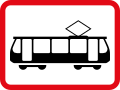
Road signs in the United Kingdom and in its associated Crown dependencies and overseas territories conform broadly to European design norms, though a number of signs are unique: direction signs omit European route numbers and road signs generally use the Imperial System of units, unlike the rest of Europe. Signs in Wales and parts of Scotland are bilingual.

Road signs in Sweden are regulated in Vägmärkesförordningen, VMF (2007:90), and are to be placed 2 metres from the road with the sign 1.6 m from the base for motorized roads. Except for route numbers, there are a maximum of three signs on a pole, with the most important sign at the top. All signs have a reflective layer added on selected parts of the sign as is custom in European countries; most larger signs also have their own illumination.

Road signs in Iceland are visual communication devices placed along roads and highways throughout the country to provide information, warnings, and guidance to motorists and pedestrians. Iceland never ratified the Vienna Convention on Road Signs and Signals, but road signs in Iceland conform to the general pattern of those used in most other European countries, with certain design elements borrowed from Danish and Swedish practice. Signs tend to be more sparsely employed than in other European countries, especially in rural areas.

Road signs in Israel are regulated by the Ministry of Transportation in the Division of Transportation Planning, most recently set forth in June 2011.

Road signs in South Korea are regulated by the Korean Road Traffic Authority.

Road signs in Finland were formerly regulated in Tieliikenneasetus (5.3.1982/182), but now are currently regulated in Siirtymäsäännökset (8.5.2020/360).

Road signs in Austria are regulated in Straßenverkehrsordnung (StVO).

Road signs in Botswana are based on the SADC Road Traffic Signs Manual, a document designed to harmonise traffic signs in member states of the Southern Africa Development Community.

Road signs in New Zealand are similar to those set by the Vienna Convention on Road Signs and Signals. While New Zealand is not a signatory to the convention, its road signs are generally close in shape and function. New Zealand uses yellow diamond-shaped signs for warnings in common with Australia, the Americas, Ireland, Japan and Thailand. Speed limit signs are a red circle with a white background and the limitation in black, and are in kilometres per hour. There are also some signs unique to New Zealand. Road signs in New Zealand are controlled by NZ Transport Agency Waka Kotahi and are prescribed in the Land Transport Rule: Traffic Control Devices 2004 and set out in the Traffic Control Devices (TCD) Manual.

Road signs in Chile are regulated in the Manual de Señalización de Tránsito, which is based on both the United States' MUTCD and the Vienna Convention on Road Signs and Signals, to which Chile is a signatory. Therefore, road signs are compliant with international standards. Chile uses yellow diamonds for warning signs in common with most of the rest of the Americas. Speed limit signs are a red circle with a white background and the limitation in black, and are in kilometres per hour. There are also some signs unique to Chile. Chile also currently uses a mixture of both types of mandatory signs: European-style signs with white symbols on a blue background and a white border, and signs with black symbols on a white background and a red border.
Road signs in Ukraine are governed by a combination of standards set out by the Vienna Convention on Road Signs and Signals, the European Union (EU), and Ukraine Transport and Roads Agency. Ukrainian signs are similar to the signs of other post-Soviet states and are set out in 7 separate categories based on meaning: warning, priority, prohibitory, mandatory, information, service, and additional plates.

Road signs in Hong Kong are standardised by the Transport Department. Due to being a former British territory, the road signage in Hong Kong is similar to road signs in the United Kingdom, with the addition of Traditional Chinese characters.

Road signs in Laos generally follow those used in most European countries as set out in the Vienna Convention on Road Signs and Signals. Despite this, the country itself has never signed the Vienna Convention on Road Signs and Signal. Inscriptions on traffic signs are in Lao, the national language of Laos. However, English is also used for stop and important public places such as tourist attractions, airports, railway stations, and immigration checkpoints. Both Lao and English are used on directional signage.

Road signs in Lithuania ensure that transport vehicles move safely and orderly, as well as to inform the participants of traffic built-in graphic icons. These icons are governed by the Vienna Convention on Road Traffic and Vienna Convention on Road Signs and Signals.

Road signs in South Africa are based on the SADC-Road Traffic Sign Manual, a document designed to harmonise traffic signs in member states of the Southern Africa Development Community. Most of these signs were in the preceding South African RTSM.

Road signs in Cuba are regulated in Ley No. 109 Código de Seguridad Vial and generally conform to the 1968 Vienna Convention on Road Signs and Signals.

Road signs in Lesotho are based on the SADC Road Traffic Signs Manual, a document designed to harmonise traffic signs in member states of the Southern Africa Development Community. Therefore, they do not differ from road signs used in neighbouring South Africa. Lesotho drives on the left.

Road signs in Namibia are based on the SADC Road Traffic Signs Manual, a document designed to harmonise traffic signs in member states of the Southern Africa Development Community. Namibia drives on the left.

Road signs in Zambia are based on the SADC Road Traffic Signs Manual, a document designed to harmonise traffic signs in member states of the Southern Africa Development Community. Zambia drives on the left.

Road signs in Eswatini are based on the SADC Road Traffic Signs Manual, a document designed to harmonise traffic signs in member states of the Southern Africa Development Community. Eswatini drives on the left.