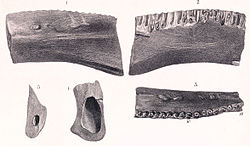
This timeline of stegosaur research is a chronological listing of events in the history of paleontology focused on the stegosaurs, the iconic plate-backed, spike-tailed herbivorous eurypod dinosaurs that predominated during the Jurassic period. The first scientifically documented stegosaur remains were recovered from Early Cretaceous strata in England during the mid-19th century. [1] However, they would not be recognized as a distinct group of dinosaurs until Othniel Charles Marsh described the new genus and species Stegosaurus armatus in 1877, which he regarded as the founding member of the Stegosauria. [2] This new taxon originally included all armored dinosaurs. It was not until 1927 that Alfred Sherwood Romer implemented the modern use of the name Stegosauria as specifically pertaining to the plate-backed and spike-tailed dinosaurs. [1]
Contents
- 19th century
- 1840s
- 1870s
- 1880s
- 1890s
- 20th century
- 1900s
- 1910s
- 1920s
- 1940s
- 1950s
- 1960s
- 1970s
- 1980s
- 1990s
- 21st century
- 2000s
- 2010s
- 2020s
- See also
- Footnotes
- References
- External links
From the time of their earliest description, the chief mystery surrounding stegosaurs was the function of their distinctive back plates. Marsh originally interpreted them as being plates of armor that would protect against predators. In 1910, Richard Swann Lull would agree with this hypothesis. Charles Whitney Gilmore disagreed in 1914 and argued that the only protection a stegosaur could gain from its plates was to appear intimidatingly larger to potential predators. Nearly forty years later, Davitashvili argued that the plates were too fragile to be used for defense and instead used to attract mates and signal the stegosaur's rank in a social hierarchy. [3]
In the late 1970s, James O. Farlow and others would propose that the thin, blood vessel-rich plates helped absorb or lose body heat, depending on the animal's own physiological requirements. [4] This hypothesis was put forth in a broader context of scientists considering the possibility that dinosaurs may have maintained body temperatures and activity levels similar to those of modern birds and mammals, [5] in which case the plates may have served primarily to shed heat rather than gain it. In the late 1980s Buffrenil and others revived the idea that stegosaur plates were display structures, an interpretation that would continue to find favor from researchers like Main and colleagues into the 21st century. [4]