and known until 2019 as Vargas State is one of the 23 states of Venezuela. Formerly named after Venezuela's first civilian president, José María Vargas, Vargas comprises a coastal region in the north of Venezuela, bordering Aragua to the west, Miranda to the east, the Caribbean Sea to the north and the Capital District to the south. It is home to both the country's largest seaport and airport. The state capital is La Guaira. The Litoral Varguense conurbation is the principal urban agglomeration in the state, which is part of the Greater Caracas Area.

The Cabinet of Ministers of Venezuela (Spanish: Gabinete de Ministros de Venezuela is one of the bodies that make up the Venezuelan executive in that country's presidential system, alongside the Council of Ministers. The Cabinet is headed by the president of Venezuela, and his corresponding vice president. The purpose of the ministries is to create, adopt, follow and evaluate policies, strategies, programs and projects in accordance with the constitution and the laws of the republic.

Municipalities of Venezuela are subdivisions of the States of Venezuela. There are 335 municipalities dividing the 23 states and the Capital District.

The Libertador Bolivarian Municipality is the only administrative division of the Capital District of Venezuela and along with the municipalities of Baruta, Chacao, El Hatillo and Sucre forms the Metropolitan District of Caracas. It is landlocked by Vargas State and also borders Miranda State on the east and south. The municipality is one of a number in Venezuela named "Libertador Municipality", in honour of Venezuelan independence hero Simón Bolívar.

The Congress of Cúcuta was a constituent assembly where the Republic of Colombia was created. The Congress elected Simón Bolívar and Francisco de Paula Santander president and vice-president, respectively.
The constitutional history of Colombia is the process of formation and evolution of the different constitutions that Colombia has had since its formation.
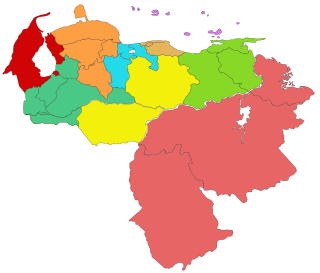
The Zulian Region is one of the 10 administrative regions into which Venezuela is divided for its development plans. This region is coterminous with Zulia State and is administrated by CORPOZULIA. The people from this region seek autonomy from the central government.

According to the Political Constitution of Costa Rica of 1949, in article 168, the territorial division of Costa Rica is organized by law into three types of subnational entity:

The United States of Venezuela was the official name of Venezuela, adopted in its 1864 constitution under the Juan Crisóstomo Falcón government. This remained the official name until 1953, when the constitution of that year renamed it the Republic of Venezuela. In 1999 under newly elected president Hugo Chávez and his modification to the Constitution, Venezuela's official name became the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela.
A Provincial Council is the administrator and governing body of a province of Spain. It is one of the entities that make up local government in Spain. The council is made up of a president, vice presidents, an executive committee and the plenary assembly of deputies.

Municipal elections were held in Venezuela on 10 December 2017, to elect 335 mayors throughout Venezuela, as well as the governor of the state of Zulia. This was the first municipal election held since 2013, when elections were delayed from 2012 following the death of Hugo Chávez. The election resulted in many members of the United Socialist Party of Venezuela being elected as heads of municipal governments throughout Venezuela.

The Sabana Grande district is divided into several middle class neighborhoods located in the Parroquia El Recreo of the Libertador Municipality, in the geographical center of the Metropolitan District of Caracas and owes its name to the old town of Sabana Grande.
The Constitution of Venezuela of 1811 was the first Constitution of Venezuela and Ibero-America, promulgated and written by Cristóbal Mendoza and Juan Germán Roscio, being sanctioned by the Constituent Congress of 1811 in the city of Caracas on December 21, 1811. It was overthrown on July 21, 1812 by the capitulation of Francisco de Miranda in San Mateo. The constitution was in force for exactly seven months.

The Constitution of Venezuela (1819), also known as the Constitution of Angostura was written by El Libertador of Venezuela, Simón Bolívar, and is the first constitution destined to the region of Venezuela within the Gran Colombia. It contains 12 Titles, a decree and an appendix related to moral power. It specified to the Venezuelans their rights, their duties, the sovereignty of the people, and the distribution of powers in the region as well as the division of society into Active Citizen and Passive Citizen ; however, both classes enjoyed the same rights.



















