
Ellesmere Island is Canada's northernmost and third largest island, and the tenth largest in the world. It comprises an area of 196,236 km2 (75,767 sq mi), slightly smaller than Great Britain, and the total length of the island is 830 km (520 mi).

Victoria Island is a large island in the Arctic Archipelago that straddles the boundary between Nunavut and the Northwest Territories of Canada. It is the eighth-largest island in the world, and at 217,291 km2 (83,897 sq mi) in area, it is Canada's second-largest island. It is nearly double the size of Newfoundland (111,390 km2 [43,010 sq mi]), and is slightly larger than the island of Great Britain (209,331 km2 [80,823 sq mi]) but smaller than Honshu (225,800 km2 [87,200 sq mi]). The western third of the island lies in the Inuvik Region of the Northwest Territories; the remainder is part of Nunavut's Kitikmeot Region. The population of 2,168 is divided among two settlements, the larger of which is Cambridge Bay (Nunavut) and the other Ulukhaktok.

The Gulf of St. Lawrence fringes the shores of the provinces of Quebec, New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, Prince Edward Island, Newfoundland and Labrador, in Canada, plus the islands Saint-Pierre and Miquelon, possessions of France, in North America.

The Arctic Archipelago, also known as the Canadian Arctic Archipelago, is an archipelago lying to the north of the Canadian continental mainland, excluding Greenland and Iceland.

Somerset Island is a large, uninhabited island of the Arctic Archipelago, that is part of the Canadian territory of Nunavut. The island is separated from Cornwallis Island and Devon Island to the north by the Parry Channel, from Baffin Island to the east by Prince Regent Inlet, from the Boothia Peninsula to the south by Bellot Strait, and from Prince of Wales Island to the west by Peel Sound. It has an area of 24,786 km2 (9,570 sq mi), making it the 46th largest island in the world and Canada's twelfth largest island.

The Churchill River is a major river in Alberta, Saskatchewan and Manitoba, Canada. From the head of the Churchill Lake it is 1,609 kilometres (1,000 mi) long. It was named after John Churchill, 1st Duke of Marlborough and governor of the Hudson's Bay Company from 1685 to 1691. The Cree name for the river is Missinipi, meaning "big waters". The Denesuline name for the river is des nëdhë́, meaning "Great River".
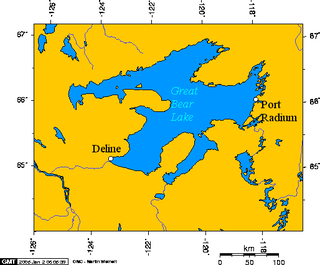
Port Radium is a mining area on the eastern shore of Great Bear Lake, Northwest Territories, Canada. It included the settlement of Cameron Bay as well as the Eldorado and Echo Bay mines. The name Port Radium did not come into use until 1936 and at the time it was in reference to the region as a whole. The Eldorado mine site at LaBine Point adopted the name for its settlement in the 1940s and it has generally stuck.

English River is an unincorporated place on the border of geographic Corman Township, Kenora District and the Unorganized Part of Thunder Bay District in Northwestern Ontario, Canada. It was a Hudson's Bay Company trading post between 1894 and 1911, and is located where Ontario Highway 17 crosses the English River at its confluence with the Scotch River.

St. Theresa Point First Nation is a First Nations community in northern Manitoba. It has 3 reserves in total, the largest and most populated of which is St. Theresa Point, which is bordered by the unorganized portion of Division No. 22, Manitoba, and by the Wasagamack First Nation.

The High Rock Range is a mountain range of the Canadian Rockies in southwestern Alberta and southeastern British Columbia, Canada.

Batchawana Bay is a small bay in Algoma District in Northeastern Ontario, Canada. It is on the eastern shore of Lake Superior, approximately 50 kilometres (31 mi) north of Sault Ste. Marie.
The Campbell Branch Little Black River is a short river in Quebec (Canada) and northern Maine.
Kitselas First Nation is the band government of the Kitselas subgroup of the Tsimshian. The band government is based at Gitaus in the Skeena Valley in the Skeena River valley to the northeast of the city of Terrace, British Columbia, Canada. Though there is no Tsimshian tribal council, they are a participant in the Tsimshian First Nations treaty council.

Port Burwell is a harbour on western Killiniq Island, formed as an arm of Ungava Bay, at the mouth of Hudson Strait. Previously within Labrador, and then the Northwest Territories, it is now situated within the borders of Nunavut, Canada. Cape Chidley is 25 miles (40 km) to the northeast. The community of Port Burwell lies on the shore at 60°25′30″N64°50′00″W.

The north magnetic pole, also known as the magnetic north pole, is a point on the surface of Earth's Northern Hemisphere at which the planet's magnetic field points vertically downward. There is only one location where this occurs, near the geographic north pole. The geomagnetic north pole is the northern antipodal pole of an ideal dipole model of the Earth's magnetic field, which is the most closely fitting model of Earth's actual magnetic field.

The La Loche River is a small river in north-west Saskatchewan. The distance from its source at the south east end of Lac La Loche to its mouth at the north end of Peter Pond Lake is 56 km. The river is bridged by Highway 956 about 5 kilometres from its source. The Kimowin River flows in from the west.
The rivière aux Plats is a tributary of the Gulf of St. Lawrence, flowing in the municipality of L'Île-d'Anticosti, in the Minganie Regional County Municipality, in the administrative region of North Shore, in province of Quebec, in Canada.














